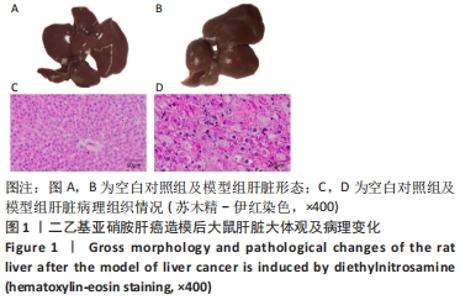
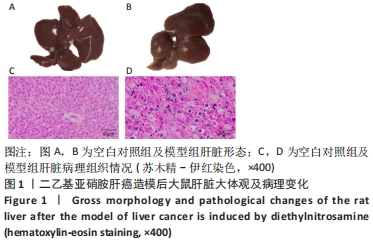
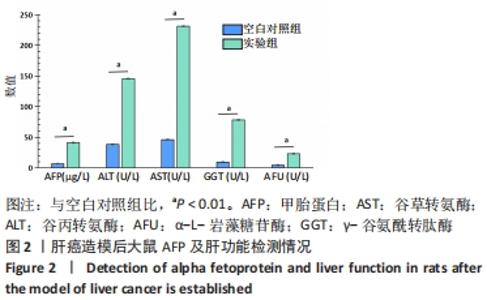
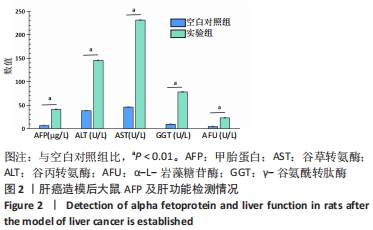
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (32): 5132-5142.doi: 10.12307/2022.905
Previous Articles Next Articles
Network pharmacology and proteomics analysis of Jiawei Xiaoyao San in the treatment of liver cancer complicated with depression in rats
Wen Xiaoyu, Sun Yuhao, Li Zhuoxian, Xu Lijing, Xia Meng
- Basic Medical School, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2021-09-26Accepted:2021-11-11Online:2022-11-18Published:2022-05-14 -
Contact:Xia Meng, MD, Associate professor, Basic Medical School, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wen Xiaoyu, Master candidate, Basic Medical School, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Regional Fund Project), No. 81860805 (to XM); Master ’s Research and Innovation Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine in 2020, No. YCSW2020191 (to WXY); the First-class Discipline Construction Open Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2019XK05 (to XM); the First-class Discipline Construction Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2018XK010 (to XM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wen Xiaoyu, Sun Yuhao, Li Zhuoxian, Xu Lijing, Xia Meng. Network pharmacology and proteomics analysis of Jiawei Xiaoyao San in the treatment of liver cancer complicated with depression in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(32): 5132-5142.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
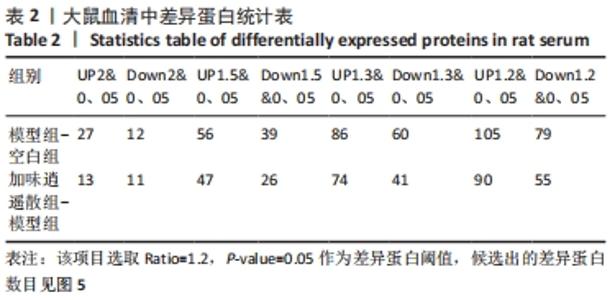
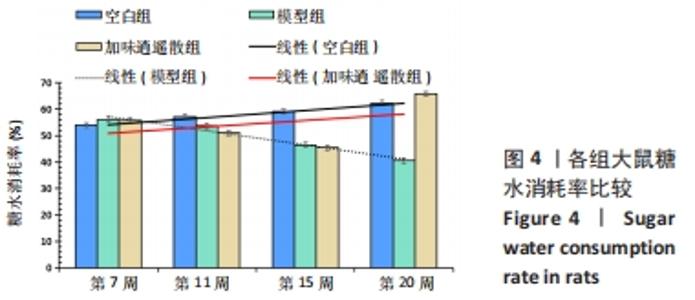
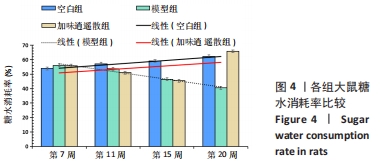
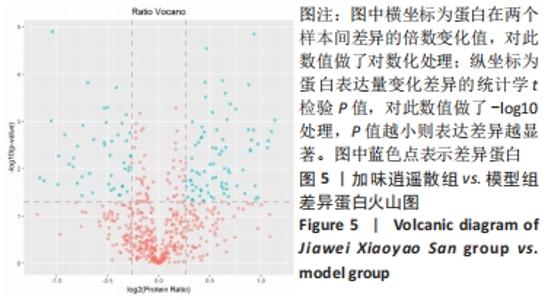
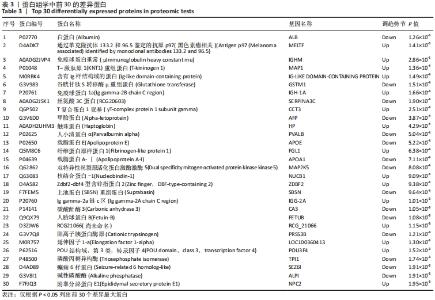
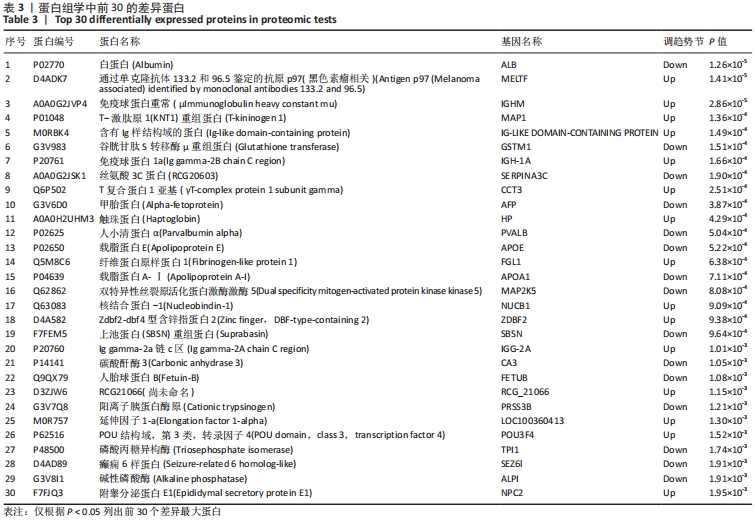
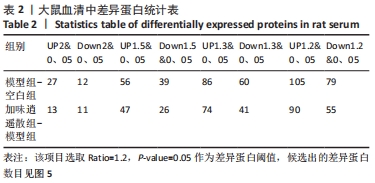
2.5 加味逍遥散治疗肝癌并发抑郁症大鼠的蛋白质组学研究 在蛋白质组学研究中,共鉴定到1 082个蛋白,其中加味逍遥散与模型组相比共145个,有90个上调,55个下调(表2、图5),上调差异最大4个蛋白分别为黑素转铁蛋白(MFI2)、微管相关蛋白1(MAP1)、人源全长重组蛋白(IGHM)、免疫球蛋白重链1a(IGH-1A),下调则是血清白蛋白(ALB)、谷胱甘肽s-转移酶(GSTM1)、丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂A3K(Serpina3c)、甲胎蛋白(AFP)。在Uniprot数据库中输入idmapping,根据此次鉴定到的蛋白uniprot 编号获得相应蛋白名称及基因名称,下调仅列出前差异最大的前30个蛋白信息,见表3。"
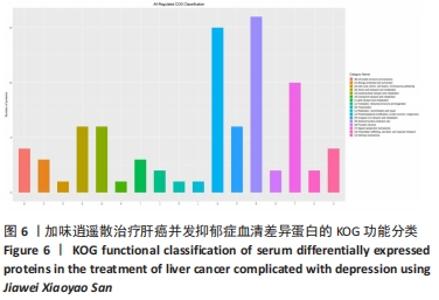
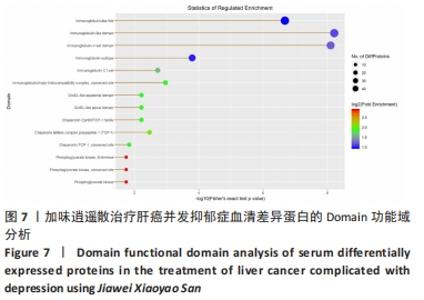
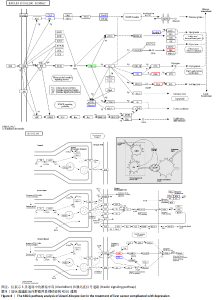
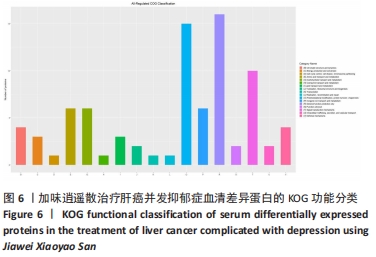
2.6 差异蛋白的KOG功能分类、Domain功能域分析及KEGG通路分析 对鉴定出的加味逍遥散与模型组表达差异蛋白进行Unigene与COG数据库比对获得KOG的分类,主要集中在:仅供一般功能预测(General function prediction only)、翻译后修饰,蛋白质周转,伴侣(Posttranslational modification,protein turnover,chaperones)、信号转导机制(Signal transduction mechanisms),见图6。Domain蛋白功能域主要集中在免疫球蛋白样结构域(Immunoglobulin-like domain)、免疫球蛋白v集结构域(Immunoglobulin V-set domain)、免疫球蛋白样折叠(Immunoglobulin-like fold),见图7。KEGG信号通路富集分析显示作主要涉及5条通路:酒精中毒(Alcoholism,KEGG PATHWAY: hsa05034)、胰岛素信号通路(Insulin signaling pathway,KEGG PATHWAY: map04910)、糖解/葡萄糖生成(Glycolysis/glucose production)、叶酸生物合成等通路(Folic acid biosynthesis and other pathways)、光合生物中的碳固定作用(Carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms),见图8,仅展示其中2条最相关通路图。"
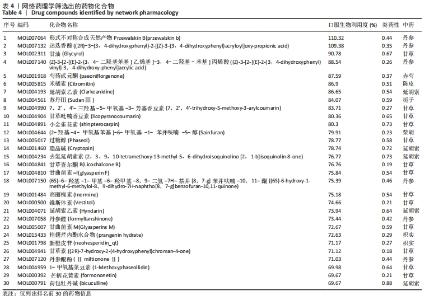
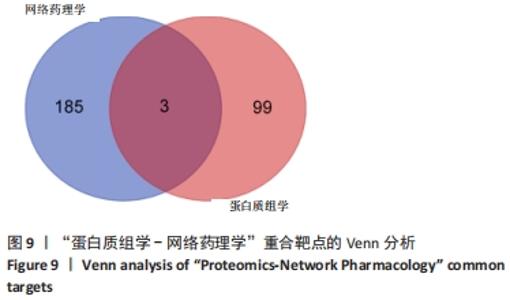
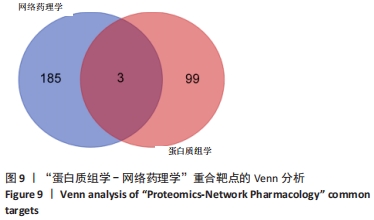
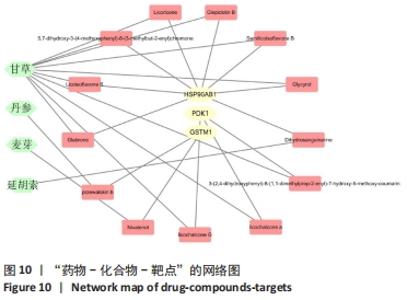
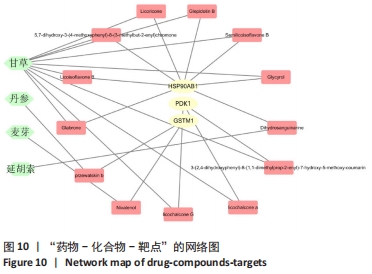
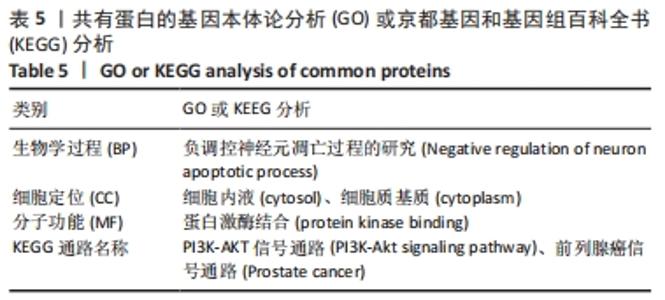
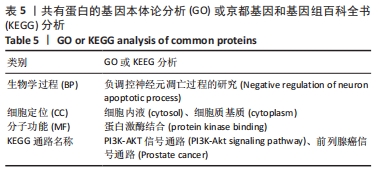
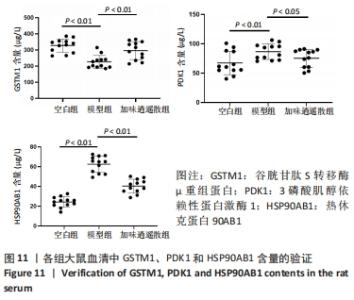
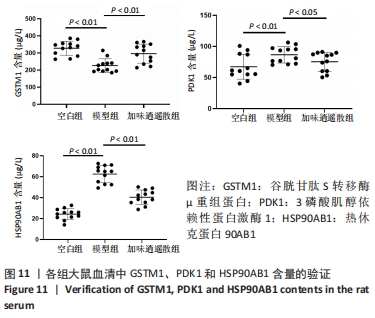
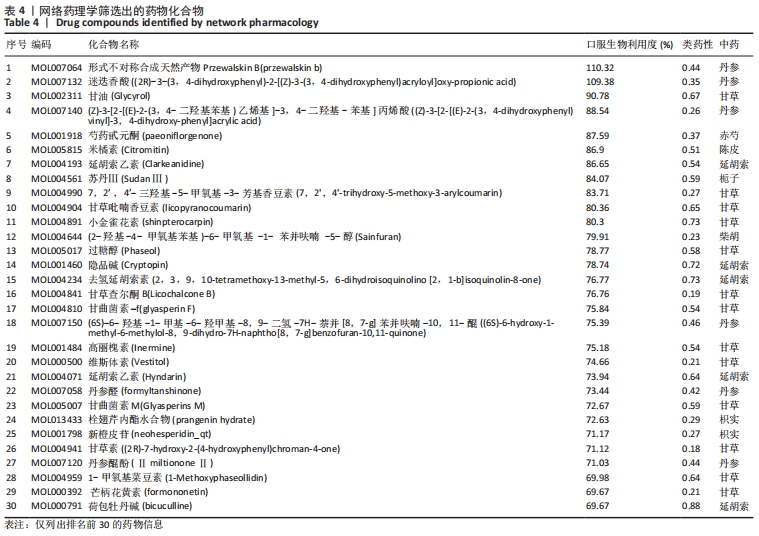
2.7 蛋白质组学研究与网络药理学分析重合靶点 将加味逍遥散组的网络药理学与蛋白质组学中鉴定出的差异蛋白取交集,发现在有3个共同作用靶点,为GSTM1、PDK1、HSP90AB1,见表4,图9。在Cytoscape软件绘制“中药-化合物-靶点”的可视化网络,见图10。全方中发挥调节这些靶点的药物为甘草[灵芝酸G、Licochalcone-G;甘草香豆素、3-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-8-(1,1-dimethylprop-2-enyl)-7-hydroxy-5-methoxy-coumarin;甘草查尔酮A、Licochalcone A;丙三醇、Glycyrol;半甘草异黄酮B、Semilicoisoflavone B;鳞叶甘草素B、Glepidotin B;甘草利酮、Licoricone;甘草宁、5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-8-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)chromone;甘草异黄酮B、Licoisoflavone B;光甘草酮、Glabrone];丹参(形式不对称合成天然产物、Przewalskin B);麦芽(雪腐镰刀菌烯醇、Nivalenol);延胡索(二氢血根碱、Dihydro sanguinarine)。"
| [1] FERRARI M, RIPAMONTI CI, HULBERT-WILLIAMS NJ, et al. Relationships among unmet needs,depression,and anxiety in non–advanced cancer patients. Tumori. 2019;105(2):144-150. [2] AHMED AE, AL-DAHMASH AM, AL-BOQAMI QT, et al. Depression, Anxiety and Stress among Saudi Arabian Dermatology Patients: Cross-sectional study. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2016;16(2):e217-223. [3] 姚嘉良,刘海涛,赵外荣,等.从少阳为枢论治肝癌合并抑郁[J].中医学报,2021,36(2):289-292. [4] 李煜,黎小斌,曹晓静.基于网络药理学和分子对接探讨二仙汤治疗卵巢早衰的作用机制[J/OL].海南医学院学报:1-15[2021-04-11]. doi: 10.13210/j.cnki.jhmu.20210409.002 [5] 崔甄甄.应用定量蛋白质组学技术对Ig A肾病肾组织蛋白的鉴定和定量分析[J].国际检验医学杂志,2017,38(20):2804-2807. [6] CHEN J, ZHAN LB, LU XG, et al. The alteration of zibupiyin recipe on proteomic profiling of forebrain postsynaptic density of db/db mice with diabetesassociated cognitive decline. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;6(2): 471-489. [7] 徐玉音,陈莉.肝癌动物模型建立的方法[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2011,27(4):405-409. [8] FUCHS BC, HOSHIDA Y, FUJII T, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition attenuates liver fibrosis and development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2014;59(4):1577-1590. [9] 徐小红,余正和,李静,等.miRNA132在抑郁症患者及慢性不可预知温和应激抑郁模型大鼠中的表达[J].中国医学科学院学报,2020, 42(5):573-577. [10] 程金来,冷静,夏猛.原发性肝癌并发抑郁症的发病机理及中西医治疗研究进展[J].广西医学,2018,40(24):2938-2941. [11] MIYASAKA T, DO K, TAKAHASHI T, et al. The interplay between neuroendocrine activity and psychological stress-induced exacerbation of allergic asthma. Allergol Int. 2018;67(1):32-42. [12] HU C, LUO Y, WANG H, et al. Re-evaluation of the interrelationships among the behavioral tests in rats exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress. PLoS One. 2017;12(9):e0185129-185138. [3] 孙世光,孙蓉. 抑郁症动物模型相关性研究:强迫游泳实验vs悬尾实验(英文)[A]//中国药学会.2014年中国药学大会暨第十四届中国药师周论文集[C].中国药学会:中国药学会,2014:9. [4] 曹晓靖,孙长岗,李有杰,等.基于中医传承辅助系统的中医药治疗原发性肝癌方剂的组成规律分析[J].中华中医药学刊,2016, 34(1):69-72. [15] 张艺,曲淼,孙文军,等.疏肝健脾法治疗阈下抑郁肝郁脾虚证随机对照双盲研究[J].现代中医临床,2021,28(2):3-8. [16] 高雪松,王永志,李丽,等.疏肝类中药复方干预抑郁症药理机制的研究进展[J].现代中医临床,2018,25(2):46-49. [17] 兰建萍,蒋晁明,郑顺.越鞠丸联合盐酸氟西汀胶囊治疗抑郁症临床研究[J].新中医,2020,52(3):29-31. [18] 张伟娜,王璐.小柴胡汤加味联合肝动脉化疗栓塞术治疗原发性肝癌疗效观察[J].河南中医,2020,40(4):529-532. [19] 吴杨.柴胡疏肝散加减治疗肝癌介入术后肝气郁结型患者的临床疗效观察[D].哈尔滨:黑龙江中医药大学,2019. [20] 楚天云,巩子汉,弓永莉,等.柴胡疏肝散联合腹针治疗慢性疼痛所致抑郁的临床观察[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(9):94-99. [21] 程金来,温小雨,孙玉浩,等.加味逍遥散对肝癌大鼠脑内多巴胺和5-羟色胺水平的影响[J].神经解剖学杂志,2020,36(2):144-148. [22] 吴一迁,陆培新,王加生,等.EPHX代谢酶的遗传多态性和肝癌易感性的相关性研究[J].肿瘤,2003(4):287-289. [23] Tiemersma EW, Omer RE, Bunschoten A, et al. Role of genetic polymorphism of glutathione-S-transferase T1 and microsomal epoxide hydrolase in aflatoxin-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2001;10(7):785-791. [24] 杨志国,鲍春花.谷胱甘肽转硫酶M1和T1基因多态性与肝癌易感性关系的研究[J].中国医学工程,2020,28(10):26-28. [25] 彭宁,李绵靖,兰超智,等.长链非编码RNA ZNF674-AS1通过Wnt信号通路调节肝癌细胞的增殖与凋亡[J].中华实验外科杂志,2019, 36(2):308-311. [26] LI S, XUE F, ZHENG Y, et al. GSTM1 and GSTT1 null genotype increase the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: evidence based on 46 studies. Cancer Cell Int. 2019;19:76. [27] MAZZETTI AP, FIORILE MC, PRIMAVERA A, et al. Glutathione transferases and neurodegenerative diseases. Neurochem Int. 2015; 82:10-18. [28] VARGAS NUNES SO, PIZZO DE CASTRO MR, MOREIRA EG, et al. Association of paraoxonase (PON)1 activity, glutathione S-transferase GST T1/M1 and STin.2 polymorphisms with comorbidity of tobacco use disorder and mood disorders. Neurosci Lett. 2015;585:132-137. [29] DANG Y, CHEN J, FENG W, et al. Interleukin 1β-mediated HOXC10 Overexpression Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis by Upregulating PDK1 and VASP. Theranostics. 2020;10(8):3833-3848. [30] MÄEMETS-ALLAS K, BELITŠKIN D, JAKS V. The inhibition of Akt-PDK1 interaction efficiently suppresses the growth of murine primary liver tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;474(1):118-125. [31] ACKERMANN TF, HÖRTNAGL H, WOLFER DP, et al. Phosphatidylinositide dependent kinase deficiency increases anxiety and decreases GABA and serotonin abundance in the amygdala. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2008; 22(5-6):735-744. [32] HOEFFER CA, KLANN E. mTOR signaling:at the crossroads of plasticity, memory and disease. Trends Neurosci. 2010;33:67-75. [33] LI N, LEE B, LIU RJ, et al. mTOR-dependent synapse formation underlies the rapid antidepressant effects of NMDA antagonists. Science. 2010; 329:959-964. [34] 王明慧,冯林,李萍,等.Hsp90AB1在非小细胞肺癌中高表达并且与肺腺癌患者不良预后相关[J].中国肺癌杂志,2016,19(2):64-69. [35] HAMAMOTO R, TOYOKAWA G, NAKAKIDO M, et al. SMYD2-dependent HSP90 methylation promotes cancer cell proliferation by regulating the chaperone complex formation. Cancer Lett. 2014;351(1):126-133. [36] JARZAB M, KOWAL M, BAL W, et al. Ratio of proliferation markers and HSP90 gene expression as a predictor of pathological complete response in breast cancer neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2016;54(4):202-209. [37] SARATHI A, PALANIAPPAN A. Novel significant stage-specific differentially expressed genes in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2019;19(1):663. [38] 梁家宏,许侨东,严江.热休克蛋白90AB1在肝细胞癌中的表达及初步验证[J].汕头大学医学院学报,2021,34(2):74-78. [39] ZHANG Y, DU L, BAI Y, et al. CircDYM ameliorates depressive-like behavior by targeting miR-9 to regulate microglial activation via HSP90 ubiquitination. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25(6):1175-1190. [40] SASUGA Y, ASAKURA M, MIYAMOTO S, et al. Influence of chronic variable stress (CVS) on the association of glucocorticoid receptor with heat-shock protein (HSP) 90 in rat hippocampus. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1997;17(5):193-200. [41] YANG ZY, KUBOYAMA T, TOHDA C. A systematic strategy for discovering a therapeutic drug for Alzheimer’s disease and its target molecule. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:340. [42] 刘殿玮. BDNF在记忆消退及缺血性脑卒中诱导的记忆损伤中的作用机制[D].济南:山东大学,2020. [43] CHANG F, LEE JT, NAVOLANIC PM.et al.Involvement of PI3K/AKT pathway in cell, cycle progreesion, apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation:a target for cancer chemotherapy. Leukemis. 2003; 17(3):590. [44] GAO H, WANG H, PENG J. Hispidulin induces apoptosis through mitochondrial dysfunction and inhibition of P13k/Akt signalling pathway in HepG2 cancer cells. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014 May;69(1):27-34. [45] 蔡岳,詹磊,王晓东,等.皂荚提取物对肝癌细胞PTEN/P13K/AKT信号通路表达的影响[J].时珍国医国药,2018,29(4):843-845. [46] BAI L, ZHANG S, ZHOU X, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophicfactor induces thioredoxin-1 expression through TrkB/Akt/CREB pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. Biochimie. 2019;160:55-60 [47] 刘淑梅,李丽华,鲁俊华,等.PI3k/Akt信号通路在维生素D促进神经递质分泌中的作用[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2020, 40(11):1597-1602. [48] WU Z, YOU Z, CHEN P, et al. Matrine Exerts Antidepressant-Like Effects on Mice: Role of the Hippocampal PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018;21(8):764-776. [49] LI J, XU B, CHEN Z, et al. PI3K/AKT/JNK/p38 signalling pathway-mediated neural apoptosis in the prefrontal cortex of mice is involved in the antidepressant-like effect of pioglitazone. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2018;45(6):525-535. [50] CHENG Y, GAO XH, LI XJ, et al. Depression promotes prostate cancer invasion and metastasis via a sympathetic-cAMP-FAK signaling pathway. Oncogene. 2018;37(22):2953-2966. |
| [1] | Zhao Yuwei, Gao Yuting, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin . Mechanism of Ermiao San in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 742-748. |
| [2] | Luo Zhen, Huang Yuxi, Chai Shengting, Li Feilong, Chen Qunqun. Bushen Jianpi Huoxue Recipe is closely related to the target of histone demethylase JMJD2B in promoting osteogenic differentiation in osteoporosis: an in vitro cell experimental verification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4643-4650. |
| [3] | Deng Bowen, Li Xiaoye, Jiang Shengyuan, Liu Gan, Zhao Yi, Zhang Houjun, He Feng, Mu Xiaohong. Mechanisms of Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu Decoction in the treatment of cervical spondylosis and anxiety disorder based on the principle of “treating different diseases with the same method”: a network pharmacology analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3650-3656. |
| [4] | Xu Wenshan, Jiang Pingli, Liu Yulu, Ding Yanyi, Yu Yan, Yang Minguang, Liu Weilin, Chen Lidian. Salvianolic acid A effects on hippocampal protein expression in ischemic stroke rats: a tandem mass tag-based proteomic analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3714-3720. |
| [5] | Li Anan, Jiang Tao, Zhan Min, Cai Yuning, Song Min, Li Congcong, Lin Wenzheng, Zhang Jiayuan, Liu Wengang. Pharmacological mechanism of Shenling Baizhu San in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 197-204. |
| [6] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Li Huanan, Chen Feng, Chai Yuan, Gan Bin, Li Song, Chen Dingpeng. Potential molecular mechanism of Guizhi Shaoyao Zhimu Decoction in the treatment of gouty arthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 245-252. |
| [7] | Shan Zhengming, Tao Shuchun, Hu Chunmei, Zhang Zhiyuan, Ding Yinan, He Mengcheng, Tang Qiusha. Extraction, identification and proteomic analysis of exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3036-3042. |
| [8] | Wang Xinyuan, Huang Xiabing, Li Juan, Deng Xin. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on Taohong Siwu Decoction for rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis based on the concept of “Treating Different Diseases with the Same Therapeutic Principle” [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(15): 2419-2425. |
| [9] | Hu Yanan, Wang Ping, Du Haitao, Jing Tianyuan, Wang Chengcheng. Mechanism by which antler glue treats avascular necrosis of the femoral head induced by retinoic acid in rats: a serum proteomics study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2243-2251. |
| [10] | An Yang, Liao Yinan, Xie Chengxin, Li Qinglong, Huang Ge, Jin Xin, Yin Dong. Mechanism of Inulae flos in the treatment of osteoporosis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [11] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [12] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [13] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [14] | Cao Xuhan, Bai Zixing, Sun Chengyi, Yang Yanjun, Sun Weidong. Mechanism of “Ruxiang-Moyao” herbal pair in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 746-753. |
| [15] | Li Yonghua, Feng Qiang, Tan Renting, Huang Shifu, Qiu Jinlong, Yin Heng. Molecular mechanism of Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients treating synovitis of knee osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 765-771. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||