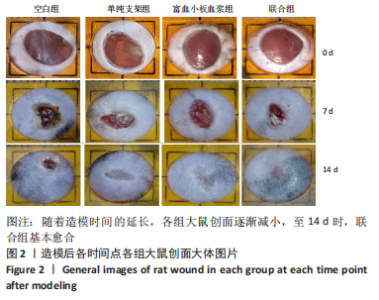
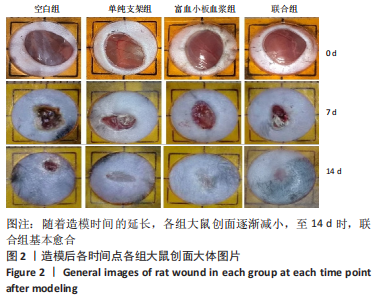
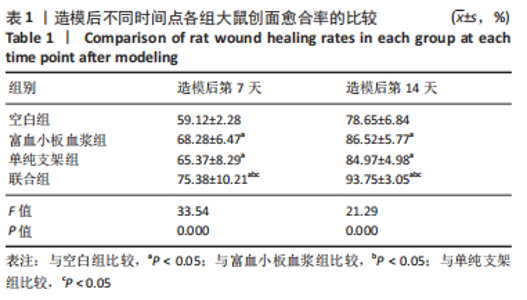
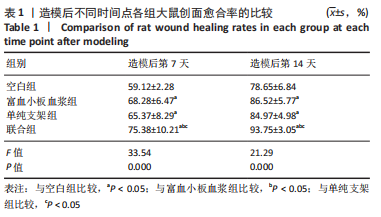
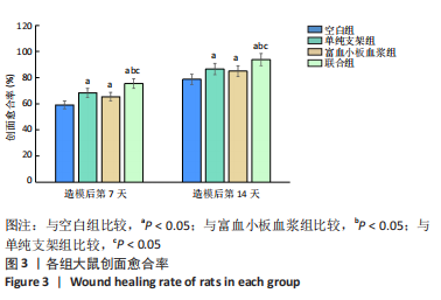
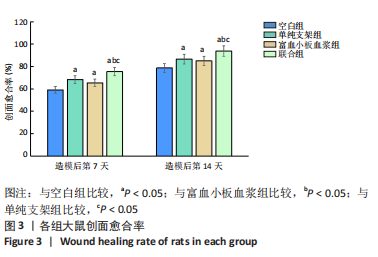
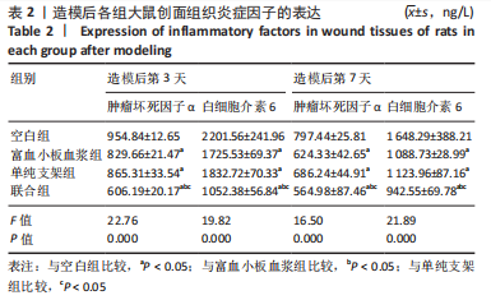
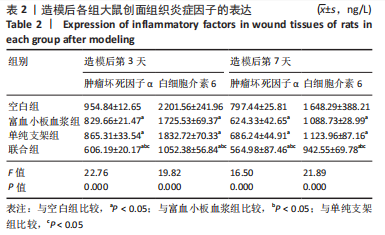
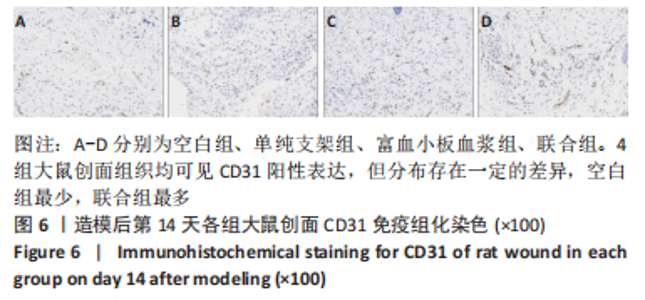
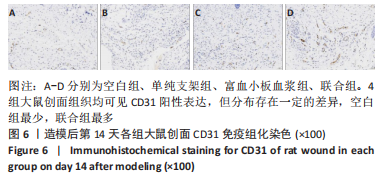
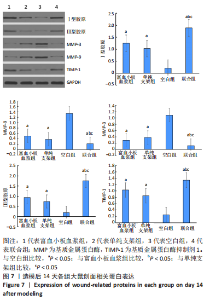
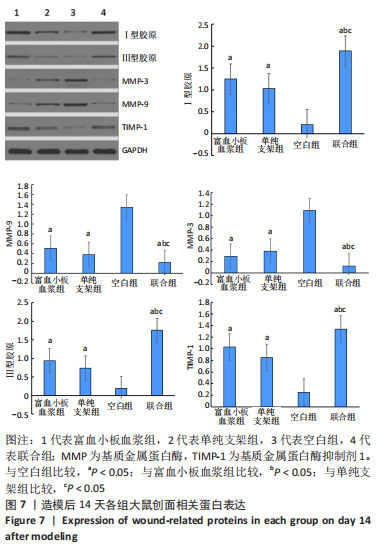
[1] LI S, MOHAMEDI AH, SENKOWSKY J, et al. Imaging in Chronic Wound Diagnostics. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2020;9(5):245-263.
[2] MONAVARIAN M, KADER S, MOEINZADEH S, et al. Regenerative Scar-Free Skin Wound Healing. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2019;25(4):294-311.
[3] ZOMER HD, TRENTIN AG. Skin wound healing in humans and mice: Challenges in translational research. J Dermatol Sci. 2018;90(1):3-12.
[4] TARASSOLI SP, JESSOP ZM, AL-SABAH A, et al. Skin tissue engineering using 3D bioprinting: An evolving research field. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018;71(5): 615-623.
[5] BHARDWAJ N, CHOUHAN D, MANDAL BB. Tissue Engineered Skin and Wound Healing: Current Strategies and Future Directions. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(24): 3455-3482.
[6] ŁABUŚ W, KITALA D, SZAPSKI M, et al. Tissue Engineering in Skin Substitute.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1345:193-208.
[7] SUN W, GREGORY DA, TOMEH MA, et al. Silk Fibroin as a Functional Biomaterial for Tissue Engineering.Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(3):1499.
[8] KALLIS PJ, FRIEDMAN AJ. Collagen Powder in Wound Healing. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17(4):403-408.
[9] LIN H, ZHENG Z, YUAN J, et al. Collagen Peptides Derived from Sipunculus nudus Accelerate Wound Healing. Molecules. 2021;26(5):1385.
[10] FELICIAN FF, YU RH, LI MZ, et al. The wound healing potential of collagen peptides derived from the jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum. Chin J Traumatol. 2019;22(1): 12-20.
[11] NIKAM VS, PUNDE DS, BHANDARI RS. cSilk fibroin nanofibers enhance cell adhesion of blood-derived fibroblast-like cells: A potential application for wound healing. Indian J Pharmacol. 2020;52(4):306-312.
[12] KULKARNI G, GUHA RAY P, BYRAM PK, et al. Tailorable hydrogel of gelatin with silk fibroin and its activation/crosslinking for enhanced proliferation of fibroblast cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;164:4073-4083.
[13] EMER J. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Current Applications in Dermatology. Skin Therapy Lett. 2019;24(5):1-6.
[14] QIAN Z, WANG H, BAI Y, et al. Improving Chronic Diabetic Wound Healing through an Injectable and Self-Healing Hydrogel with Platelet-Rich Plasma Release. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(50):55659-55674.
[15] GENTILE P, CALABRESE C, DE ANGELIS B, et al. Impact of the Different Preparation Methods to Obtain Autologous Non-Activated Platelet-Rich Plasma (A-PRP) and Activated Platelet-Rich Plasma (AA-PRP) in Plastic Surgery: Wound Healing and Hair Regrowth Evaluation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(2):431.
[16] LOVISOLO F, CARTON F, GINO S, et al. Platelet rich plasma-derived microvesicles increased in vitro wound healing. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(18):9658-9664.
[17] CUI B, ZHANG C, GAN B, et al. Collagen-tussah silk fibroin hybrid scaffolds loaded with bone mesenchymal stem cells promote skin wound repair in rats. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;109:110611.
[18] 李青,全仁夫,陈利红,等.负载纳米氧化锌丝素胶原蛋白支架修复皮肤创面[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(14):2157-2161.
[19] HESSELER MJ, SHYAM N. Platelet-rich plasma and its utility in medical dermatology: A systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81(3):834-846.
[20] KOBAYASHI E, FLÜCKIGER L, FUJIOKA-KOBAYASHI M, et al. Comparative release of growth factors from PRP, PRF, and advanced-PRF. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(9):2353-2360.
[21] CHOUKROUN J, GHANAATI S. Reduction of relative centrifugation force within injectable platelet-rich-fibrin (PRF) concentrates advances patients’ own inflammatory cells, platelets and growth factors: the first introduction to the low speed centrifugation concept. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2018;44(1):87-95.
[22] WILKINSON HN, HARDMAN MJ. Wound healing: cellular mechanisms and pathological outcomes. Open Biol. 2020;10(9):200223.
[23] SHEN C, YE W, GONG L, et al. Serum interleukin-6, interleukin-17A, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in patients with recurrent aphthous stomatitis. J Oral Pathol Med. 2021;50(4):418-423.
[24] KANESHIRO K, SAKAI Y, SUZUKI K, et al. Interleukin-6 and tumour necrosis factor-α cooperatively promote cell cycle regulators and proliferate rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cells. Scand J Rheumatol. 2019;48(5):353-361.
[25] KIM YH, YANG IJ, NGUYEN LTH, et al. Effect of Diquafosol on Hyperosmotic Stress-induced Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Interleukin-6 Expression in Human Corneal Epithelial Cells. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2020;34(1):1-10.
|