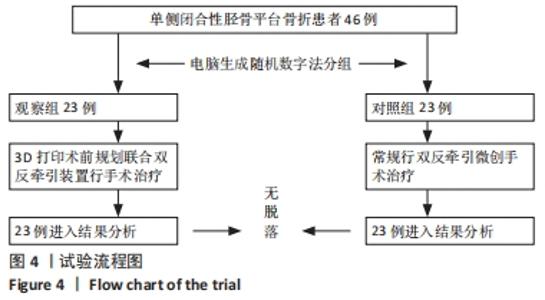
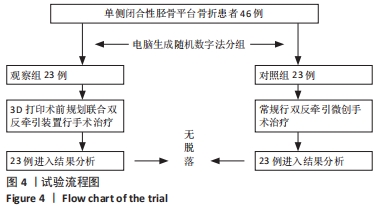
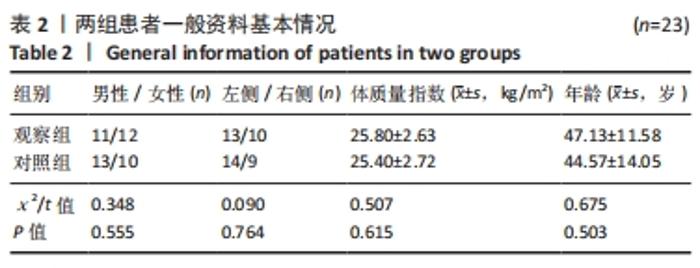
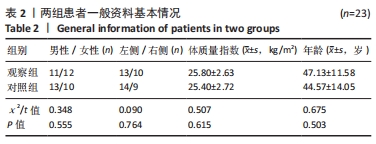
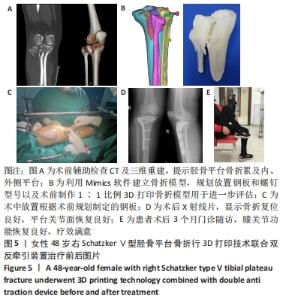
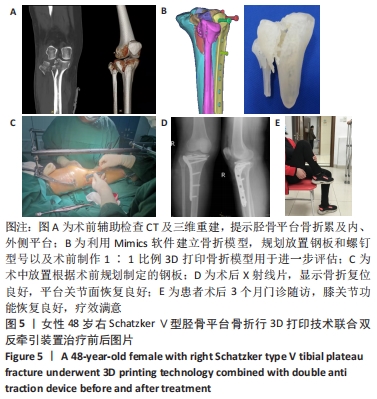
[1] 邵佳申,郑占乐,吕红芝,等.反牵引微创治疗后外侧胫骨平台骨折的疗效分析[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2017,3(5):302-305.
[2] 陈美凯, 许一凡, 陈雪荣. 胫骨平台骨折临床分型研究进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(2):222-224.
[3] 廖志坚,曾小青,邹建生.内外侧联合入路对SchatzkerⅤ型、Ⅵ型胫骨平台骨折的治疗效果分析[J]. 当代医学,2021,27(3):183-184.
[4] 许多红,赵光宇.关节镜联合经皮微创锁定钢板固定治疗30 例胫骨平台骨折的临床效果[J].上海医药,2017,38(7):33-35.
[5] 苏喧,张英泽.双反牵引微创复位固定治疗胫骨平台骨折[J].中国医药学,2016,6(5):1-3.
[6] 郭杰坤,刘国强,曾令国,等.双反牵引复位微创内固定治疗老年Schatzker Ⅳ型胫骨平台粉碎性骨折的临床疗效观察[J].现代医院, 2021,21(4):627-628+632.
[7] 肖占宇,连涛,崔国航.双反牵引微创复位植骨内固定治疗SchatzkerⅡ-Ⅳ型胫骨平台骨折的效果观察[J].微创医学,2019, 14(5):677-679.
[8] HUANG H, HSIEH MF, ZHANG G, et al. Improved accuracy of 3D-printed navigational template during complicated tibial plateau fracture surgery. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2015;38:109-117.
[9] 胡栢均,高大伟,吴宇峰,等.双反牵引架辅助微创治疗难治性胫骨平台骨折临床价值研究[J].陕西医学杂志,2020,49(9):1090-1093.
[10] GROSS BC, ERKAL JL, LOCKWOOD SY, et al. Evaluation of 3D printing and its potential impact on biotechnology and the chemical sciences. Anal Chem. 2014;86(7):3240-3253.
[11] 魏建仝,邹永刚,钱军,等. 3D打印技术在骨科临床诊疗中的应用[A]. 中国自动化学会.2020中国自动化大会(CAC2020)论文集[C].中国自动化学会:中国自动化学会,2020:7.
[12] INSALL JN, RANAWAT CS, AGLIETTI P, et al.A comparison of four models of total knee- replacement prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976; 58(6):754-765.
[13] 陈瑞全,吴建贤,沈显山.中文版Fugl-Meyer运动功能评定量表 的最小临床意义变化值的研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,2015(4):519-521,522.
[14] 刘佩雷,张乐,彭成,等. 3D打印联合关节镜微创治疗胫骨平台骨折[J].实用医学杂志,2021,37(3):353-357.
[15] MTHETHWA J,CHIKATE A. A review of the management of tabial plateau frature.Musculoskelet Surg.2018;102(2):119 -127.
[16] 旦锋,谢鹏,阮文辉,等.双钢板内固定治疗胫骨平台 Schatzker Ⅴ、Ⅵ骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2019,22(4):489-491.
[17] 王友良,冯庆虎,衣龙云,等.前正中入路双钢板固定在Schatzker分型Ⅴ、Ⅵ型胫骨平台骨折中的研究应用[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2021,18(1):43-46+50.
[18] RAZA A, KUMAR S, KUMAR D, et al. Complex Tibial Plateau Fractures: Primary Fixation Using the Ilizarov External Fixator. A Two-year Study at Civil Hospital Karachi, Pakistan. Cureus. 2019;11(8):e5375.
[19] 冯仕华,陈转,郑开达.双反牵引微创复位治疗胫骨平台骨折的效果分析及膝关节功能影响[J]. 现代诊断与治疗,2019,30(23):4230-4231.
[20] 鲍飞龙,刘涛,亢世杰,等.双反牵引装置治疗Schatzker分型Ⅴ、Ⅵ型胫骨平台骨折的优势[J]. 中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2018, 4(5):266-270.
[21] 魏学忠,丁少成,曹家俊.双钢板结合克氏针治疗SchatzkerⅤ、Ⅵ型胫骨平台骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2020,23(3):430-432.
[22] 张擎柱,万乾,张义,等.3D打印技术辅助改良后内侧倒L 入路切开复位内固定术治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折的疗效分析[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2018,32(11):57-59.
[23] GIANNETTI S, BIZZOTTO N, STANCATI A, et al. Minimally invasive fixation in tibial plateau fractures using an pre-operative and intra-operative real size 3D printing. Injury.2017;48(3):784-788.
[24] ATESOK K, SCHEMITSCH EH.Computer-assisted trauma surgery.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18:247-258.
[25] 邵佳申,常恒瑞,郑占乐,等. 3D打印辅助手术治疗胫骨平台骨折疗效的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(23):3767-3772.
[26] HUANG H, HSIEH MF, ZHANG G, et al. Improved accuracy of 3D-printed navigational template during complicated tibial plateau fracture surgery. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2015;38:109-117
[27] GIANNETTI S, BIZZOTTO N, STANCATI A, et al. Minimally invasive fixation in tibial plateau fractures using an pre-opera-tive and intra-operative real size 3D printing. Injury. 2017;48(3):784-788.
[28] HUNG CC, LI Y T, CHOU YC, et al. Conventional plate fixation method versus pre-operative virtual simulation and three-dimensional printing-assisted contoured plate fixation method in the treatment of anterior pelvic ring fracture. Int Orthop. 2019;43(2):425-431.
[29] LOU Y, CAI L, WANG C, et al. Comparison of traditional surgery and surgery assisted by three dimensional printing technology in the treatment of tibial plateau fractures.Int Orthop. 2017;41(9):1875-1880.
[30] SHEN S, WANG P, LI X, et al. Pre-operative simulation using a three-dimensional printing model for surgical treatment of old and complex tibial plateau fractures. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):6044.
|