Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (31): 4975-4981.doi: 10.12307/2022.709
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of eriodictyol on the imbalance of mitochondrial dynamics and apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells induced by hydrogen peroxide
Li Suyao1, 2, Guo Minfang2, Yu Jingwen2, Meng Tao2, Mu Bingtao2, Li Mengdi1, 2, Li Na1, 2, Song Lijuan1, 3, Ma Cungen1, 2, Yu Jiezhong1, 2, 4
- 1Research Center of Neurobiology, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China; 2Institute of Brain Science, Shanxi Datong University, Datong 037009, Shanxi Province, China; 3Department of Neurology, First Affiliated Hospital, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 4Datong Fourth People’s Hospital, Datong 037009, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2021-08-24Accepted:2021-10-11Online:2022-11-08Published:2022-04-25 -
Contact:Yu Jiezhong, MD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Research Center of Neurobiology, The Key Research Laboratory of Benefiting Qi for Acting Blood Circulation Method to Treat Multiple Sclerosis of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China; Institute of Brain Science, Shanxi Datong University, Datong 037009, Shanxi Province, China; Datong Fourth People’s Hospital, Datong 037009, Shanxi Province, China Ma Cungen, MD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Research Center of Neurobiology, The Key Research Laboratory of Benefiting Qi for Acting Blood Circulation Method to Treat Multiple Sclerosis of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China; Institute of Brain Science, Shanxi Datong University, Datong 037009, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Li Suyao, Master candidate, Research Center of Neurobiology, The Key Research Laboratory of Benefiting Qi for Acting Blood Circulation Method to Treat Multiple Sclerosis of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China; Institute of Brain Science, Shanxi Datong University, Datong 037009, Shanxi Province, China Guo Minfang, Master, Associate professor, Institute of Brain Science, Shanxi Datong University, Datong 037009, Shanxi Province, China Li Suyao and Guo Minfang contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:General Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81473577 (to MCG); Open Project of the State Key Laboratory of Molecular Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 2020-MDB-KF-09 (to SLJ); Shanxi Provincial Applied Basic Research Project, No. 201901D211538 (to SLJ); Shanxi Provincial Colleges and Universities Science and Technology Innovation Project, No. 2019L0734 (to SLJ); Shanxi Provincial Colleges and Universities Science and Technology Innovation Project, No. 2020L0484 (to GMF); the Leading Team of Medical Science and Technology of Shanxi Provincial Health Commission, No. 2020TD05 (to MCG); Young Scientist Training Program of Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2021-PY-QN-09 (to SLJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Suyao, Guo Minfang, Yu Jingwen, Meng Tao, Mu Bingtao, Li Mengdi, Li Na, Song Lijuan, Ma Cungen, Yu Jiezhong. Effect of eriodictyol on the imbalance of mitochondrial dynamics and apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells induced by hydrogen peroxide[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4975-4981.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
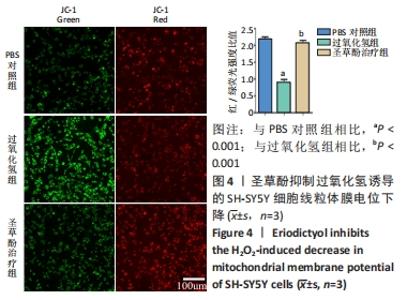
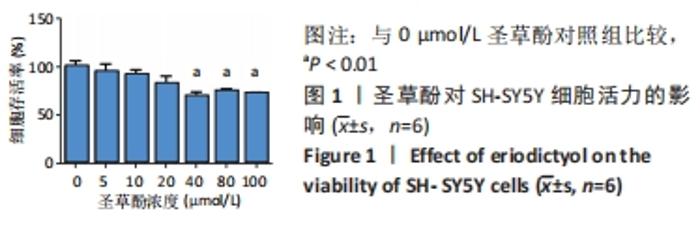
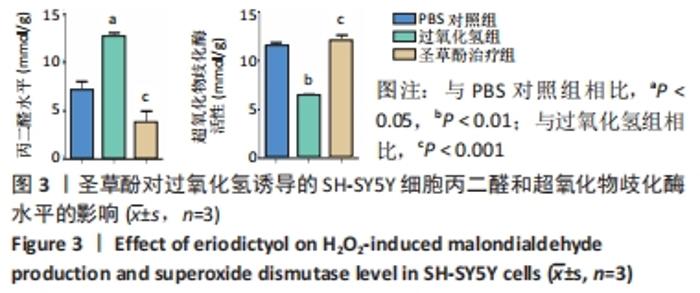
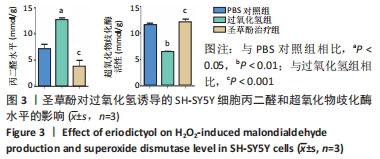
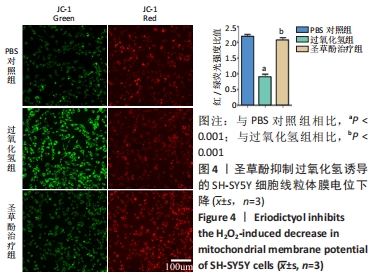
2.4 圣草酚对过氧化氢诱导的SH-SY5Y细胞线粒体膜电位的影响 JC-1常用于检测线粒体膜电位的变化,JC-1探针的灵敏度使其在线粒体膜电位较高时聚集在线粒体基质中,形成聚合物产生红色荧光;当线粒体膜电位下降时JC-1探针则不能聚集,此时产生绿色荧光;通过荧光颜色的变化可以检测到线粒体膜电位的变化;与PBS对照组相比,过氧化氢组的红/绿荧光强度比值低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.001),表明线粒体膜电位降低;与过氧化氢组比较,圣草酚治疗组的红/绿荧光强度比值升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.001),表明线粒体膜电位恢复正常状态。与PBS对照组比较,圣草酚治疗组红/绿荧光强度比值无明显差异(P > 0.05),见图4,说明圣草酚治疗可以恢复线粒体膜电位,发挥保护作用。"
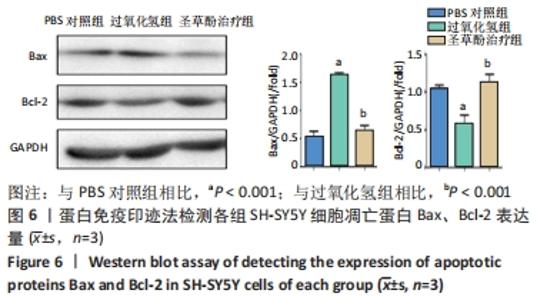
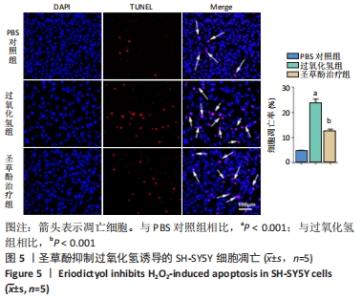
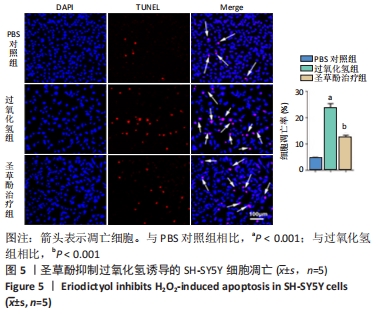
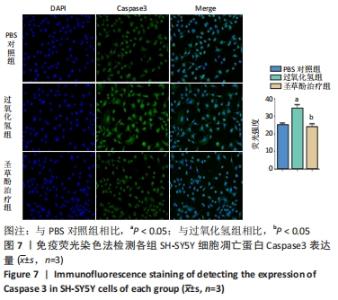
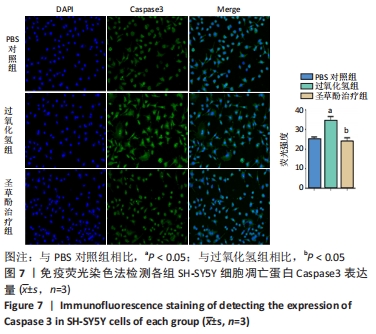
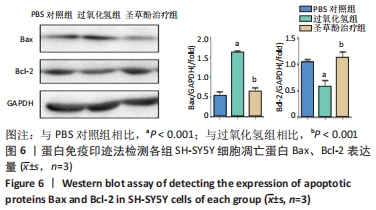
2.6 圣草酚对过氧化氢诱导的SH-SY5Y细胞凋亡相关蛋白的影响 Western blot结果显示,与PBS对照组相比,过氧化氢组促凋亡蛋白Bax的表达显著增加(P < 0.001),抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2的表达明显下降(P < 0.001)。与过氧化氢组相比,圣草酚治疗组Bax的表达下调(P < 0.001),Bcl-2的表达增加(P < 0.001),见图6;免疫荧光结果显示,与PBS对照组相比,过氧化氢组Caspase3增高(P < 0.05),而与过氧化氢组相比,圣草酚治疗组Caspase3表达降低(P < 0.05),见图7,说明圣草酚可以抑制促凋亡蛋白的表达水平,增加抗凋亡蛋白的表达水平。"
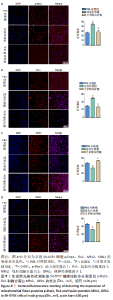
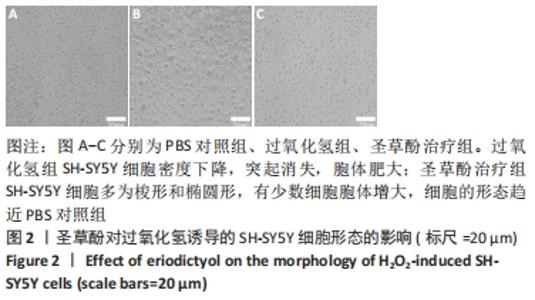
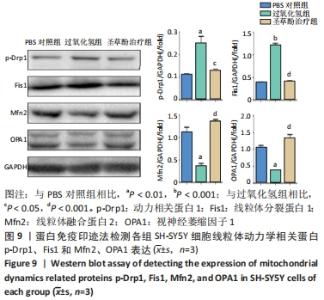
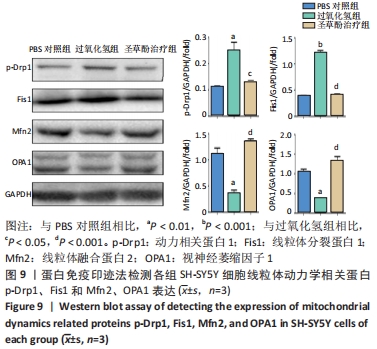
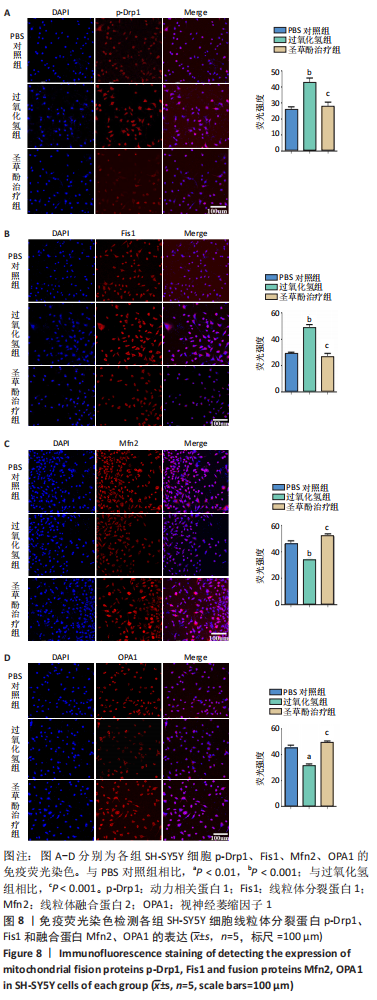
2.7 圣草酚调控线粒体动力学 免疫荧光结果显示,与PBS对照组比较,过氧化氢组线粒体分裂蛋白p-Drp1和Fis1的表达增加(P < 0.001),而线粒体融合蛋白Mfn2、OPA1的表达降低(P < 0.01)。与过氧化氢组比较,圣草酚治疗组p-Drp1和Fis1的表达降低(P < 0.001),Mfn2、OPA1的表达增加(P < 0.001),见图8。Western blot结果显示,与PBS对照组比较,过氧化氢组线粒体分裂蛋白p-Drp1和Fis1的表达增加(P < 0.01,P < 0.001),而线粒体融合蛋白Mfn2、OPA1的表达降低(P < 0.01)。与过氧化氢组比较,圣草酚治疗组p-Drp1和Fis1的表达下调(P < 0.05,P < 0.001),Mfn2、OPA1的表达增加(P < 0.001),见图9。免疫荧光和Western blot结果说明圣草酚可以抑制线粒体分裂蛋白的表达水平,增加线粒体融合蛋白的表达水平。"
| [1] ELFAWY HA, DAS B. Crosstalk between mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and age related neurodegenerative disease: Etiologies and therapeutic strategies. Life Sci. 2019;218:165-184. [2] KONOVALOVA J, GERASYMCHUK D, PARKKINEN I, et al. Interplay between MicroRNAs and Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):6055. [3] SINGH A, KUKRETI R, SASO L, et al. Oxidative Stress: A Key Modulator in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules. 2019;24(8):1583. [4] MOREIRA PI, SIEDLAK SL, WANG X, et al. Increased autophagic degradation of mitochondria in Alzheimer disease. Autophagy. 2007; 3(6):614-615. [5] SALIM S. Oxidative Stress and the Central Nervous System. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2017;360(1):201-205. [6] FLIPPO KH, STRACK S. Mitochondrial dynamics in neuronal injury, development and plasticity. J Cell Sci. 2017;130(4):671-681. [7] SUBRAMANIAM SR, CHESSELET MF. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol. 2013;106-107: 17-32. [8] BHATTI JS, BHATTI GK, REDDY PH. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in metabolic disorders - A step towards mitochondria based therapeutic strategies. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017; 1863(5):1066-1077. [9] MANCZAK M, CALKINS MJ, REDDY PH. Impaired mitochondrial dynamics and abnormal interaction of amyloid beta with mitochondrial protein Drp1 in neurons from patients with Alzheimer’s disease: implications for neuronal damage. Hum Mol Genet. 2011;20(13):2495-2509. [10] MARÍN-GARCÍA J, AKHMEDOV AT. Mitochondrial dynamics and cell death in heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 2016;21(2):123-136. [11] REDDY PH, REDDY TP, MANCZAK M, et al. Dynamin-related protein 1 and mitochondrial fragmentation in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Rev. 2011;67(1-2):103-118. [12] LOSÓN OC, CHEN H, CHAN DC. Fis1, Mff, MiD49 and MiD51 facilitate Drp1 recruitment for mitochondrial fission. FASEB J. 2013;27(5):659-667. [13] FLANNERY PJ, TRUSHINA E. Mitochondrial dynamics and transport in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2019;98:109-120. [14] KNIGHT T, LUEDTKE D, EDWARDS H, et al. A delicate balance - The BCL-2 family and its role in apoptosis, oncogenesis, and cancer therapeutics. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;162:250-261. [15] ABATE M, FESTA A, FALCO M, et al. Mitochondria as playmakers of apoptosis, autophagy and senescence. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020;98: 139-153. [16] ESTAQUIER J, VALLETTE F, VAYSSIERE JL, et al. The mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;942:157-183. [17] HE P, YAN S, ZHENG J, et al. Eriodictyol Attenuates LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation, Amyloidogenesis, and Cognitive Impairments via the Inhibition of NF-κB in Male C57BL/6J Mice and BV2 Microglial Cells. J Agric Food Chem. 2018;66(39):10205-10214. [18] JING X, SHI H, ZHU X, et al. Eriodictyol Attenuates β-Amyloid 25-35 Peptide-Induced Oxidative Cell Death in Primary Cultured Neurons by Activation of Nrf2. Neurochem Res. 2015;40(7):1463-1471. [19] YANG R, WEI L, FU QQ, et al. SOD3 Ameliorates H2O2-Induced Oxidative Damage in SH-SY5Y Cells by Inhibiting the Mitochondrial Pathway. Neurochem Res. 2016;41(7):1818-1830. [20] 张婧.圣草酚通过促进小胶质细胞增殖改善阿尔茨海默病认知功能[D].太原:山西中医药大学,2020. [21] LIN MT, BEAL MF. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature. 2006;443(7113):787-795. [22] JI T, ZHANG X, XIN Z, et al. Does perturbation in the mitochondrial protein folding pave the way for neurodegeneration diseases? Ageing Res Rev. 2020;57:100997. [23] BHAT AH, DAR KB, ANEES S, et al. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases; a mechanistic insight. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015;74:101-110. [24] LEJRI I, AGAPOUDA A, GRIMM A, et al. Mitochondria- and Oxidative Stress-Targeting Substances in Cognitive Decline-Related Disorders: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Evidence. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:9695412. [25] 顾婷,徐占玲,曹玲,等.圣草酚对Aβ(25-35)诱导的PC12细胞损伤的保护作用及其机制[J].现代生物医学进展,2018,18(7):1230-1233. [26] HE P, YAN S, WEN X, et al. Eriodictyol alleviates lipopolysaccharide-triggered oxidative stress and synaptic dysfunctions in BV-2 microglial cells and mouse brain. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(9): 14756-14770. [27] 张群子,范瑛,汪年松.线粒体损伤在糖尿病肾病发病机制中的研究进展[J].世界临床药物,2020,41(10):776-782. [28] DUBOFF B, FEANY M, GÖTZ J. Why size matters - balancing mitochondrial dynamics in Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Neurosci. 2013; 36(6):325-335. [29] OLIVER D, REDDY PH. Dynamics of Dynamin-Related Protein 1 in Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cells. 2019;8(9):961. [30] QI Z, HUANG Z, XIE F, et al. Dynamin-related protein 1: A critical protein in the pathogenesis of neural system dysfunctions and neurodegenerative diseases. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(7):10032-10046. [31] LONG JM, HOLTZMAN DM. Alzheimer Disease: An Update on Pathobiology and Treatment Strategies. Cell. 2019;179(2):312-339. |
| [1] | Cui Wei, Cui Di, Ouyang Ting, Li Xiang, Wei Huiting, Xue Weiyue, Zhou Gang, Qiu Ye. Inhibiting NOX alleviates alcoholic liver damage and lipid metabolism disorder [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | LIU Danni, SUN Guanghua, ZHOU Guijuan, LIU Hongya, ZHOU Jun, TAN Jinqu, HUANG Xiarong, PENG Ting, FENG Wei-bin, LUO Fu. Effect of electroacupuncture on apoptosis of neurons in cerebral cortex of rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury at "Shuigou" and "Baihui" points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [3] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [4] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [5] | Wen Xiaoyu, Sun Yuhao, Xia Meng. Effects of serum containing Wuzang Wenyang Huayu Decoction on phosphorylated-tau protein expression in Alzheimer’s disease cell model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1068-1073. |
| [6] | Zhang Yujie, Yang Jiandong, Cai Jun, Zhu Shoulei, Tian Yuan. Mechanism by which allicin inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of rat vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1080-1084. |
| [7] | Deng Shuang, Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Zhang Jianchao, Yuan Lingyan . Effects of exercise preconditioning on myocardial protection and apoptosis in a mouse model of myocardial remodeling due to early stress overload [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 717-723. |
| [8] | Tang Jiping, Zhang Yeting. Exercise regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease: mechanism and role [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 798-803. |
| [9] | Zhang Lili, Ou Ya, Yuan Xiaodong, Zhang Pingshu. Bax/Bcl-2 protein and apoptosis during adipose-derived stromal cell differentiation into astrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4982-4987. |
| [10] | Wei Hewei, Zheng Weipeng, Liu Zhijun, Zhao Guoyuan, Fang Weihua, Chen Sheng, Liao Zhihao, Wan Lei. Expression of autophagy in rotator cuff tendon stem cells induced by oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4954-4961. |
| [11] | Wang Kang, Zhi Xiaodong, Zhang Yuqiang, Gong Chao, Wang Chenliang, Wang Wei. Human amniotic epithelial cells regulate the proliferation, apoptosis and extracellular matrix synthesis of articular chondrocytes by activating the EGFR/ERK1 signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4967-4974. |
| [12] | Zheng Meijie, Yang Weizhe, Liu Jialin, Han Xiangzhen, Zhou Qiqi, He Huiyu. Apoptosis of mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages induced by lipopolysaccharide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4962-4966. |
| [13] | Gu Chao, Chen Weikai, Liu Tao, Yang Huilin, He Fan. Mitochondrial dysfunction affects osteogenic differentiation potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4921-4927. |
| [14] | Wu Huiting, Zhu Dacheng, Xu Xiaoming, Chang Na. Ethanol extract of toosendan induces apoptosis of leukemia CEM cells through mitochondrial pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4873-4878. |
| [15] | Zhang Xin, Ma Xiaoru, Xue Jingwen, Wang Fangfang, Wu Lan, Li Yue. Protective effect of Ganoderma lucidum spores on epididymis and authophage in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4632-4637. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||