Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (25): 3964-3970.doi: 10.12307/2023.418
Previous Articles Next Articles
Sealing effect of nano hydroxyapatite on dentinal tubules
Yu Lanning1, Wang Qian2, Jin Youshi1, Fei Xiaowen1, Wang Qingshan1
- 1Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256603, Shandong Province, China; 2Shangdi Branch of Ruitai Stomatological Hospital, Beijing100085, China
-
Received:2022-04-03Accepted:2022-06-15Online:2023-09-08Published:2023-01-17 -
Contact:Wang Qingshan, Chief physician, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256603, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Yu Lanning, Master, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256603, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, No. ZR2018LH010 (to WQS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yu Lanning, Wang Qian, Jin Youshi, Fei Xiaowen, Wang Qingshan. Sealing effect of nano hydroxyapatite on dentinal tubules[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(25): 3964-3970.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
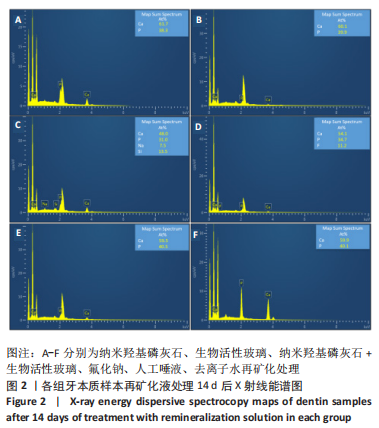
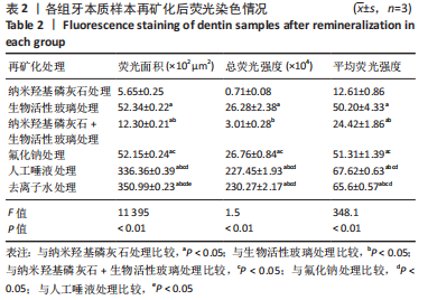
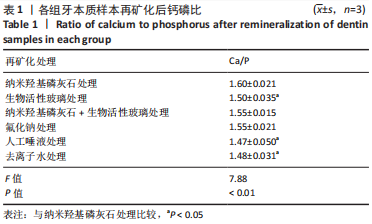
利用X射线能谱仪检测各组牙本质样本表面Ca、P、Na、Si、F元素的原子百分比,并计算出各样本中Ca/P元素比。A组Ca/P约为1.6,与健康牙本质Ca/P比1.67相近。B组Ca/P约为1.50,未检测到Na、Si元素。C组Ca/P约为1.55,并含有7.5%Na元素、13.5%Si元素,说明混合溶液中纳米羟基磷灰石和生物活性玻璃在牙本质的再矿化中都发挥了作用。D组Ca/P约为1.56,有11.2%的氟元素,提示F-与牙本质发生结合。E、F组Ca/P比分别为1.47和1.49,与健康牙本质的Ca/P比理论值差异较大(P < 0.01),说明极少或没有羟基磷灰石晶体结构的存在。 单因素方差统计结果表明,6组样本Ca/P比总体比较差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01);组间比较显示,A组与B、E、F组比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),其余组间两两比较差异无显著性意义,表明含有纳米羟基磷灰石及NaF的处理液其牙本质表面矿化度高于其他组,见表1。"
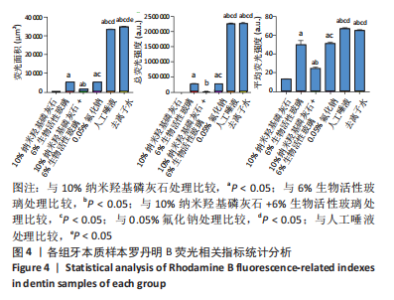
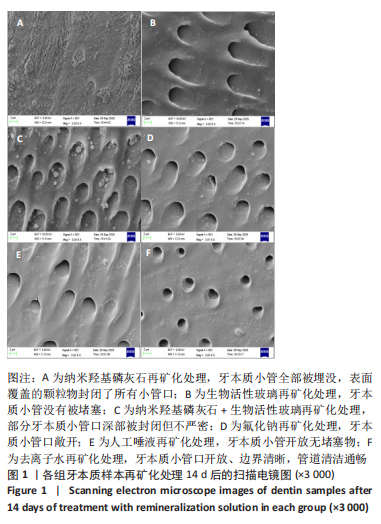
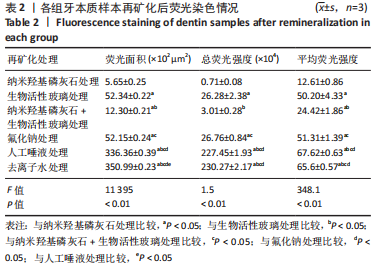
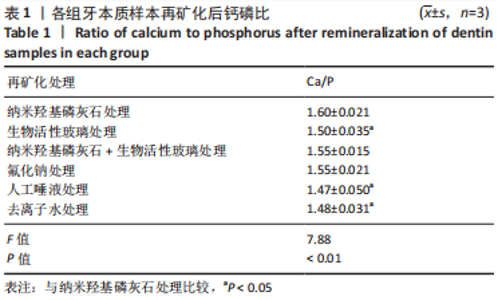
罗丹明B荧光染液可沿牙本质小管口进入牙本质内部,且牙本质小管开放程度越高,染料自样本工作面进入牙本质小管的深度越深,在激光共聚焦显微镜下呈现越宽的荧光带;牙本质结构越疏松荧光染液进入牙本质的量越多镜下荧光强度越强;反之,镜下荧光带越窄荧光强度越弱。 A组荧光带最为微弱,几乎不可见,说明纳米羟基磷灰石严密覆盖了牙本质表面并封堵了牙本质小管口。B组荧光带较宽,荧光度较强。C组荧光带可见但较窄、不连续,强度弱,表明牙本质小管部分封闭。D组荧光强度、宽度与B组相近。E组和F组相似,荧光带宽度大、强度高,明显高于其他4组,提示唾液及去离子水对牙本质表面基本没有封闭作用。 各组间总荧光面积和平均荧光强度单因素方差分析结果显示,A组最小,与其他5组比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);C组总荧光面积和平均荧光强度小于B、E、F组(P < 0.05),其余组间两两比较差异见图4,表2。"
| [1] 沈烨青, 朱亚琴. Nd:YAG 激光治疗牙本质敏感的研究进展[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2020,29(2):43-46. [2] LIU XX, TENENBAUM HC, WILDER RS, et al. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of dentin hypersensitivity: an evidence-based overview for dental practitioners. BMC Oral Health. 2020;20(1):220-230. [3] TRIEU A, MOHAMED A, LYNCH E. Silver diamine fluoride versus sodium fluoride for arresting dentine caries in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):2115-2124. [4] POLLICK H. The Role of Fluoride in the Prevention of Tooth Decay. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2018;65(5):923-940. [5] 殷凌云,于鸿滨,杨向红,等.两种参数设置的激光联合氟化物治疗牙本质敏感症的临床评价[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2022,3(11):34-39. [6] TANWAR YS, FERREIRA N. The role of bioactive glass in the management of chronic osteomyelitis: a systematic review of literature and current evidence. Infect Dis (Lond). 2020;52(4):219-226. [7] 孟宪敏,张志华,宫琳,等.牙本质敏感症患者患病状况与行为的相关性分析[J].山西医科大学学报,2014,45(8):722-725. [8] 王薇,窦丽鑫,王宏远.生物活性玻璃骨修复支架材料的研究进展[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2018,19(6):362-366. [9] FREITAS SAA, OLIVEIRA NMA, DE GEUS JL, et al. Bioactive toothpastes in dentin hypersensitivity treatment: A systematic review. Saudi Dent J. 2021;33(7):395-403. [10] 岳阳丽,马贵霞,刘翠丽,等.生物活性玻璃促进牙本质再矿化的时间相关性体外研究[J].口腔医学研究,2020,36(12):1137-1141. [11] GALLOB J, LING MR, AMINI P, et al. Efficacy of a dissolvable strip with calcium sodium phosphosilicate (NovaMin®) in providing rapid dentine hypersensitivity relief. J Dent. 2019;91:100003-100009. [12] YU J, YANG H, LI K, et al. A novel application of nanohydroxyapatite/mesoporous silica biocomposite on treating dentin hypersensitivity: An in vitro study. J Dent. 2016;50:21-29. [13] HIGUCHI J, FORTUNATO G, WOZNIAK B, et al. Polymer Membranes Sonocoated and Electrosprayed with Nano-Hydroxyapatite for Periodontal Tissues Regeneration. Nanomaterials. 2019;9(11):1625-1649. [14] JEONG WJ. A Study on the Deposition of Hydroxyapatite Nano Thin Films Fabricated by Radio-Frequency Magnetron Sputtering for Biomedical Applications. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2020;20(7):4114-4119. [15] ZIA I, MIRZA S, JOLLY R, et al. Trigonella foenum graecum seed polysaccharide coupled nano hydroxyapatite-chitosan: A ternary nanocomposite for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019; 124:88-101. [16] SHUAI C, XU Y, FENG P, et al. Co-enhance bioactive of polymer scaffold with mesoporous silica and nano-hydroxyapatite. J Biomater Sci. 2019; 30(12):1097-1113. [17] Hu ML, Zheng G, Lin H, et al. Network meta-analysis on the effect of desensitizing toothpastes on dentine hypersensitivity. J Dent. 2019; 88:103170-103181. [18] WEST NX, ADDY M, JACKSON RJ, et al. Dentine hypersensitivity and the placebo response. A comparison of the effect of strontium acetate, potassium nitrate and fluoride toothpastes. J Clin Periodontol. 1997;24(4):209-215. [19] PASHLEY DH. How can sensitive dentine become hypersensitive and can it be reversed. J Dent. 2013;41(Suppl 4):S49-S55. [20] FAVARO ZEOLA L, SOARES PV, CUNHA-CRUZ J. Prevalence of dentin hypersensitivity: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent. 2019; 81:1-6. [21] 马贵霞.生物活性玻璃促进牙本质再矿化的时间相关性体外研究[D].郑州:郑州大学,2020. [22] NIU LN, JEE SE, JIAO K, et al. Collagen intrafibrillar mineralization as a result of the balance between osmotic equilibrium and electroneutrality. Nat Mater. 2017;16(3):370-378. [23] 吴媛媛,潘海华,唐睿康.胶原矿化与仿生修复[J].化学进展,2018, 30(10):1503-1510. [24] BERTASSONI LE, HABELITZ S, KINNEY JH, et al. Biomechanical perspective on the remineralization of dentin. Caries Res. 2009;43(1): 70-77. [25] GANDOLFI MG, TADDEI P, SIBONI F, et al. Biomimetic remineralization of human dentin using promising innovative calcium-silicate hybrid “smart” materials. Dent Mater. 2011;27(11):1055-1069. [26] 周学东,梁景平.龋病学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2011:113-120. [27] 田子璐,朱松.诱导牙本质再矿化以堵塞牙本质小管的研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2021,37(1):11-14. [28] YUAN PY, LIU SY, LV Y, et al. Effect of a dentifrice containing different particle sizes of hydroxyapatite on dentin tubule occlusion and aqueous Cr (VI) sorption. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:5243-5256. [29] 毕良佳,李虹,刘来发,等.羟磷灰石同质间吸附效果及对牙本质小管封闭效果的研究[J].口腔医学研究,2006,22(5):501-503. [30] DAAS I, BADR S, OSMAN E. Comparison between Fluoride and Nano-hydroxyapatite in Remineralizing Initial Enamel Lesion: An in vitro Study. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2018;19(3):306-312. [31] BAGLAR S, ERDEM U, DOGAN M, et al. Dentinal tubule occluding capability of nano-hydroxyapatite; The in-vitro evaluation Microsc Res Tech. 2018;81(8):843-854. [32] MEDVECKY L, STULAJTEROVA R, GIRETOVA M, et al. Effect of tetracalcium phosphate/monetite toothpaste on dentin remineralization and tubule occlusion in vitro. Dent Mater. 2018;34(3): 442-451. [33] FIUME E, BARBERI J, VERNÉ E, et al. Bioactive Glasses: From Parent 45S5 Composition to Scaffold-Assisted Tissue-Healing Therapies. J Funct Biomater. 2018;9(1):1-33. [34] 朱庆霞,徐琼琼,罗民华.碳酸羟基磷灰石的生物矿化研究[J].陶瓷学报,2010,31(2):234-239. [35] 吴民行,谢玉芬,翟智皓,等.生物活性玻璃的制备与应用研究进展[J].人工晶体学报,2019,48(1):137-143,148. [36] 张峻峰,蒋明慧,张顺锋,等.多孔羟基磷灰石生物陶瓷的制备及研究进展[J].中国陶瓷,2017,53(3):6-12. [37] OSORIO R, TOLEDANO-OSORIO M, OSORIO E, et al. Zinc and silica are active components to efficiently treat in vitro simulated eroded dentin. Clin Oral Investig. 2018;22(8):2859-2870. [38] 申思敏,陈新梅,王盼盼,等.六氟硅酸铵溶液封闭牙本质小管的扫描电镜观察[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2013;23(7):424-427. [39] 万方.HAP/SiO2复合材料的制备与性能研究[D].郑州:郑州大学, 2011. |
| [1] | Lin Xiaohui, Yang Mengyuan, Li Chunnian. Role and mechanism of biomimetic remineralization therapy for early enamel demineralization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 856-865. |
| [2] | Israrguli · Maimeti, Jia Sen, Liu Jia. Bone morphogenetic protein 2-loaded hydrogel induces osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3301-3310. |
| [3] | Cheng Ruiqing, Sun Honglei, Geng Shuangshuang, Wang Chao, Li Junke, Chen Yanfang. Effects of erythropoietin on restorative dentin formation and expression of bone morphogenetic protein 2 after pulp injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2231-2242. |
| [4] | Wang Jianchun, Yang Shuqing, Su Xin, Wang Hongyuan. Different contents of B2O3 affect mechanical properties and bioactivity of bioactive glass scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 712-716. |
| [5] | Xu Yinghua, Liu Jing, You Quan, Wen Zhihao, Gao Lu. Effect of neodymium-doped:yttrium aluminum perovskite laser combined with two kinds of remineralizers on remineralization of early enamel caries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 360-365. |
| [6] | Gao Hua, Che Hui, Hu Dan, Hao Yuefeng. Bioactive glass: different application forms and functions by adjusting preparation process and doping elements [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(29): 4726-4733. |
| [7] | Wang Lu, Xu Jie, Xia Yijing, Zhang Xinsong, Zhao Bin. Preparation and characterization of silk fibroin/bioactive glass composite fiber membrane [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(22): 3457-3463. |
| [8] | Li Xingyu, Zhou Jie, Li Shasha, Zhang Tianxi, Guo Guoning, Yu Anyong, Deng Jiang, Ye Peng. Repair of infected osteochondral defect with sustained release vancomycin three-dimensional scaffold in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(22): 3509-3516. |
| [9] | Liu Yan, Zheng Xuexin. Performance of 3D-printed polylactic acid-nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan/doxycycline antibacterial scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(22): 3532-3538. |
| [10] | Cheng Mengke, Yang Dujuan, Liu Jia. Preparation and performance of gelatin modified by methacrylic anhydride/treated dentin matrix bioactive scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(22): 3555-3560. |
| [11] | Zhou Zhi, Chen Zhijie, Huo Shicheng, Li Zhanchun. Strontium-containing mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles loaded with bisphosphonates ameliorate bone loss in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(17): 2653-2658. |
| [12] | Zhao Kang, Lin Si, Ge Xiaotian, Du Xinrui, Han Yingchao. Biosafety evaluation of poly(lactic acid)/nano-hydroxyapatite composite microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(34): 5497-5504. |
| [13] | Xu Shicai, Ma Fei, Tang Chao, Liao Yehui, Tang Qiang, Chen Shiyu, Li Yang, Zhou Jiajun, Wang Qing, Zhong Dejun. Effect of nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-66 intervertebral fusion cage shape on the efficacy of anterior cervical discectomy and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(30): 4830-4835. |
| [14] | Liu Huan, Li Han, Ma Yunhao, Zhong Weijian, Ma Guowu. Osteogenic capacity of partially demineralized dentin particles in the maxillary sinus lift [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 354-359. |
| [15] | Wang Ziyang, Zuo Enjun. Application of biological materials in vital pulp therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 427-433. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||