[1] ADELANI MA, KEENEY JA, PALISCH A, et al. Has total hip arthroplasty in patients 30 years or younger improved? A systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(8):2595-2601.
[2] KURTZ S, ONG K, LAU E, et al. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(4):780-785.
[3] 何伟.如何把握股骨头坏死患者的保髋治疗时机[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2016,5(2):82-86.
[4] 张长青.股骨头坏死保髋治疗指南(2016版)[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2016,2(2):65-70.
[5] SODHI N, ACUNA A, ETCHESON J, et al. Management of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Bone Joint J. 2020;102-B(7_Supple_B):122-128.
[6] 陈冬冬,郝阳泉,张高魁,等.3D打印导航模板辅助髓芯减压植骨治疗ARCOⅡ期非创伤性股骨头坏死[J].中国组织工程研究,2020, 24(27):4322-4327.
[7] 陈冬冬,鲁超,宇文星,等.富血小板血浆联合髓芯减压植骨术治疗ARCOⅡ期非创伤性股骨头坏死[J].中国骨伤,2020,33(11): 1048-1052.
[8] LANDGRAEBER S, WARWAS S, CLAßEN T, et al. Modifications to advanced Core decompression for treatment of Avascular necrosis of the femoral head. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):479.
[9] ZALAVRAS CG, LIEBERMAN JR. Lieberman, Osteonecrosis of the femoral head: evaluation and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014;22(7): 455-464.
[10] 赵春鹏,王军强,苏永刚,等.机器人辅助经皮螺钉内固定治疗骨盆和髋臼骨折[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2017,49(2):274-280.
[11] 曹旭含,白子兴,孙承颐,等.机器人在骨科手术中应用的可靠性与提升空间[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(9):1416-1421.
[12] 徐兆红,宋成利,闫士举.机器人在微创外科手术中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(35):6598-6601.
[13] MONT MA, SALEM HS, PIUZZI NS, et al. Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Where Do We Stand Today?: A 5-Year Update. Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(12):1084-1099.
[14] YOON BH, MONT MA, KOO KH, et al. The 2019 Revised Version of Association Research Circulation Osseous Staging System of Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Arthroplasty. 2020;35(4):933-940.
[15] ZHAO D, ZHANG F, WANG B, et al. Guidelines for clinical diagnosis and treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in adults (2019 version). J Orthop Translat. 2020;21:100-110.
[16] 陈卫衡,何伟,赵德伟.股骨头坏死中医疗效评价标准(2019年版)[J].中医正骨,2019,31(6):3-6.
[17] WAMPER KE, SIEREVELT IN, POOLMAN RW, et al. The Harris hip score: Do ceiling effects limit its usefulness in orthopedics? Acta Orthop. 2010;81(6):703-707.
[18] 高万露,汪小海.视觉模拟疼痛评分研究的进展[J].医学研究杂志, 2013,42(12):144-146.
[19] SEHAT KR, EVANS R, NEWMAN JH. How much blood is really lost in total knee arthroplasty?: Correct blood loss management should take hidden loss into account. Knee. 2000;7(3):151-155.
[20] Huang Z, Li T, Lin N, et al. Evaluation of Radiographic Outcomes after Core Decompression for Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: The Beijing University of Chinese Medicine X-ray Evaluation Method. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022;104(Suppl 2):25-32.
[21] CHOI H, STEINBERG M, CHENG E. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head: diagnosis and classification systems.Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2015;8:210-220.
[22] Zalavras C, Lieberman J. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head: evaluation and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014;22:455-464.
[23] Bastian JD, Jost J, Cullmann JL, et al. Percutaneous screw fixation of the iliosacral joint: optimal screw pathways are frequently not completely intraosseous. Injury. 2015;46:2003-2009.
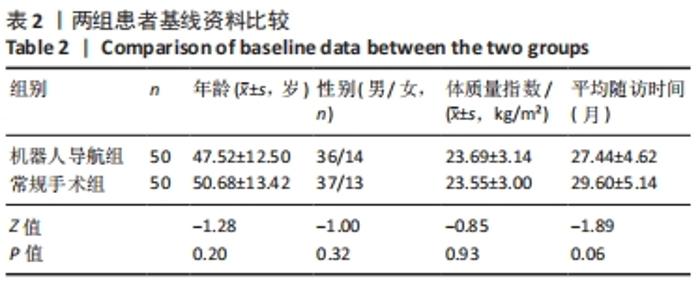
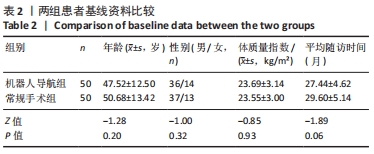
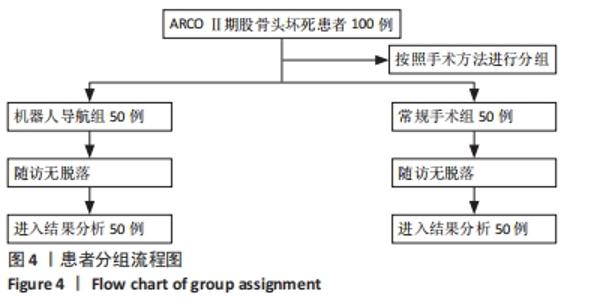
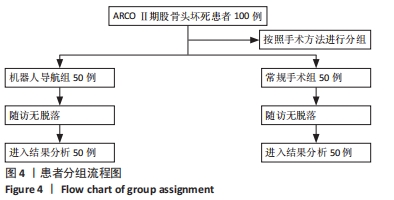
|