Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (18): 2914-2921.doi: 10.12307/2022.703
Previous Articles Next Articles
Reasonable choice and application of bio-ink sterilization technology for 3D bioprinting
Yuan Long1, Li Sen1, Bian Jichao1, Li Wanxiang1, Wang Guodong2
- 1Department of Clinic, Jining Medical University, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2021-10-27Accepted:2021-11-17Online:2022-06-28Published:2022-01-30 -
Contact:Wang Guodong, MD, Associate chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Yuan Long, Master candidate, Department of Clinic, Jining Medical University, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81871814 (to WGD); Jining Key Research and Development Program, No. 2020YXNS022 (to WGD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yuan Long, Li Sen, Bian Jichao, Li Wanxiang, Wang Guodong. Reasonable choice and application of bio-ink sterilization technology for 3D bioprinting[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(18): 2914-2921.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
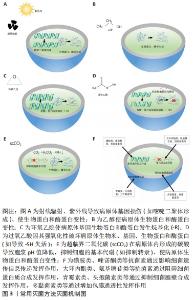
2.1 灭菌方法概述 生物墨水是在3D生物打印过程中,生物材料或几种生物材料的混合物以水凝胶形式负载着所需的种子细胞,这种用于重建组织结构的混合材料。生物墨水可由天然或合成的生物材料制成,也可以将两者作为组合而成。在某些情况下,无需任何额外生物材料载体的细胞也可以用作生物墨水。在生物墨水的临床应用中,应根据灭菌的目的和要灭菌的材料,选择不同的灭菌方法,其中,高压蒸汽灭菌、射线辐射、紫外线、乙醇以及气体灭菌等是相对常用的灭菌技术。 2.1.1 高压蒸汽灭菌 因其效率高、效果好和成本低而被广泛应用于医疗器械灭菌[18]。该方法使用高温加压水蒸汽对微生物进行热破坏。然而,高温将对温度敏感生物材料产生不利影响[19]。 2.1.2 射线辐射灭菌 是应用于外科手术、食品保存以及生物制药在内的多个领域的常用灭菌技术[20],例如γ射线25- 40 kGy的辐射剂量即可达到灭菌要求。来自γ射线光子的能量转移到暴露材料的电子中,被激发的电子产生大量的自由基,进而破坏存在材料表面的微生物DNA[21]。当DNA遭到不可逆转地破坏时,微生物将不再具有生物活性,从而产生灭菌作用,见图3A。 2.1.3 紫外线灭菌 其原理与射线灭菌相似,但紫外线使用的光子能量较低;通常认为波长在290-200 nm的紫外线灭菌效果最好[22]。紫外线通过引发两个胸腺嘧啶分子之间发生交联反应形成共价二聚体来破坏DNA双螺旋结构,从而造成DNA产生不可逆的损伤,导致病原体活性丧失。虽然紫外线处理并不是的完全有效的灭菌方法[23],但它是基础实验室材料常用的灭菌方法之一[24],见图3A。 2.1.4 乙醇处理 是一种消毒方法,而不是灭菌方法,因为乙醇不会对微生物的芽孢起作用,限制了其作为表面灭菌剂的使用[25]。但是,乙醇处理许多文献报道中对生物墨水最常用的消毒方法之一[23,26-30]。实验中常使用体积分数为70%的乙醇,在此浓度下,乙醇分子能够导致微生物的蛋白质变性而不会产生表面保护膜,从而起到消毒目的,见图3B。 2.1.5 环氧乙烷灭菌 其机制是使脱氧核糖核酸、核糖核酸和酶分子的侧链的烷基化,导致微生物新陈代谢和则增值过程受到抑制[30]。该方法灭菌效果显著,现已被广泛用于医疗设备的消毒。但是由于环氧乙烷的易燃易爆性及其残留物的毒性和致癌性,致使环氧乙烷灭菌在生物工程上的使用受限[18],见图3C。 2.1.6 过氧乙酸灭菌 过氧乙酸是一种常见的强氧化物,化学性质不稳定性,易于分解。其灭菌机制是其分解产物过氧化氢和醋酸氧化某些特定氨基酸,如色氨酸(Trp)、甲硫氨酸(Met)和组氨酸(His)等[31]。从而对微生物的细胞膜以及生物酶系统造成损害,达到灭菌目的,见图3D。 2.1.7 超临界二氧化碳(supercritical carbon dioxide,scCO2) 是通过将CO2气体压强加压到近10倍大气压,高于CO2气体形成液相的临界点[32]。当前scCO2方法灭菌的确切机制尚未阐明,学者们推测CO2气体扩散到细胞内形成碳酸,发生酸化反应和化学氧化,从而产生灭菌作用[33]。事实证明,使用scCO2可以实现灭菌,而不会对材料结构产生负面影响。因此scCO2被建议用于温度敏感型生物材料的灭菌[34],见图3E。 2.1.8 抗菌素 是指对细菌有抑制或杀灭作用的药物,包括抗生素和人工合成药物(如磺胺类药物、喹诺酮类药物等)。抗菌素主要通过特异性抑制细菌的新陈代谢,破坏细菌结构,影响细菌功能,是细菌丧失增殖能力,从而达到灭菌或杀菌的目的。不同类型抗菌素的作用机制不同,主要有以下几点:抑制细菌细胞壁合成(如青霉素类、头孢菌素类等)、改变胞质膜的通透性(如多黏菌素类等)、抑制细菌蛋白质合成(如氨基糖苷类等)、影响叶酸代谢(如磺胺类药物等),见图3F。"

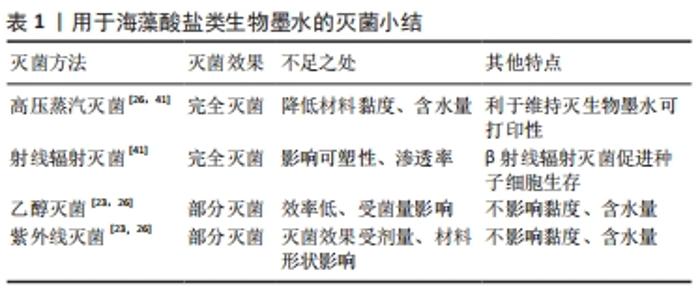
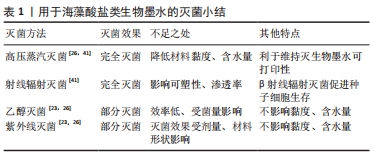
2.2 海藻酸盐类生物墨水的灭菌 海藻酸盐是一种广泛使用的生物材料,在生物医学领域得到广泛应用,包括药物输送、伤口愈合和组织工程等[35]。海藻酸盐是来自海藻的一种天然共聚物,含有的β-D-甘露糖醛酸和α-L-古罗糖醛酸形成一个类似于人体组织细胞外基质超微结构的聚合链网[36]。链的长度取决于海藻酸盐的分子质量,β-D-甘露糖醛酸和α-L-古罗糖醛酸基团的出现并没有明确的序列。相邻糖醛酸链中暴露的羧基(R-COOH)和羟基(R-OH)可以通过添加Ca2+或Ba2+等二价阳离子结合在一起,这是海藻酸盐可以发生交联和凝胶化的结构基础。作为水凝胶,海藻酸盐可用于封装细胞,从而将种子细胞与宿主免疫系统隔离开来,用于涉及细胞输送和蛋白质生产的重要载体[37]。海藻酸盐本身不于细胞发生相互作用,并能为细胞长时间提供生长环境,这对于要求保留细胞表型和细胞形态的药物试验来说是至关重要的[36-37]。在组织工程应用中,海藻酸盐可以与肽结合用于细胞黏附,从而促进细胞增殖和细胞外基质的产生[38]。海藻酸盐的化学交联可以协同控制和优化,使其适合用于组织和器官的生物打印,这进一步突出了海藻酸盐的多功能性[39-41]。 为了研究了不同灭菌方法对海藻酸盐特性的影响,学者们进行了广泛的研究。 CHANSORIA等[26]首先将3组2%海藻酸盐标本分别做以下处理:①在121 ℃ 、110 kPa环境下处理15 min、②体积分数为70%的乙醇浸泡3 h、③波长250 nm紫外线照射1 h。 在评估灭菌效果时发现,无论细菌类型或负载量如何,高压蒸汽灭菌完全可以完成对海藻酸盐的灭菌。而乙醇灭菌和紫外线灭菌的有效性取决于细菌类型和负载量。在3种灭菌方法中,乙醇灭菌的效率最低,只能对负载每毫升104 CFU大肠杆菌的标本完成灭菌。STOPPEL等[23]发现20 min的乙醇灭菌足以去除1.5 mm厚的海藻酸盐水凝胶中的微生物,而紫外线照射消除微生物的效果不够稳定,其有效性在很大程度上取决于紫外线剂量,因此STOPPEL等[23]指出乙醇灭菌是海藻酸盐或复合海藻酸盐生物墨水灭菌的最佳方法。LAFUENTE-MERCHAN等[42]运用高压蒸汽灭菌、β射线辐射灭菌和γ射线辐射辐射灭菌3种方法对含海藻酸盐的标本进行灭菌后,在灭菌效果评估时发现3组灭菌后没有监测到微生物,达到欧洲药典有关生物墨水无菌性的标准,这说明以上3种灭菌方法都可用于基于海藻酸盐生物墨水的灭菌。 CHANSORIA等[26]实验中每个灭菌组的β-D-甘露糖醛酸/α-L-古罗糖醛酸以及相应的β-D-甘露糖醛酸和α-L-古罗糖醛酸含量与空白组相似。而β-D-甘露糖醛酸和α-L-古罗糖醛酸比率值的轻微变化可以归因于核磁光谱分析中算法的误差,这表明灭菌过程不会显著影响海藻酸盐的自身结构的影响性较小。动态测试灭菌后标本在0.1-1 s剪切速率下黏度发现乙醇灭菌和紫外线灭菌不影响海藻酸盐的黏度。然而,高压蒸汽灭菌后将导致标本黏度显著降低。根据文献报道,高压蒸汽灭菌导致标本黏度降低的原因可能是降低了标本的分子质量[43]。LAFUENTE等[42]发现短周期和长周期高压蒸汽灭菌后的生物墨水黏度未发生明显变化,γ射线辐射灭菌后导致生物墨水的黏度大幅下降。高压蒸汽灭菌和γ射线辐射灭菌处理提高了生物墨水的渗透率。相比之下,β射线辐射灭菌后,只对部分含海藻酸盐生物墨水渗透率有所影响。因此,可以推测,由于灭菌过程而发生的生物聚合物结构变化会增加生物墨水渗透率。随着渗透率的提升,生物墨水所搭载细胞的新陈代谢将会加快,这会促进细胞的生存[26]。另外,与高压蒸汽灭菌相比,射线辐射灭菌造成的海藻酸盐主链断裂和交联影响了生物墨水的可塑性,打印的支架难以保持形状,因此在维持灭菌后的生物墨水可打印性方面,高压蒸汽灭菌有其优势所在[42-43]。但高压蒸汽灭菌会导致海藻酸盐生物墨水水分大量丢失,而使用乙醇灭菌和紫外线灭菌时,不会显著改变生物墨水的含水量。海藻酸盐类生物墨水的灭菌特点,见表1。"
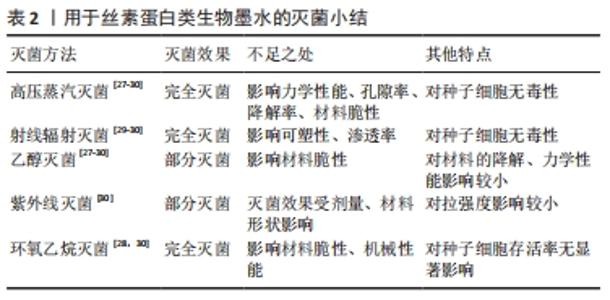
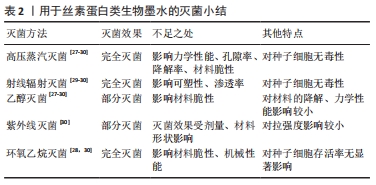
2.3 丝素蛋白类生物墨水的灭菌 丝素蛋白是从家蚕茧中提取的一种纤维蛋白。丝素蛋白表现出2种构象形式,称为丝素Ⅰ和丝素Ⅱ。丝素Ⅰ的水溶性较强,由无规卷曲和α螺旋结构组成。丝素Ⅱ是一种疏水形式,以热力学稳定的β折叠结构为主,其间具有强大的氢键和范德华力[30]。丝素蛋白的相对分子质量较大,有200 000-350 000 或更大,这是因为丝素蛋白含有庞大的重复的疏水区域,众多重复的疏水区域之间还夹杂着许多亲水基团[44]。家蚕的丝素蛋白由重链和轻链组成,它们通过二硫键连接在一起,重链和轻链上有许多与其非共价相连的糖蛋白 P25 (因其相对分子质量为25 000而得名),糖蛋白P25在维持丝素蛋白的完整性方面发挥着重要作用。 重链的疏水结构域包含甘氨酸-X(X包括丙氨酸、丝氨酸、苏氨酸及缬氨酸)重复序列,可以形成反平行的 β-折叠。可以通过有机溶剂或物理剪切实现丝素Ⅰ与丝素Ⅱ之间的变换[45]。丝素蛋白具有良好的生物相容性、良好的透气性、生物可降解性强以及免疫反应相对较弱,丝素蛋白的可塑性好,可以加工成多种形态,而且加工后的丝素蛋白具有较高的机械强度、热稳定性和抗微生物性[46]。当前,丝素蛋白在生物医学和组织材料领域已经得到广泛的应用,如酶学研究、伤口敷料、骨骼、软骨和肌腱再生的支架等。此外,丝素蛋白还可制成不可吸收缝合线用于软组织的生物修复。 GIL等[27]研究了高压蒸汽灭菌和在体积分数70%的乙醇溶液中浸泡灭菌对多孔基于丝素蛋白生物墨水支架的影响,他们发现,高压蒸汽灭菌导致丝素蛋白的关键结构重新排列,影响了支架的降解和力学性能,而体积分数70%乙醇灭菌导致丝素蛋白微小的晶体结构发生重新排列,对材料的降解或力学性能影响较小。HOFFMAN等[28]研究了高压蒸汽灭菌、干热灭菌、环氧乙烷灭菌和浸入体积分数70%的乙醇灭菌对丝素蛋白生物墨水的影响。他们发现,高压蒸汽灭菌会影响丝素蛋白3D支架的孔隙率,而干热灭菌则会影响支架的力学性能,所有的灭菌方法都会对丝素蛋白支架物理性能产生不同程度的影响。GEORGE等[29]研究了体积分数70%的乙醇灭菌、高压蒸汽灭菌和γ射线辐射灭菌对用于角膜组织工程的丝素蛋白生物墨水的影响,他们发现,高压蒸汽灭菌导致丝素蛋白角膜透明度和降解率下降,并改变了丝素蛋白角膜的表面拓扑结构,并发现高压蒸汽灭菌对丝素蛋白纤维的二级结构和力学性能发造成负面影响。DE MORAES等[30]研究灭菌方法对丝素蛋白的影响时发现,紫外线辐射灭菌和γ射线辐射灭菌过程没有导致致密型丝素蛋白发生任何物理变化或化学交联;体积分数70%的乙醇灭菌、高压蒸汽灭菌和环氧乙烷灭菌增加了丝素蛋白膜的脆性;紫外线辐射灭菌没有对丝素蛋白多孔膜的抗拉强度产生影响。由体积分数70%的乙醇灭菌、高压蒸汽灭菌、环氧乙烷灭菌和γ射线辐射灭菌的丝素蛋白致密膜对细胞没有毒性,细胞存活率保持在90%-100%,与未经灭菌处理的材料相比,无显著性差异。用于丝素蛋白类生物墨水的灭菌研究内容,见表2。"
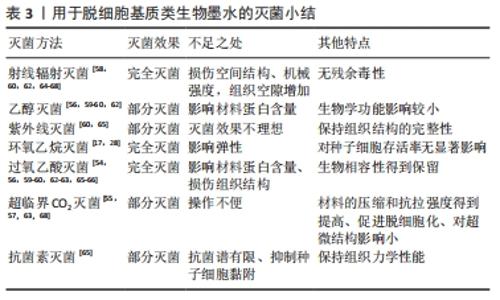
2.4 脱细胞基质类生物墨水的灭菌 在组织和器官中,细胞外基质包含各种维持细胞新陈代谢的生物大分子(主要是多糖、胶原蛋白和糖蛋白),在组织生长和成熟中发挥重要作用[47-48]。细胞外基质为细胞黏附提供物理支持,并显著影响细胞的生物学行为,比如细胞的迁移、增殖和分化。此外,来自不同组织和器官的细胞外基质有其独特的结构和成分,这将对细胞、组织和器官的功能产生不同的影响。作为存储生长因子和细胞因子的载体,细胞外基质可以调节生物代谢平衡。来自不同组织的细胞外基质为细胞有丝分裂、定向分化、凋亡、黏附和形态发生提供了特定的组织微环境,由此来调控细胞行为[49-50]。研究还发现,细胞外基质在癌症进展中发挥着关键作用。不同组织的细胞外基质的对共孵化癌细胞的生物行为有显著影响。例如,肿瘤相关组织的细胞外基质显著促进白细胞介素8和血管内皮生长因子的分泌,并提高了癌细胞的迁移和入侵能力,而来自健康组织的细胞外基质对癌细胞增殖和入侵表现出抑制作用[51]。由于细胞外基质结构和成分对组织健康的重要作用,细胞外基质变化可能会导致某些疾病发生。例如,关节软骨细胞外基质中糖胺聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白的减少可能会导致骨关节炎的发生[52]。 通过物理或化学方法从组织中去除细胞获得的即为脱细胞基质生物墨水。脱细胞基质生物墨水就像是一个复杂的分子网络,保留了组织中许多固有的成分,如胶原蛋白、弹性蛋白、糖蛋白、透明质酸以及生长因子等其他生物大分子[53]。脱细胞基质生物墨水的成分和结构于自然组织近乎一致,另外,由于脱细胞基质生物墨水的生物相容性好、免疫原性低,在过去几年里逐渐成为生物材料的研究热点。理想的脱细胞基质生物墨水灭菌方法不仅可以有效去除微生物,确保消毒材料无毒,还能保持生物墨水的物理和化学特性以及生物活性。因此,选择合适的灭菌方法非常重要。 由于脱细胞基质材料的成分、结构、体积和功能不同,因此灭菌方法多种多样。然而,对于同一组织或器官,因为缺乏统一的标准,所以当前文献中报告的灭菌方法常不同。 (1)循环系统: FIDALGO等[54]研究发现,依次使用抗生素和抗真菌药物的混合物与过氧乙酸联合对牛心包脱细胞基质灭菌后,可以获得无菌的材料,同时组织原始的结构和生物相容性得到了充分的保留。CHOE等[55]用scCO2对猪心包脱细胞基质灭菌后,发现灭菌后材料的压缩和抗拉强度得到提高。FERCANA 等[56]使用体积分数0.1%过氧乙酸和体积分数4%乙醇溶液对动脉血管外膜脱细胞基质进行灭菌处理。处理后,将动脉外膜脱细胞基质冷冻干燥,然后研磨并制备成水凝胶,该水凝胶仍可促进血管生成,这说明此灭菌方法对动脉外膜脱细胞基质的生物学功能影响不大。GULER等[57]用scCO2对绵羊主动脉脱细胞基质进行1 h的灭菌处理,结果表明scCO2不仅可以灭菌,还可以进一步实现组织的脱细胞化,经过处理后,材料仍然保持了原始组织厚度和刚度。有研究用辐射剂量为1.5 kGy 和 3 kGy的γ射线对猪心脏瓣膜脱细胞基质进行灭菌,结果1.5 kGy辐射剂量的瓣膜没有达到完全灭菌的标准,而3 kGy辐射剂量的瓣膜则可以对瓣膜彻底灭菌,而且瓣膜的机械强度随着辐射剂量的增加而下降[58]。 (2)消化系统:HUSSEIN等[59]分别用过氧乙酸和乙醇对猪肝脱细胞基质进行灭菌2 h后发现,乙醇不能有效地对材料进行灭菌,而过氧乙酸可以;此外乙醇处理组后的材料中胶原蛋白含量明显低于过氧乙酸处理组。GOSZTYLA等[60]对大鼠小肠脱细胞基质进行以下4种处理:①体积分数0.1%过氧乙酸处理3 h、②体积分数0.08%过氧乙酸/体积分数1%过氧化氢溶液处理3 h、③体积分数0.18%过氧乙酸/体积分数4.8%乙醇溶液处理3 h、④在波长254 nm的紫外线下辐射90 s。结果表明,上面4种灭菌方法都可以达到灭菌目的,每组灭菌后的组织中胶原蛋白和糖胺聚糖的含量并没有很大的差异,灭菌前后小肠脱细胞基质促进细胞生长的的能力未发生明显变化;然而,化学灭菌导致组织结构部分丧失,比如小肠绒毛部分边缘的磨损,而紫外线灭菌可以保持组织结构的完整性。FENG等[61]用12 kGy的辐射剂量(射线来源:钴60)对大鼠胃脱细胞基质进行灭菌,同样发现灭菌后组织的空间结构和机械强度没有显著变化。 (3)呼吸系统:BONENFANT等[62]比较了2种小鼠肺脱细胞基质的灭菌方法,一种是用5 Gy/min辐射12 min,另一种是用体积分数0.1%过氧乙酸/体积分数4%乙醇溶液对脱细胞后的肺组织洗涤3次,结果表明,过氧乙酸/乙醇可以溶解细胞外基质,过氧乙酸/乙醇处理组肺的整体外观与天然肺相似。在辐射组肺中,肺泡间隔膜增厚、肺泡相互融合以及出现肺大疱。有研究用scCO2对肺脱细胞基质灭菌后发现scCO2灭菌对脱细胞肺中的胶原蛋白、弹性蛋白和糖胺聚糖的含量和材料的力学性能没有不利影响;而过氧乙酸处理的样本力学性能没有发生显著变化[63]。有研究用辐射剂量为25 kGy的γ射线辐射小鼠气管脱细胞基质,结果表明25 kGy的γ射线辐射足以对气管脱细胞基质有效灭菌,但组织的超微结构收到严重损害,导致组织空隙增加和基质结构紊乱[64]。 (4)泌尿系统:ROSARIO等[17]用环氧乙烷和体积分数0.1%过氧乙酸对猪膀胱脱细胞基质进行灭菌,结果表明,过氧乙酸灭菌材料的杨氏模量减小,而用环氧乙烷灭菌材料的杨氏模量增大。MORADI等[65]对兔肾脱细胞基质进行以下4种处理:①在体积分数0.5%的过氧乙酸溶液中处理2 h,结果表明,过氧乙酸可以有效灭菌,并保留组织的力学性能和基质的主要成分;②在青霉素G、两性霉素B和庆大霉素组成的抗生素混合物中处理30 min,发现上述处理能够有效灭菌并能保持组织的力学性能,但不能促进兔脂肪间充质干细胞的黏附;③在无菌PBS中浸泡,并用波长为320-480 nm紫外线照射2 h后,检测发现,此方法无法达到灭菌目的;④在辐射剂量5 kGy的γ射线辐射3-5 min后,材料的机械强度下降,微观结构发生变化。 (5)免疫系统:免疫系统中常见的脱细胞基质是脱细胞的脾脏组织。一些研究使用过氧乙酸对其进行灭菌,例如,GAO等[66]使用体积分数0.1%过氧乙酸对大鼠脾脏脱细胞基质处理3 h,完成了对大鼠脾脏脱细胞基质的灭菌。 (6)运动系统:EDWARDS等[67]研究了γ射线辐射对猪肌腱脱细胞基质的灭菌作用,结果证实射线辐射改变了其生物力学性能,包括降低抗拉强度和杨氏模量。SUN等[68]比较了γ射线辐射和scCO2对绵羊肌腱的脱细胞基质灭菌效果,结果发现肌腱脱细胞基质在γ射线辐射后干燥、收缩。γ射线辐射的肌腱横截面有明显孔洞,而scCO2处理的肌腱的超微结构完好无损。骨与软骨修复多年来一直是研究热点,但文献报道对骨与软骨脱细胞基质的灭菌方法相对较少。骨与软骨脱细胞基质灭菌方法以射线辐射和乙醇处理为主要方法[69-70]。用于脱细胞基质类生物墨水的灭菌研究总结见表3。"

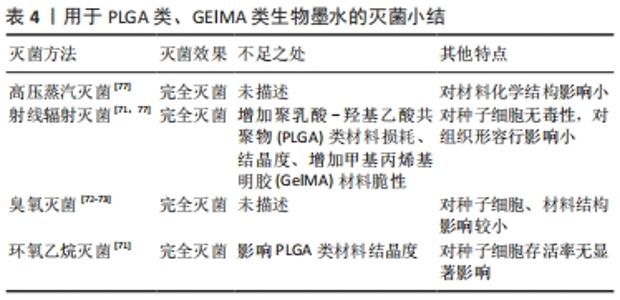
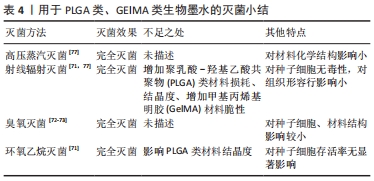
2.5 其他类型的生物墨水灭菌 2.5.1 聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物类 聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物[poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid),PLGA]已被广泛用作生物材料。由于其既定的生物相容性、可调生物降解性和良好的力学性能,它可能是3D生物打印领域使用最广泛的合成聚合物之一,并用于设计许多组织类型,包括软骨、骨骼、肝脏、神经、皮肤和血管。GRADWOHL等[71]用γ射线、β射线和环氧乙烷对含有PLGA的生物墨水进行灭菌,研究发现这3种方法都能有效地对实验样本灭菌。将经γ射线、β射线和环氧乙烷灭菌的PLGA样本与未经灭菌处理的样本进行比较,结果发现环氧乙烷对PLGA样本的重量几乎没有发生变化,而经过两种射线处理的样本重量随着辐射剂量的增大而减少。此外,环氧乙烷灭菌后导致PLGA样本结晶度从1.15%大幅降至0.50%。对于γ和β射线辐射后,只有辐射剂量为15 kGy和25 kGy的γ射线辐射处理组在对样本的结晶度有所影响,而其他处理组的结晶度未发生明显变化[71]。REDIGUIERI等[72]用臭氧气体对3D打印的PLGA支架进行灭菌,臭氧处理48 h后的PLGA支架即可达到完全灭菌标准。电镜下观察到灭菌处理前后,所有支架PLGA纤维之间没有明显的差异,没有发现损坏迹象。此外,臭氧灭菌对PLGA支架对细胞的黏附和生长繁殖没有产生显著的负面影响。 2.5.2 甲基丙烯基明胶类 甲基丙烯基明胶(Gelatin methacryloyl,GelMA)水凝胶因其可促进细胞与支架相互作用来维持细胞功能和新组织发育的能力而被广泛用作组织工程中[73]。GelMA支架含有天然存在的细胞黏合配体,GelMA水凝胶的生物力学特性可以通过改变分子浓度、紫外线交联参数进行调控[74]。GelMA生物墨水因其可控的打印性和良好的细胞黏附性也是3D生物打印最常用的生物墨水之一[75-76]。RIZWAN等[77]研究发现,使用高压蒸汽灭菌、γ射线辐射灭菌和环氧乙烷灭菌3种方法对GelMA灭菌后对聚合物进行核磁光谱分析表明,高压蒸汽灭菌组和环氧乙烷灭菌组样本的甲基在灭菌前后甲基的含量接近一致。γ射线辐射灭菌组样本的甲基减少。凝胶上甲基流失可能导致GelMA水凝胶强度变弱,因此γ射线辐射灭菌后水凝胶将变得更加脆性增大,在操作中容易解体。在研究3种灭菌方法处理前后GelMA对人真皮成纤维细胞和人脐血管内皮细胞的影响时指出,无论使用何种灭菌方法,人真皮成纤维细胞和人脐血管内皮细胞在GelMA上生长状况均良好,细胞生长面积没有显著差异。与对照组相比,虽有些许不同但不具有统计学差异。这说明高压蒸汽灭菌、γ射线辐射灭菌和环氧乙烷灭菌3种灭菌方法对GelMA处理后,对其生物相容性的影响甚微。用于PLGA类、GElMA类生物墨水的灭菌研究总结见表4。"
| [1] DERAKHSHANFAR S, MBELECK R, XU K, et al. 3D bioprinting for biomedical devices and tissue engineering: a review of recent trends and advances. Bioact Mater. 2018;3(2):144-156. [2] NGUYEN D, HÄGG DA, FORSMAN A, et al. Cartilage tissue engineering by the 3d bioprinting of ips cells in a nanocellulose/alginate bioink. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):658-658. [3] SINGH YP, BANDYOPADHYAY A, MANDAL BB. 3D Bioprinting using cross-linker-free silk–gelatin bioink for cartilage tissue engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(37):33684-33696. [4] KIM BS, DAS S, JANG J, et al. Decellularized extracellular matrix-based bioinks for engineering tissue- and organ-specific microenvironments. Chem Rev. 2020;120(19):10608-10661. [5] XIE Z, GAO M, LOBO AO, et al. 3D bioprinting in tissue engineering for medical applications:the classic and the hybrid. Polymers (Basel). 2020; 12(8):1717. [6] VARKEY M, VISSCHER DO, VAN ZUIJLEN PPM, et al. Skin bioprinting:the future of burn wound reconstruction? Burns Trauma. 2019;7:4. [7] HE P, ZHAO J, ZHANG J, et al. Bioprinting of skin constructs for wound healing. Burns Trauma. 2018;6:5. [8] FUEST M, YAM GHF, MEHTA JS, et al. Prospects and challenges of translational corneal bioprinting. Bioengineering (Basel). 2020;7(3):71. [9] FAROOQI KM, COOPER C, CHELLIAH A, et al. 3D printing and heart failure: the present and the future. JACC: Heart Failure. 2019;7(2):132-142. [10] POTYONDY T, UQUILLAS JA, TEBON PJ, et al. Recent advances in 3D bioprinting of musculoskeletal tissues. Biofabrication. 2021;13(2): 022001. [11] HODDER E, DUIN S, KILIAN D, et al. Investigating the effect of sterilisation methods on the physical properties and cytocompatibility of methyl cellulose used in combination with alginate for 3D-bioplotting of chondrocytes. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(1):10. [12] GALANTE R, PINTO TJA, COLAÇO R, et al. Sterilization of hydrogels for biomedical applications: a review. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(6):2472-2492. [13] DI FOGGIA M, CORDA U, PLESCIA E, et al. Effects of sterilisation by high-energy radiation on biomedical poly-(ε-caprolactone)/hydroxyapatite composites. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(6):1789-1797. [14] SONG JJ, OTT HC. Organ engineering based on decellularized matrix scaffolds. Trends Mol Med. 2011;17(8):424-432. [15] SCHENKE-LAYLAND K, VASILEVSKI O, OPITZ F, et al. Impact of decellularization of xenogeneic tissue on extracellular matrix integrity for tissue engineering of heart valves. J Struct Biol. 2003;143(3):201-208. [16] GOUK SS, LIM TM, TEOH SH, et al. Alterations of human acellular tissue matrix by gamma irradiation: histology, biomechanical property, stability, in vitro cell repopulation, and remodeling. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008;84B(1):205-217. [17] ROSARIO DJ, REILLY GC, ALI SALAH E, et al. Decellularization and sterilization of porcine urinary bladder matrix for tissue engineering in the lower urinary tract. Regen Med. 2008;3(2):145-156. [18] DAI Z, RONHOLM J, TIAN Y, et al. Sterilization techniques for biodegradable scaffolds in tissue engineering applications. J Tissue Eng. 2016. doi:10.1177/2041731416648810. [19] AHMED EM. Hydrogel:Preparation, characterization, and applications: a review. J Adv Res. 2015;6(2):105-121. [20] EL-ASHHAB F, SHEHA L, ABDALKHALEK M, et al. The influence of gamma irradiation on the intrinsic properties of cellulose acetate polymers. J Assoc Arab Univ Basic App Sci. 2013;14(1):46-50. [21] PALMER I, CLARKE S, NELSON J, et al. Identification of a suitable sterilisation method for collagen derived from a marine Demosponge. Int J Nano Biomater. 2012;4:148-163. [22] MEECHAN P, WILSON C. Use of ultraviolet lights in biological safety cabinets:a contrarian view. Applied Biosafety. 2006;11(4):222-227. [23] STOPPEL WL, WHITE JC, HORAVA SD, et al. Terminal sterilization of alginate hydrogels:efficacy and impact on mechanical properties. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2014;102(4):877-884. [24] PAN T, SONG W, CAO X, et al. 3D bioplotting of gelatin/alginate scaffolds for tissue engineering: influence of crosslinking degree and pore architecture on physicochemical properties. J Mater Sci Technol. 2016; 32(9):889-900. [25] SIRITIENTONG T, SRICHANA T, ARAMWIT P. The effect of sterilization methods on the physical properties of silk sericin scaffolds. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2011;12(2):771-781. [26] CHANSORIA P, NARAYANAN LK, WOOD M, et al. Effects of autoclaving, etoh, and uv sterilization on the chemical, mechanical, printability, and biocompatibility characteristics of alginate. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(9):5191-5201. [27] GIL ES, PARK SH, HU X, et al. Impact of sterilization on the enzymatic degradation and mechanical properties of silk biomaterials. Macromol Biosci. 2014;14(2):257-269. [28] HOFMANN S, STOK KS, KOHLER T, et al. Effect of sterilization on structural and material properties of 3-D silk fibroin scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(1):308-317. [29] GEORGE KA, SHADFORTH AMA, CHIRILA TV, et al. Effect of the sterilization method on the properties of Bombyx mori silk fibroin films. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(2):668-674. [30] DE MORAES MA, WESKA RF, BEPPU MM. Effects of sterilization methods on the physical, chemical, and biological properties of silk fibroin membranes. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2014;102(4): 869-876. [31] BEDNARSKI DM, LANTZ EE, BOBST CE, et al. Sterilization of epidermal growth factor with supercritical carbon dioxide and peracetic acid; analysis of changes at the amino acid and protein level. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2020;1868(2):140334. [32] KARAJANAGI SS, YOGANATHAN R, MAMMUCARI R, et al. Application of a dense gas technique for sterilizing soft biomaterials. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2011;108(7):1716-1725. [33] BERNHARDT A, WEHRL M, PAUL B, et al. Improved sterilization of sensitive biomaterials with supercritical carbon dioxide at low temperature. PLoS One. 2015;10(6):e0129205-e0129205. [34] RIBEIRO N, SOARES GC, SANTOS-ROSALES V, et al. A new era for sterilization based on supercritical CO2 technology. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(2):399-428. [35] LEE KY, MOONEY DJ. Alginate: properties and biomedical applications. Prog Polym Sci. 2012;37(1):106-126. [36] ANDERSEN T, STRAND B, FORMO K, et al. Alginates as biomaterials in tissue engineering. Carbohydrate Chem. 2011;37(6):227-258. [37] SILVA R, SINGH R, SARKER B, et al. Hydrogel matrices based on elastin and alginate for tissue engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;114:614-625. [38] SHACHAR M, TSUR-GANG O, DVIR T, et al. The effect of immobilized RGD peptide in alginate scaffolds on cardiac tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(1):152-162. [39] CHANSORIA P, NARAYANAN LK, SCHUCHARD K, et al. Ultrasound-assisted biofabrication and bioprinting of preferentially aligned three-dimensional cellular constructs. Biofabrication. 2019;11(3):035015. [40] JOVIC T, KUNGWENGWE G, MILLS A, et al. Plant-derived biomaterials:a review of 3d bioprinting and biomedical applications. Front Mechan Eng. 2019;5:19. [41] CHANSORIA P, SHIRWAIKER R. 3D bioprinting of anisotropic engineered tissue constructs with ultrasonically induced cell patterning. Add Manufact. 2020;32:101042. [42] LAFUENTE-MERCHAN M, RUIZ-ALONSO S, ESPONA-NOGUERA A, et al. Development, characterization and sterilisation of Nanocellulose-alginate-(hyaluronic acid)- bioinks and 3D bioprinted scaffolds for tissue engineering. Materi Sci Eng C. 2021;126:112160. [43] FU S, THACKER A, SPERGER DM, et al. Relevance of rheological properties of sodium alginate in solution to calcium alginate gel properties. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2011;12(2):453-460. [44] AYOUB NA, GARB JE, TINGHITELLA RM, et al. Blueprint for a high-performance biomaterial: full-length spider dragline silk genes. PLoS One. 2007;2(6):e514-e514. [45] YANG M. Silk-based biomaterials. Microsc Res Tech. 2017;80(3):321-330. [46] MACINTOSH AC, KEARNS VR, CRAWFORD A, et al. Skeletal tissue engineering using silk biomaterials. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2008;2(2-3):71-80. [47] BONNANS C, CHOU J, WERB Z. Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(12):786-801. [48] YAO Q, CHOI JH, DAI Z, et al. Improving tumor specificity and anticancer activity of dasatinib by dual-targeted polymeric micelles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(42):36642-36654. [49] LINDE-MEDINA M, MARCUCIO R. Living tissues are more than cell clusters: the extracellular matrix as a driving force in morphogenesis. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2018;137:46-51. [50] HOSHIBA T, CHEN G, ENDO C, et al. Decellularized extracellular matrix as an in vitro model to study the comprehensive roles of the ECM in stem cell differentiation. Stem Cells Int. 2016. doi:10.1155/2016/6397820. [51] BINDER M J, MCCOOMBE S, WILLIAMS ED, et al. The extracellular matrix in cancer progression: role of hyalectan proteoglycans and ADAMTS enzymes. Cancer Lett. 2017;385:55-64. [52] SUTHERLAND AJ, CONVERSE GL, HOPKINS RA, et al. The bioactivity of cartilage extracellular matrix in articular cartilage regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(1):29-39. [53] YU T, WEN L, HE J, et al. Fabrication and evaluation of an optimized acellular nerve allograft with multiple axial channels. Acta Biomater. 2020;115:235-249. [54] FIDALGO C, IOP L, SCIRO M, et al. A sterilization method for decellularized xenogeneic cardiovascular scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2018;67:282-294. [55] CHOE J A, JANA S, TEFFT B J, et al. Biomaterial characterization of off-the-shelf decellularized porcine pericardial tissue for use in prosthetic valvular applications. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(7):1608-1620. [56] FERCANA GR, YERNENI S, BILLAUD M, et al. Perivascular extracellular matrix hydrogels mimic native matrix microarchitecture and promote angiogenesis via basic fibroblast growth factor. Biomaterials. 2017;123: 142-154. [57] GULER S, ASLAN B, HOSSEINIAN P, et al. Supercritical carbon dioxide-assisted decellularization of aorta and cornea. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2017;23(9):540-547. [58] HELDER MRK, HENNESSY RS, SPOON DB, et al. Low-dose gamma irradiation of decellularized heart valves results in tissue injury in vitro and in vivo. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;101(2):667-674. [59] HUSSEIN KH, PARK KM, TEOTIA PK, et al. Sterilization using electrolyzed water highly retains the biological properties in tissue-engineered porcine liver scaffold. Int J Artif Organs. 2013;36(11):781-792. [60] GOSZTYLA C, LADD MR, WERTS A, et al. A Comparison of sterilization techniques for production of decellularized intestine in mice. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2020;26(2):67-79. [61] FENG L, HU YL, MA P, et al. Decellularized gastric matrix as a mesh for gastric perforation repair. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2021;109(3):451-462. [62] BONENFANT NR, SOKOCEVIC D, WAGNER DE, et al. The effects of storage and sterilization on de-cellularized and re-cellularized whole lung. Biomaterials. 2013;34(13):3231-3245. [63] BALESTRINI JL, LIU A, GARD AL, et al. Sterilization of lung matrices by supercritical carbon dioxide. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2016;22(3): 260-269. [64] JOHNSON CM, GUO D, RYALS S, et al. The feasibility of gamma radiation sterilization for decellularized tracheal grafts. Laryngoscope. 2017; 127(8):E258-E264. [65] MORADI L, MOHAMMADI JOBANIA B, JAFARNEZHAD-ANSARIHA F, et al. Evaluation of different sterilization methods for decellularized kidney tissue. Tissue Cell. 2020;66:101396. [66] GAO R, WU W, XIANG J, et al. Hepatocyte culture in autologous decellularized spleen matrix. Organogenesis. 2015;11(1):16-29. [67] EDWARDS J H, HERBERT A, JONES GL, et al. The effects of irradiation on the biological and biomechanical properties of an acellular porcine superflexor tendon graft for cruciate ligament repair. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105(8):2477-2486. [68] SUN Y, LOVRIC V, WANG T, et al. Effects of SCCO(2), Gamma irradiation, and sodium dodecyl sulfate treatments on the initial properties of tendon allografts. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(5):1565. [69] YOU L, WEIKANG X, LIFENG Y, et al. In vivo immunogenicity of bovine bone removed by a novel decellularization protocol based on supercritical carbon dioxide. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018; 46(sup2):334-344. [70] KAKABADZE A, MARDALEISHVILI K, LOLADZE G, et al. Reconstruction of mandibular defects with autogenous bone and decellularized bovine bone grafts with freeze-dried bone marrow stem cell paracrine factors. Oncol Lett. 2017;13(3):1811-1818. [71] GRADWOHL M, CHAI F, PAYEN J, et al. Effects of two melt extrusion based additive manufacturing technologies and common sterilization methods on the properties of a medical grade PLGA copolymer. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(4):572. [72] REDIGUIERI CF, PINTO T, BOU-CHACRA NA, et al. Ozone gas as a benign sterilization treatment for PLGA nanofiber scaffolds. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2016;22(4):338-347. [73] YUE K, TRUJILLO-DE SANTIAGO G, ALVAREZ MM, et al. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2015;73:254-271. [74] ADIB AA, SHEIKHI A, SHAHHOSSEINI M, et al. Direct-write 3D printing and characterization of a GelMA-based biomaterial for intracorporeal tissue engineering. Biofabrication. 2020;12(4):045006. [75] XIE M, GAO Q, ZHAO H, et al. Electro-Assisted Bioprinting of Low-Concentration GelMA Microdroplets. Small. 2019;15(4):1804216. [76] YING G, JIANG N, YU C, et al. Three-dimensional bioprinting of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA). Bio-Design and Manufacturing. 2018;1(4):215-224. [77] RIZWAN M, PEH GSL, ANG HP, et al. Sequentially-crosslinked bioactive hydrogels as nano-patterned substrates with customizable stiffness and degradation for corneal tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials. 2017;120:139-154. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [3] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [4] | Yang Feng, Zhao Qian, Zhang Shixuan, Zhao Tienan, Feng Bo. Effectiveness and safety of rapamycin combined with CD133 antibody stent in preventing vascular restenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 579-584. |
| [5] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [6] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [7] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [8] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [9] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [10] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [11] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [12] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [13] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [14] | Zeng Yuwei, Huang Chuang, Wei Jianguo, Duan Dongming, Wang Le. Tracing transplanted bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rat calvarial defect by bioluminescence imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 3968-3973. |
| [15] | He Qi, Xu Faya, Li Xiyan, Han Lei, Xiao Yanbing, Tu Jiao. Preparation and sterilization method of human acellular amniotic membrane scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4028-4033. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||