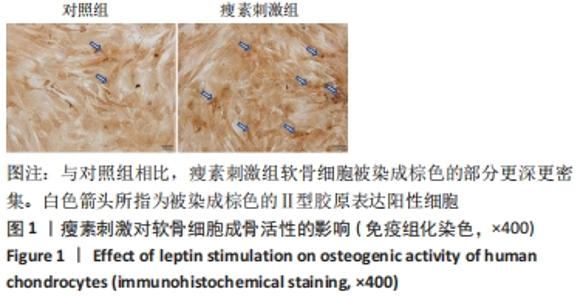
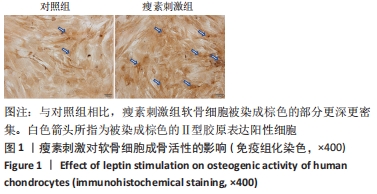
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (26): 4160-4165.doi: 10.12307/2022.818
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 on osteogenic activity in the cartilage of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
Sun Jinpeng, Liu Jun, Bai Yunfeng, Hua Feng, Wang Haoran, Zheng Hongrui, Wu Tao
- Department of Orthopedics, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210011, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2021-07-17Accepted:2021-08-21Online:2022-09-18Published:2022-03-07 -
Contact:Wu Tao, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210011, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Sun Jinpeng, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210011, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Youth Fund), No. 81301523 (to WT); the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (General Project), No. BK20181499 (to WT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Jinpeng, Liu Jun, Bai Yunfeng, Hua Feng, Wang Haoran, Zheng Hongrui, Wu Tao. Effects of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 on osteogenic activity in the cartilage of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4160-4165.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
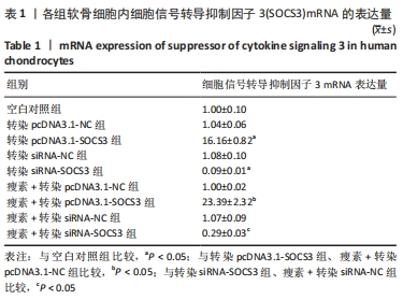
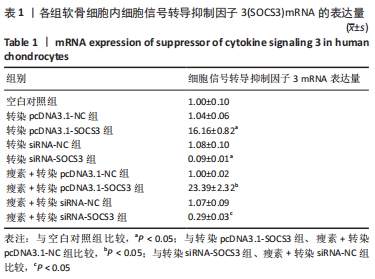
与空白对照组比较,转染pcDNA3.1-NC、siRNA-NC组SOCS3 mRNA表达量无明显变化(P > 0.05),表明空载体质粒和空载体siRNA不会对软骨细胞SOCS3的mRNA水平产生影响。与空白对照组比较,转染pcDNA3.1-SOCS3组SOCS3 mRNA表达量升高(P < 0.05),转染siRNA-SOCS3组SOCS3 mRNA表达量降低(P < 0.05),表明转染pcDNA3.1-SOCS3使软骨细胞内过表达SOCS3,转染siRNA-SOCS3使软骨细胞内低表达SOCS3。 与转染pcDNA3.1-NC组比较,瘦素+转染pcDNA3.1-NC组SOCS3 mRNA表达量无明显变化(P > 0.05);与转染siRNA-NC组比较,瘦素+转染siRNA-NC组SOCS3 mRNA表达量无明显变化(P > 0.05),说明转染空载体质粒或siRNA时,瘦素预刺激不会影响软骨细胞内SOCS3 mRNA的表达。 与转染pcDNA3.1-SOCS3组比较,瘦素+转染pcDNA3.1-SOCS3组SOCS3 mRNA表达量升高(P < 0.05);与转染siRNA-SOCS3组比较,瘦素+转染siRNA-SOCS3组SOCS3 mRNA表达量升高(P < 0.05),结果表明,瘦素可与pcDNA3.1-SOCS3质粒协同作用提升SOCS3表达水平,瘦素可部分抵消转染siRNA-SOCS3造成的软骨细胞SOCS3表达降低。 与瘦素+转染pcDNA3.1-NC组比较,瘦素+转染pcDNA3.1- SOCS3组SOCS3 mRNA表达量升高(P < 0.05);与瘦素+转染pcDNA3.1-NC组比较,瘦素+转染siRNA-SOCS3组SOCS3 mRNA表达量降低(P < 0.05)。结果表明经瘦素预刺激后,转染pcDNA3.1-SOCS3可使软骨细胞SOCS3 mRNA的表达升高,转染siRNA-SOCS3可使软骨细胞SOCS3 mRNA的表达降低。 2.3 瘦素刺激及SOCS3表达量改变对软骨细胞内成骨活性的影响 见表2。"
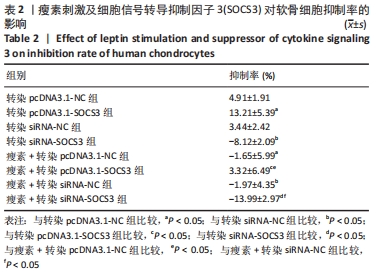

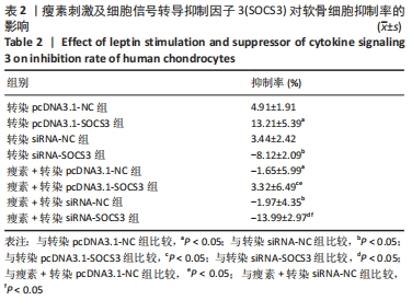
与转染pcDNA3.1-NC组比较,转染pcDNA3.1-SOCS3组细胞抑制率升高(P < 0.05);与转染siRNA-NC组比较,转染siRNA-SOCS3组细胞抑制率降低(P < 0.05);与瘦素+转染pcDNA3.1-NC组比较,瘦素+转染pcDNA3.1-SOCS3组细胞抑制率升高(P < 0.05);与瘦素+转染siRNA-NC组比较,瘦素+转染siRNA-SOCS3组细胞抑制率降低(P < 0.05)。结果表明,上调SOCS3表达量可提高软骨细胞抑制率,表明SOCS3可通过瘦素抵抗抑制瘦素对软骨细胞内成骨活性的提高。 与转染pcDNA3.1-NC组比较,瘦素+转染pcDNA3.1-NC组细胞抑制率降低(P < 0.05);与转染siRNA-NC组比较,瘦素+转染siRNA-NC组细胞抑制率降低(P < 0.05);与转染转染pcDNA3.1-SOCS3组比较,瘦素+转染pcDNA3.1-SOCS3组细胞抑制率降低(P < 0.05);与转染siRNA-SOCS3组比较,瘦素+转染siRNA-SOCS3组细胞抑制率降低(P < 0.05),提示瘦素刺激可显著提高软骨细胞内成骨活性。"

| [1] ROGALA EJ, DRUMMOND DS, GURR J. Scoliosis: Incidence and natural history. A prospective epidemiological study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978;60(2):173-176. [2] PEREZ-MACHADO G, BERENGUER-PASCUAL E, BOVEA-MARCO M, et al. From genetics to epigenetics to unravel the etiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Bone. 2020;140:115563. [3] YIM APY, YEUNG HY, HUNG VWY, et al. Abnormal skeletal growth patterns in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis--a longitudinal study until skeletal maturity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(18):E1148-E1154. [4] CHEUNG PWH, MANNEM A, CHEUNG JPY. Prediction of final body height for female patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Global Spine J. 2021;11(6):833-844. [5] LIU J, YANG X, YU S, et al. The leptin signaling. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018; 1090:123-144. [6] MATUSIK E, DURMALA J, OLSZANECKA-GLINIANOWICZ M, et al. Association between bone turnover markers, leptin, and nutritional status in girls with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (ais). Nutrients. 2020; 12(9):2657. [7] SIU KING CHEUNG C, TAK KEUNG LEE W, KIT TSE Y, et al. Abnormal peri-pubertal anthropometric measurements and growth pattern in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A study of 598 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(18):2152-2157. [8] QIU Y, SUN X, QIU X, et al. Decreased circulating leptin level and its association with body and bone mass in girls with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(24):2703-2710. [9] LIANG G, GAO W, LIANG A, et al. Normal leptin expression, lower adipogenic ability, decreased leptin receptor and hyposensitivity to leptin in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36648. [10] 张臻.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸可溶性瘦素受体水平异常的机制研究及脊柱畸形相关临床研究[D].南京:南京大学,2017. [11] CAROW B, ROTTENBERG ME. Socs3, a major regulator of infection and inflammation. Front Immunol. 2014;5:58. [12] MORI H, HANADA R, HANADA T, et al. Socs3 deficiency in the brain elevates leptin sensitivity and confers resistance to diet-induced obesity. Nat Med. 2004;10(7):739-743. [13] QIAO J, XIAO L, XU L, et al. Genetic variant of socs3 gene is functionally associated with lumbar adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Clin Spine Surg. 2018;31(3):E193-E196. [14] QIN S, SUN D, MU J, et al. Purple sweet potato color improves hippocampal insulin resistance via down-regulating socs3 and galectin-3 in high-fat diet mice. Behav Brain Res. 2019;359:370-377. [15] DO CARMO JM, DA SILVA AA, FREEMAN JN, et al. Neuronal suppressor of cytokine signaling 3: Role in modulating chronic metabolic and cardiovascular effects of leptin. Hypertension. 2018;71(6):1248-1257. [16] TAN J, XU J, WEI G, et al. Hnf1 controls liver lipid metabolism and insulin resistance via negatively regulating the socs-3-stat3 signaling pathway. J Diabetes Res. 2019;2019(5483946. [17] 邱勇,朱丽华,宋知非,等.脊柱侧凸的临床病因学分类研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2000,20(5):5-8. [18] ZHU F, QIU Y, YEUNG HY, et al. Histomorphometric study of the spinal growth plates in idiopathic scoliosis and congenital scoliosis. Pediatr Int. 2006;48(6):591-598. [19] CORDERO-BARREAL A, GONZÁLEZ-RODRÍGUEZ M, RUIZ-FERNÁNDEZ C, et al. An update on the role of leptin in the immuno-metabolism of cartilage. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2411. [20] ZHANG B, YANG L, ZENG Z, et al. Leptin potentiates bmp9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through the activation of jak/stat signaling. Stem Cells Dev. 2020;29(8):498-510. [21] REID IR, BALDOCK PA, CORNISH J. Effects of leptin on the skeleton. Endocr Rev. 2018;39(6):938-959. [22] ZHAO X, HUANG P, LI G, et al. Activation of the leptin pathway by high expression of the long form of the leptin receptor (ob-rb) accelerates chondrocyte senescence in osteoarthritis. Bone Joint Res. 2019;8(9):425-436. [23] LIANG J, FENG J, WU WKK, et al. Leptin-mediated cytoskeletal remodeling in chondrocytes occurs via the rhoa/rock pathway. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(3):369-374. [24] SCOTECE M, MOBASHERI A. Leptin in osteoarthritis: Focus on articular cartilage and chondrocytes. Life Sci. 2015;140:75-78. [25] FU R, HAN F, LIU L, et al. The effects of leptin on the proliferation and differentiation of primary chondrocytes in vitro and cartilage regeneration in vivo. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5(4):1907-1919. [26] ZHAO CQ, LIU D, LI H, et al. Expression of leptin and its functional receptor on disc cells: Contribution to cell proliferation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(23):E858-E864. [27] WANG L, SHAO YY, BALLOCK RT. Leptin synergizes with thyroid hormone signaling in promoting growth plate chondrocyte proliferation and terminal differentiation in vitro. Bone. 2011;48(5):1022-1027. [28] WANG YJ, YU HG, ZHOU ZH, et al. Leptin receptor metabolism disorder in primary chondrocytes from adolescent idiopathic scoliosis girls. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(7):1160. [29] MORRIS DL, RUI L. Recent advances in understanding leptin signaling and leptin resistance. 2010;297(6):E1247-1259. [30] LI X, SHI S, CHEN J, et al. Leptin differentially regulates endochondral ossification in tibial and vertebral epiphyseal plates. Cell Biol Int. 2018; 42(2):169-179. [31] BURWELL RG, DANGERFIELD PH, MOULTON A, et al. Etiologic theories of idiopathic scoliosis: Autonomic nervous system and the leptin-sympathetic nervous system concept for the pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2008;140: 197-207. [32] ENGIN A. Diet-induced obesity and the mechanism of leptin resistance. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;960:381-397. [33] ANDREOLI MF, DONATO J, CAKIR I, et al. Leptin resensitisation: A reversion of leptin-resistant states. J Endocrinol. 2019;241(3):R81-R96. [34] LIU Z, TAM EMS, SUN GQ, et al. Abnormal leptin bioavailability in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: An important new finding. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(7):599-604. [35] BJØRBAEK C, ELMQUIST JK, FRANTZ JD, et al. Identification of socs3 as a potential mediator of central leptin resistance. Mol Cell. 1998; 1(4):619-625. [36] REED AS, UNGER EK, OLOFSSON LE, et al. Functional role of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 upregulation in hypothalamic leptin resistance and long-term energy homeostasis. Diabetes. 2010;59(4):894-906. [37] JORGENSEN SB, O’NEILL HM, SYLOW L, et al. Deletion of skeletal muscle socs3 prevents insulin resistance in obesity. Diabetes. 2013;62(1):56-64. [38] ZIEBA DA, BIERNAT W, SZCZESNA M, et al. Hypothalamic-pituitary and adipose tissue responses to the effect of resistin in sheep: The integration of leptin and resistin signaling involving a suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 and the long form of the leptin receptor. Nutrients. 2019;11(9):2180. |
| [1] | Zhang Yufang, Lü Meng, Mei Zhao. Construction and verification of a full spine biomechanical model of adolescent scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1351-1356. |
| [2] | Wang Shuai, Wang Liancheng, Zhang Shuhao, Li Fuli, Dong Jiaxing, Zhang Yajie. Correlation of the electromyography ratio of the paraspinal muscles on the convex and concave sides with Cobb angle, apical vertebra translation, and coronal balance distance in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1402-1406. |
| [3] | Wu Cong, Jia Quanzhong, Liu Lun. Relationship between transforming growth factor beta1 expression and chondrocyte migration in adult articular cartilage after fragmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1167-1172. |
| [4] | Lin Xuchen, Zhu Hainian, Wang Zengshun, Qi Tengmin, Liu Limin, Suonan Angxiu. Effect of xanthohumol on inflammatory factors and articular cartilage in a mouse mode of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 676-681. |
| [5] | Xu Lei, Han Xiaoqiang, Zhang Jintao, Sun Haibiao. Hyaluronic acid around articular chondrocytes: production, transformation and function characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 768-773. |
| [6] | Zhong Ziling, Qu Shenhong, Han Xing, Wu Di. Isolation, culture and identification of rabbit auricular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3633-3637. |
| [7] | Xie Yan, Li Wuyin, Xing Weipeng, Pei Yuanyuan, Wang Na. Screening of drugs for inhibiting growth plate chondrocyte apoptosis and the effect of resveratrol on delaying epiphyseal closure in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3644-3649. |
| [8] | Yang Demeng, Wang Changgeng, Hu Xinyuan, Ao Fei. Protective effect of eucommia alcohol extract on articular cartilage of osteoarthritis model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3756-3761. |
| [9] | Han Zhi, Wang Zhimiao, Gaxi Sijia, Lu Qingling, Guo Tao. Tissue engineered cartilage constructed by polyurethane composite chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3455-3459. |
| [10] | Wang Wei, Tang Xiangyu, Yi Zhiqian, Liu Zhaoxu. Mechanism of osteoarthritis induced chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3133-3140. |
| [11] | Gu Xiaodong, Li Fei, Che Xianda, Li Pengcui. Relationship between apoptosis of osteoarthritis chondrocytes and reduction of histone deacetylase 4 content [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3147-3151. |
| [12] | Guan Hong, Zhang Hongbo, Shao Yan, Guo Dong, Zhang Haiyan, Cai Daozhang. PDZ domain containing 1 deficiency promotes chondrocyte senescence in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 182-189. |
| [13] | Shi Hang, Li Jia, Liu Xia, Jiang Haiyue. Heterogeneity of chondrocytes derived from human ribs based on single-cell transcriptome sequencing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3011-3017. |
| [14] | Ma Dujun, Peng Liping, Zhou Ziqiong, Zhao Jing, Zhu Houjun, Jiang Shunwan, Zhong Jing, She Ruihao. Effect of RAB39B gene based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology on cartilage differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 2978-2984. |
| [15] | Ren Dong, Zhu Ye, Lei Lei, Wang Yuren. Orthopedic force applied to the rib influences the displacement and rotation angle of thoracic vertebrae: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(18): 2812-2816. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||