Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (32): 5209-5213.doi: 10.12307/2023.821
Previous Articles Next Articles
Expression and significance of pyroptosis-related factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Wang Qiuyuan1, 2, Liu Youwen2, Yue Chen2, Hou Hongli2, Zhang Xue2
- 1Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2Luoyang Orthopedic-Traumatological Hospital of Henan Province (Henan Provincial Orthopedic Hospital), Luoyang 471000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2022-09-08Accepted:2022-11-27Online:2023-11-18Published:2023-03-23 -
Contact:Zhang Xue, MD, Attending physician, Luoyang Orthopedic-Traumatological Hospital of Henan Province (Henan Provincial Orthopedic Hospital), Luoyang 471000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Wang Qiuyuan, Master candidate, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; Luoyang Orthopedic-Traumatological Hospital of Henan Province (Henan Provincial Orthopedic Hospital), Luoyang 471000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82004396 (to ZX); Science and Technology of Henan Province No. 212102311089 (to ZX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Qiuyuan, Liu Youwen, Yue Chen, Hou Hongli, Zhang Xue. Expression and significance of pyroptosis-related factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5209-5213.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
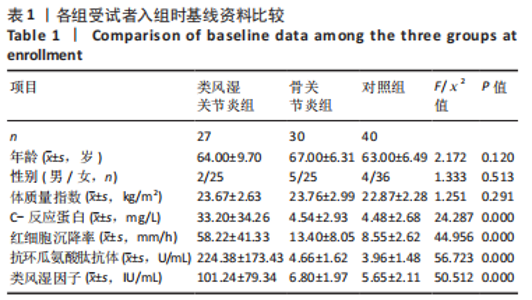
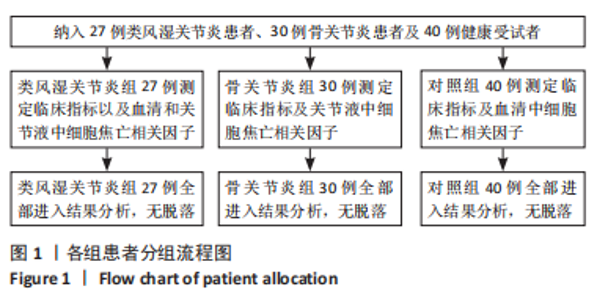
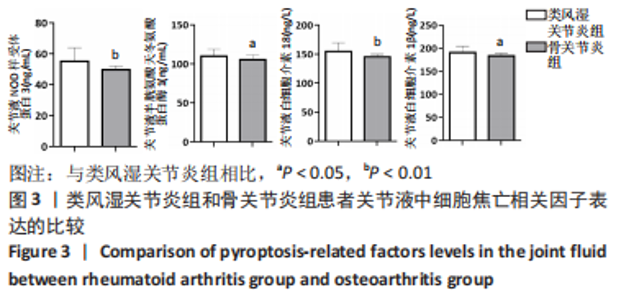
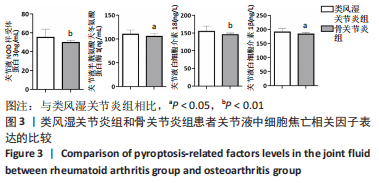
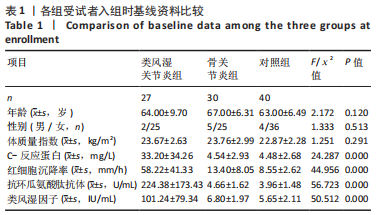
2.3 各组一般资料比较 类风湿关节炎组女25例,男2例;年龄28-77岁,平均(64.00±9.70)岁;体质量指数19.1-28.2 kg/m2,平均(23.67±2.63) kg/m2。骨关节炎组女25例,男5例;年龄55-79岁,平均(67.00±6.31)岁,体质量指数为18.3-28.2 kg/m2,平均(23.76±2.99) kg/m2。对照组女36例,男4例;年龄47-74岁,平均(63.00±6.49)岁;体质量指数为18.9-26.8 kg/m2,平均(22.87±2.28) kg/m2。3组受试者的性别、年龄和体质量指数均衡可比,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。3组间C-反应蛋白、红细胞沉降率、抗环瓜氨酸肽抗体和类风湿因子的表达差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表1。"
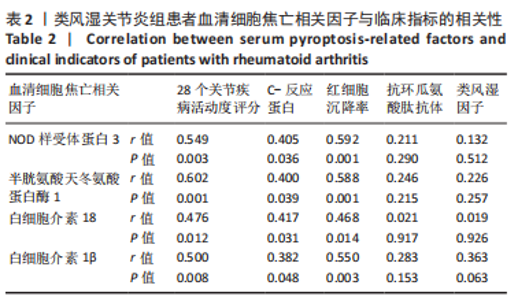
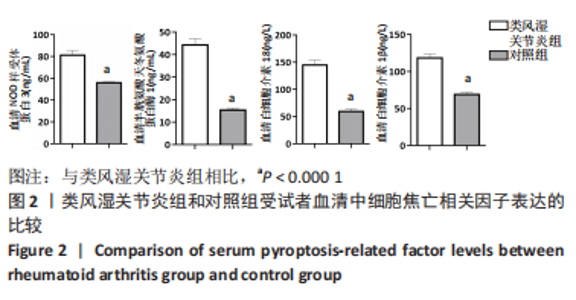
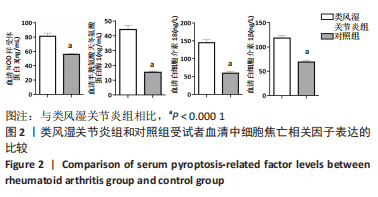
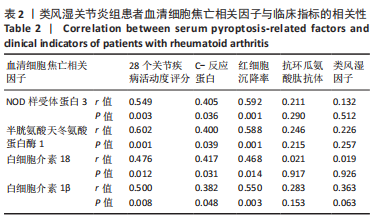
2.5 类风湿关节炎患者血清细胞焦亡相关因子与临床指标的相关性分析 在类风湿关节炎组中,患者血清细胞焦亡相关因子与临床指标的相关性进行Pearson相关性分析。结果显示,类风湿关节炎组患者血清中NLRP3、Caspase-1、白细胞介素18及白细胞介素1β表达水平分别与DAS28评分呈正相关性(r=0.549,P=0.003;r=0.602,P=0.001;r=0.476,P=0.012;r=0.500,P=0.008);与C-反应蛋白水平呈正相关(r=0.405,P=0.036;r=0.400,P=0.039;r=0.417,P=0.031;r=0.382,P=0.048);与红细胞沉降率水平呈正相关(r=0.592,P=0.001;r=0.588,P=0.001;r=0.468,P=0.014;r=0.550,P=0.003)。但类风湿关节炎组患者血清中NLRP3、Caspase-1、白细胞介素18及白细胞介素1β表达水平与抗环瓜氨酸肽抗体水平均无相关性(r=0.211,P=0.290;r=0.246,P=0.215;r=0.021,P=0.917;r=0.283,P=0.153);与类风湿因子水平也无相关性(r=0.132,P=0.512;r=0.226,P=0.257;r=0.019,P=0.926;r=0.363,P=0.063)。见表2。"
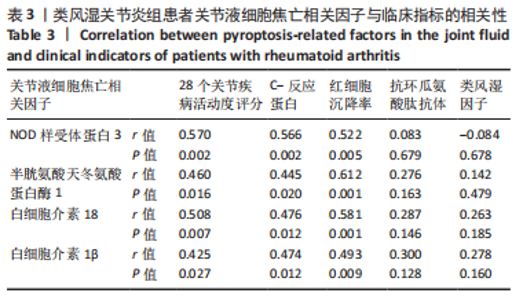
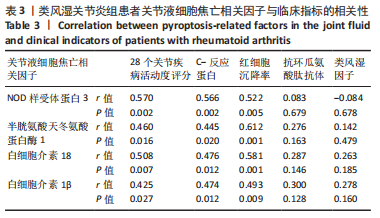
2.6 类风湿关节炎患者关节液细胞焦亡相关因子与临床指标的相关性分析 在类风湿关节炎组中,患者关节液中细胞焦亡相关因子与临床指标的相关性进行Pearson相关性分析。结果显示,类风湿关节炎组患者关节液中NLRP3、Caspase-1、白细胞介素18及白细胞介素1β表达水平分别与DAS28评分呈正相关(r=0.570,P=0.002;r=0.460,P=0.016;r=0.508,P=0.007;r=0.425,P=0.027);与C-反应蛋白水平呈正相关(r=0.566,P=0.002;r=0.445,P=0.020;r=0.476,P=0.012;r=0.474,P=0.012);与红细胞沉降率水平呈正相关(r=0.522,P=0.005;r=0.612,P=0.001;r=0.581,P=0.001;r=0.493,P=0.009)。但类风湿关节炎组患者关节液中NLRP3、Caspase-1、白细胞介素18及白细胞介素1β表达水平与抗环瓜氨酸肽抗体水平均无相关性(r=0.083,P=0.679;r=0.276,P=0.163;r=0.287,P=0.146;r=0.300,P=0.128);与类风湿因子水平也无相关性(r=-0.084,P=0.678;r=0.142,P=0.479;r=0.263,P=0.185;r=0.278,P=0.160)。见表3。"
| [1] MCINNES IB, SCHETT G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. New Engl J Med. 2011;365:2205-2219. [2] SMOLEN JS, ALETAHA D, Barton A, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18001. [3] LIU X, ZHANG Z, RUAN J, et al. Inflammasomeactivated gasdermin D causes pyroptosis by forming membrane pores. Nature. 2016;535(7610):153-158. [4] VANDE WALLE L, LAMKANFI M. Pyroptosis. Curr Biol. 2016;26(13):R568-R572. [5] WU XY, LI KT, YANG HX, et al. Complement C1q synergizes with PTX3 in promoting NLRP3 inflammasome over-activation and pyroptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2020;106:102336. [6] GUO C, FU R, WANG S, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018;194(2):231-243. [7] ALETAHA D, NEOGI T, SILMAN AJ, et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(9):1580-1588. [8] FRANSEN J, VAN RIEL PL. The Disease Activity Score and the EULAR response criteria. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2009;35(4):745-757. [9] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组, 中国医师协会骨科医师分会骨关节炎学组, 国家老年疾病临床医学研究中心(湘雅医院), 等.中国骨关节炎诊疗指南(2021年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2021,41(18):1291-1314. [10] 苏芮,赵向聪,穆艳飞,等.细胞焦亡在类风湿关节炎发病机制中的研究进展[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2019,23(5):341-344. [11] MAN SM, KARKI R, KANNEGANTI TD. Molecular mechanisms and functions of pyroptosis, inflammatory caspases and inflammasomes in infectious diseases. Immunol Rev. 2017;277(1):61-75. [12] MIAO EA, LEAF IA, TREUTING PM, et al. Caspase-1-induced pyroptosis is an innate immune effector mechanism against intracellular bacteria. Nat Immunol. 2010;11(12):1136-1142. [13] CHADHA S, BEHL T, BUNGAU S, et al. Mechanistic insights into the role of pyroptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Res Transl Med. 2020;68(4):151-158. [14] DEETS KA, VANCE RE. Inflammasomes and adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol. 2021;22(4):412-422. [15] BROZ P, DIXIT VM. Inflammasomes: mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016;16(7):407-420. [16] BARKER BR, TAXMAN DJ, TING JP. Cross-regulation between the IL-1β/IL-18 processing inflammasome and other inflammatory cytokines. Curr Opin Immunol. 2011;23(5):591-597. [17] SPEL L, MARTINON F. Inflammasomes contributing to inflammation in arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2020;294(1):48-62. [18] ZENG C, WANG R, TAN H. Role of Pyroptosis in Cardiovascular Diseases and its Therapeutic Implications. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(7):1345-1357. [19] DEANE KD, O’DONNELL CI, HUEBER W, et al. The number of elevated cytokines and chemokines in preclinical seropositive rheumatoid arthritis predicts time to diagnosis in an age-dependent manner. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(11):3161-3172. [20] KOKKONEN H, SÖDERSTRÖM I, ROCKLÖV J, et al. Up-regulation of cytokines and chemokines predates the onset of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(2):383-391. [21] HUGHES-AUSTIN JM, DEANE KD, DERBER LA, et al. Multiple cytokines and chemokines are associated with rheumatoid arthritis-related autoimmunity in first-degree relatives without rheumatoid arthritis: Studies of the Aetiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis (SERA). Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(6):901-907. [22] YUAN S, LI X, LIN A, et al. Interleukins and rheumatoid arthritis: bi-directional Mendelian randomization investigation. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2022;53:151958. [23] HAREL M, FAUTEUX-DANIEL S, GIRARD-GUYONVARC’H C, et al. Balance between Interleukin-18 and Interleukin-18 binding protein in auto-inflammatory diseases. Cytokine. 2022;150:155781. [24] CHOULAKI C, PAPADAKI G, REPA A, et al. Enhanced activity of NLRP3 inflammasome in peripheral blood cells of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17(1):257. [25] MATHEWS RJ, ROBINSON JI, BATTELLINO M, et al. Evidence of NLRP3-inflammasome activation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA); genetic variants within the NLRP3-inflammasome complex in relation to susceptibility to RA and response to anti-TNF treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(6):1202-1210. [26] ADDOBBATI C, DA CRUZ HLA, ADELINO JE, et al. Polymorphisms and expression of inflammasome genes are associated with the development and severity of rheumatoid arthritis in Brazilian patients. Inflamm Res. 2018;67(3):255-264. [27] XIE Q, WEI M, ZHANG B, et al. MicroRNA33 regulates the NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway in macrophages. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(2):3318-3327. [28] KIM HW, KWON YJ, PARK BW, et al. Differential expressions of NOD-like receptors and their associations with inflammatory responses in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017;35(4):630-637. [29] ZHAO J, JIANG P, GUO S, et al. Apoptosis, Autophagy, NETosis, Necroptosis, and Pyroptosis Mediated Programmed Cell Death as Targets for Innovative Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021;24;12:809806. [30] YOU R, HE X, ZENG Z, et al. Pyroptosis and Its Role in Autoimmune Disease: A Potential Therapeutic Target. Front Immunol. 2022;25;13:841732. [31] ZHANG Y, ZHENG Y, LI H. NLRP3 inflammasome plays an important role in the pathogenesis of collagen-induced arthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:9656270. [32] JENKO B, PRAPROTNIK S, TOMŠIC M, et al. NLRP3 and CARD8 polymorphisms influence higher disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. J Med Biochem. 2016; 35(3):319-323. [33] YANG Z, CAO J, YU C, et al. Caspase-1 mediated interleukin-18 activation in neutrophils promotes the activity of rheumatoid arthritis in a NLRP3 inflammasome independent manner. Joint Bone Spine. 2016;83(3):282-289. [34] WAWROCKI S, DRUSZCZYNSKA M, KOWALEWICZ-KULBAT M, et al. Interleukin 18 (IL-18) as a target for immune intervention. Acta Biochim Pol. 2016;63(1):59-63. [35] JUNG SM, KIM KW, YANG CW, et al. Cytokine-mediated bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:263625. |
| [1] | Zhang Xuebin, Ao Wenjun, Jiang Xin, Song Chenglin. Improvement of delayed-onset muscle soreness by pre-exercise whole-body vibration at 50 Hz [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5085-5090. |
| [2] | Wang Hao, Ma Chenghao, Qin Zuohai, Zhou Haibo, Ding Haoyuan, Han Dapeng, Nie Zhixing, Pan Peijun, Gao Chenxin, Ouyang Guilin. Effect of tourniquet use on perioperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4943-4948. |
| [3] | Wei Qin, Amanguli·Ruze, Chen Bingxin, Zhao Ling, Zhao Banghao, Jiang Tao, Zhang Chun, Li Zhiqiang, Gao Xiaoming, Duan Mingjun. Relaxin protects myocardial microvascular endothelial cells from hypoxia-reoxygenation injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4519-4524. |
| [4] | Liu Xingyu, Liu Riguang, Li Guangdi, Wang Jian, Li Long, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Competing endogenous RNA regulates the development of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4559-4565. |
| [5] | Lu Xiaojun, Xiong Bohan, Yang Tengyun, Wang Xu, Zhang Yaozhang, Zhong Ruiying, Li Yanlin. Novel programmed cell death of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4571-4576. |
| [6] | Song Jianhui, Mu Jihong, Li Shiwen. miR-23b effects on transforming growth factor beta1 and osteoclast activity in synovial tissue of rats with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4175-4180. |
| [7] | Long Zhisheng, Fu Liuxiang, Gong Feipeng, Wen Jiabin, Deng Ying, Min Huan, Deng Zhuan, Chen Gang. Expression and significance of pyroptosis associated protein in peripheral tissues with tantalum cage loosening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(25): 4057-4062. |
| [8] | Li Qingru, Wang Yifan, Chen Guanting, Shi Ruoyu, Zhang Linqi. Extracellular vesicles for acute kidney injury in preclinical research: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3926-3936. |
| [9] | Wang Chenyu, Yao Jiawei, Xu Xiongfeng, Qiu Bo. Screening and analysis of differentially expressed genes in synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3224-3229. |
| [10] | Zhao Yan, Xia Qiuqiu, Xiang Shaojie, Mao Qiming, Kong Weijun, Du Qian, Liao Wenbo, Xin Zhijun. Exosomal miRNA in the repair mechanism of degenerative diseases of the spine and joints [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(19): 3040-3051. |
| [11] | Zhang Ziyu, Wang Yiming, Li Han, Wang Zhonghan, Lu Jialin, Xu Rui, Jin Hui. Platelet-rich plasma meets the therapeutic needs of different articular cartilage defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(17): 2772-2779. |
| [12] | Lin Yanchen, Li Jingjing, Lu Guangxu, Dai Erqing, Chen Jing, Zhong Shijiang. Effects of neural stem cell transplantation in different ways on neuroinflammation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2363-2370. |
| [13] | Li Fang, Cao Jianmin, Zhai Pengfei, Wang Jianshe, Hong Da. Effects of resveratrol on albumin-induced pyroptosis-related proteins in HK-2 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(14): 2164-2169. |
| [14] | Zhang Haobo, Zhao Yunan, Yang Xuejun. Role and therapeutic implications of pyroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1445-1451. |
| [15] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||