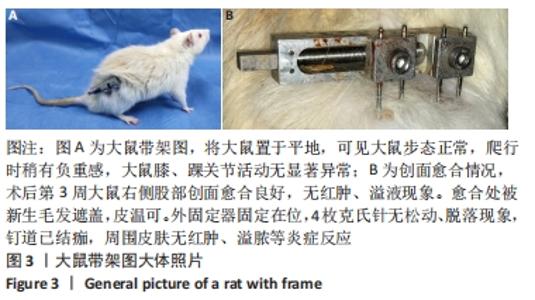
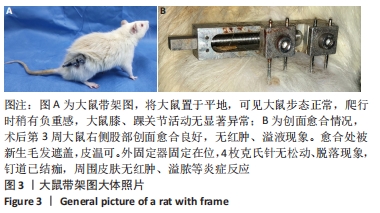
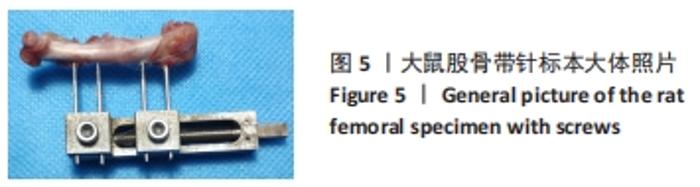
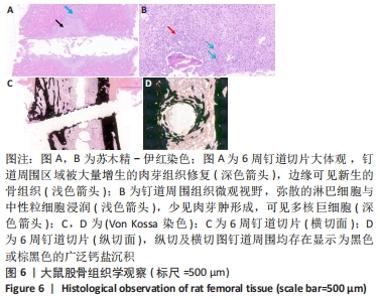
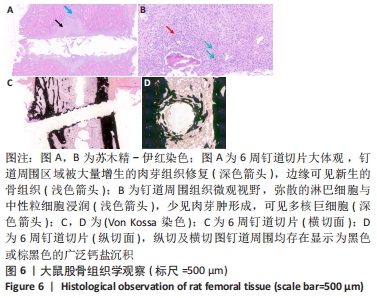
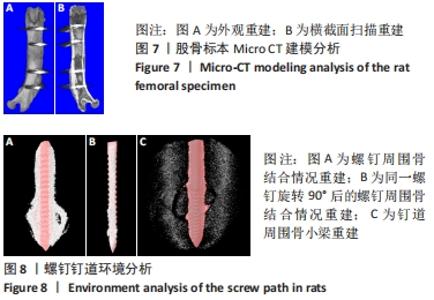
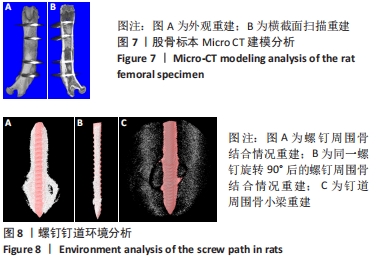
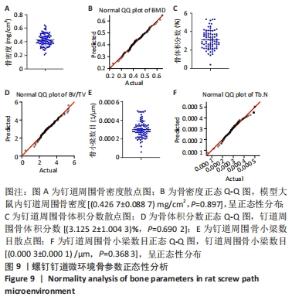
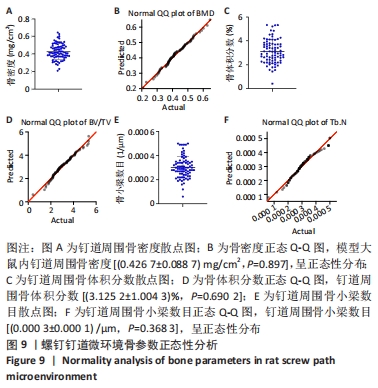
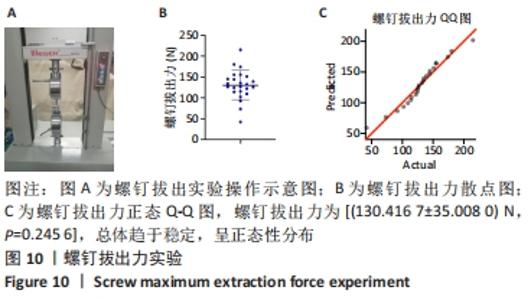
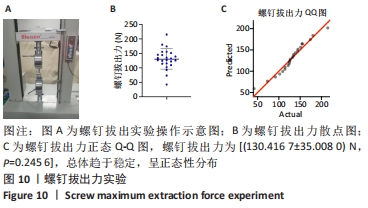
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (18): 2854-2861.doi: 10.12307/2022.694
Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishment and evaluation of a validation model for the efficacy of external femoral fixator screws in rats
Jia Qiyu1, Guo Jian1, Wei Qin2, 3, Guo Xiaobin4, Chen Dongsheng1, Feng Dongwei1, Liu Yanshi1, Ma Chuang1
- 1Department of Microprosthetic Surgery, 4Department of Joint Surgery, Orthopaedic Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Animal Experiment Center, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3Key Laboratory for Research on New Medical Animal Models, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2021-08-19Accepted:2021-10-11Online:2022-06-28Published:2022-01-29 -
Contact:Ma Chuang, MD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Microprosthetic Surgery, Orthopaedic Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Jia Qiyu, Master candidate, Department of Microprosthetic Surgery, Orthopaedic Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760397 (to MC); the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2020D01C263 (to GXB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jia Qiyu, Guo Jian, Wei Qin, Guo Xiaobin, Chen Dongsheng, Feng Dongwei, Liu Yanshi, Ma Chuang. Establishment and evaluation of a validation model for the efficacy of external femoral fixator screws in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(18): 2854-2861.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] 阮洪江, 范存义. 改善外固定支架钉-骨界面强度相关技术研究进展[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2007,28(6):356-358. [2] TUNALI O, SAGLAM Y, BALCI HI, et al. Gustilo type IIIC open tibia fractures with vascular repair: minimum 2-year follow-up. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2017;43(4):505-512. [3] PALEY D. Problems, Obstacles, and Complications of Limb Lengthening by the Ilizarov Technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;(250):81-104. [4] YANAGISAWA Y, ITO A, HARA Y, et al. Initial clinical trial of pins coated with fibroblast growth factor-2–apatite composite layer in external fixation of distal radius fractures. J Orthop. 2018;16(1):69-73. [5] GATHEN M, PLOEGER MM, JAENISCH M, et al. Outcome evaluation of new calcium titanate schanz-screws for external fixators. First clinical results and cadaver studies. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(11):124. [6] BAKHSH K, ZIMRI FK, ATIQ UR R, et al. Outcome of complex non-unions of femoral fractures managed with Ilizarov method of distraction osteogenesis. Pak J Med Sci. 2019;35(4):1055-1059. [7] KOSEKI H, ASAHARA T, SHIDA T, et al. Clinical and histomorphometrical study on titanium dioxide-coated external fixation pins. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:593-599. [8] BLUM AL, BONGIOVANNI JC, MORGAN SJ, et al. Complications associated with distraction osteogenesis for infected nonunion of the femoral shaft in the presence of a bone defect: a retrospective series. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(4):565-570. [9] BATTLE J, CARMICHAEL KD. Incidence of pin track infections in children’s fractures treated with Kirschner wire fixation. J Pediatr Orthop. 2007;27(2):154-157. [10] MAIMAITI B, ZHANG N, YAN L, et al. Stable ZnO-doped hydroxyapatite nanocoating for anti-infection and osteogenic on titanium. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;186:110731. [11] PATEL A, GHAI A, ANAND A. Clinical Benefit of Hydroxyapatite-Coated Versus Uncoated External Fixation: A Systematic Review. Int J Orthop. 2016;3(3):581-590. [12] PAN G, SUN S, ZHANG W, et al. Biomimetic Design of Mussel-Derived Bioactive Peptides for Dual-Functionalization of Titanium-Based Biomaterials. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138(45):15078-15086. [13] FU X, LIU P, ZHAO D, et al. Effects of Nanotopography Regulation and Silicon Doping on Angiogenic and Osteogenic Activities of Hydroxyapatite Coating on Titanium Implant. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:4171-4189. [14] KONONOVICH NA, POPKOV AV, GORBACH EN, et al. The Effect of Nanostructured Hydroxyapatite Coating on Distraction Osteogenesis. Key Engineering Materials. 2020;854:216-222. [15] GNEDENKOV SV, SINEBRYUKHOV SL, PUZ AV, et al. In vivo study of osteogenerating properties of calcium-phosphate coating on titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. Biomed Mater Eng. 2016;27(6):551-560. [16] JEBAHI S, SAOUDI M, BADRAOUI R, et al. Biologic response to carbonated hydroxyapatite associated with orthopedic device: experimental study in a rabbit modelKorean J Pathol. 2012;46(1):48-54. [17] HARMANKAYA N, IGAWA K, STENLUND P, et al. Healing of complement activating Ti implants compared with non-activating Ti in rat tibia. Acta Biomaterialia. 2012;8(9):3532-3540. [18] SCHELL H, REUTHER T, DUDA GN, et al. The pin-bone interface in external fixator: a standardized analysis in a sheep osteotomy model. J Orthop Trauma. 2011;25(7):438-445. [19] WANG ZL, HE RZ, TU B, et al. Enhanced biocompatibility and osseointegration of calcium titanate coating on titanium screws in rabbit femur. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017;37(3):362-370. [20] GLATT V, MATTHYS R. Adjustable stiffness, external fixator for the rat femur osteotomy and segmental bone defect models. J Vis Exp. 2014; (92):e51558. [21] KASPAR K, SCHELL H, TOBEN D, et al. An easily reproducible and biomechanically standardized model to investigate bone healing in rats, using external fixation. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2007;52(6):383-390. [22] MULLER M, HENNIG FF, HOTHORN T, et al. Bone-implant interface shear modulus and ultimate stress in a transcortical rabbit model of open-pore Ti6Al4V implants. J Biomech. 2006;39(11):2123-2132. [23] HARRISON LJ, CUNNINGHAM JL, STROMBERG L, et al. Controlled induction of a pseudarthrosis: a study using a rodent model. J Orthop Trauma. 2003;17(1):11-21. [24] MARK H, BERGHOLM J, NILSSON A, et al. An external fixation method and device to study fracture healing in rats. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003; 74(4):476-482. [25] WILLIE B, ADKINS K, ZHENG X, et al. Mechanical characterization of external fixator stiffness for a rat femoral fracture model. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(5):687-693. [26] 吴硕, 买买艾力·玉山, 魏琴, 等. 大鼠股骨牵张成骨模型的建立[J]. 中华显微外科杂志,2020,43(6):578-582. [27] DROSSE I, VOLKMER E, SEITZ S, et al. Validation of a femoral critical size defect model for orthotopic evaluation of bone healing: a biomechanical, veterinary and trauma surgical perspective. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2008;14(1):79-88. [28] ZHAO X, YOU L, WANG T, et al. Enhanced Osseointegration of Titanium Implants by Surface Modification with Silicon-doped Titania Nanotubes.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:8583-8594. [29] CHAI H, GUO L, WANG X, et al. Antibacterial effect of 317L stainless steel contained copper in prevention of implant-related infection in vitro and in vivo. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011;22(11) 2525-2535. [30] MORONI A, CADOSSI M, ROMAGNOLI M, et al. A biomechanical and histological analysis of standard versus hydroxyapatite-coated pins for external fixation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008;86(2): 417-421. [31] KALINICHENKO SG, MATVEEVA NY, KOSTIV RY, et al. The topography and proliferative activity of cells immunoreactive to various growth factors in rat femoral bone tissues after experimental fracture and implantation of titanium implants with bioactive biodegradable coatings. Biomed Mater Eng. 2019;30(1):85-95. [32] HERSH-BOYLE RA, KAPATKIN AS, GARCIA TC, et al. Comparison of torsional properties between a Fixateur Externe du Service de Sante des Armees and an acrylic tie-in external skeletal fixator in a red-tailed hawk (Buteo jamaicensis) synthetic tibiotarsal bone model. Am J Vet Res. 2020;81(7):557-564. [33] ZOETIS T, TASSINARI MS, BAGI C, et al. Species comparison of postnatal bone growth and development. Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol. 2003;68(2):86-110. [34] EINHORN TA. The cell and molecular biology of fracture healing. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(355 Suppl):S7-21. [35] GUO X, LIU Y, BAI J, et al. Efficient Inhibition of Wear-Debris-Induced Osteolysis by Surface Biomimetic Engineering of Titanium Implant with a Mussel-Derived Integrin-Targeting Peptide. Adv Biosyst. 2019; 3(2):e1800253. [36] SMIT TH. The use of a quadruped as an in vivo model for the study of the spine - biomechanical considerations. Eur Spine J. 2002;11(2):137-144. [37] BERGMANN G, GRAICHEN F, ROHLMANN A. Hip joint forces in sheep. J Biomech. 1999;32(8):769-777. [38] IBRAHIMI DISHA S, FURLANI B, DREVENSEK G, et al. The role of endothelin B receptor in bone modelling during orthodontic tooth movement: a study on ETB knockout rats. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):14226. [39] FUJII T, HIROTA K, YASODA A, et al. Rats deficient C-type natriuretic peptide suffer from impaired skeletal growth without early death. PLoS One. 2018;13(3):e0194812. [40] ANRAKU Y, MIZUTA H, SEI A, et al. The chondrogenic repair response of undifferentiated mesenchymal cells in rat full-thickness articular cartilage defects. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16(8):961-964. [41] KERZNER B, MARTIN HL, WEISER M, et al. A Reliable and Reproducible Critical-Sized Segmental Femoral Defect Model in Rats Stabilized with a Custom External Fixator. J Vis Exp. 2019;(145). doi: 10.3791/59206 [42] YANG Y, PAN Q, ZOU K, et al. Administration of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells in lengthening phase accelerates early bone consolidation in rat distraction osteogenesis model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1): 129. [43] STREET J, BAO M, DEGUZMAN L, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates bone repair by promoting angiogenesis and bone turnover. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(15):9656-9661. [44] 陈红浩, 康庆林, 贾亚超, 等. 大鼠股骨牵张成骨模型制作技巧[J]. 解剖学杂志,2017,40(1):104-106. |
| [1] | Tan Xinfang, Guo Yanxing, Qin Xiaofei, Zhang Binqing, Zhao Dongliang, Pan Kunkun, Li Yuzhuo, Chen Haoyu. Effect of uniaxial fatigue exercise on patellofemoral cartilage injury in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [2] | Xu Xinzhong, Wu Zhonghan, Yu Shuisheng, Zhao Yao, Xu Chungui, Zhang Xin, Zheng Meige, Jing Juehua. Biomechanical analysis of different ways of inserting Steinmann Pins into the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1313-1317. |
| [3] | Wei Guoqiang, Li Yunfeng, Wang Yi, Niu Xiaofen, Che Lifang, Wang Haiyan, Li Zhijun, Shi Guopeng, Bai Ling, Mo Kai, Zhang Chenchen, Xu Yangyang, Li Xiaohe. Biomechanical analysis of non-uniform material femur under different loads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1318-1322. |
| [4] | Pan Baoshun, Fang Zhen, Gao Mingjie, Fang Guiming, Chen Jinshui. Design for posterior atlantoaxial internal fixation system with fusion cage based on imaging data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1372-1376. |
| [5] | Li Kun, Gao Erke, Xiong Feng, Wang Xing, Wu Danqi, Li Zhijun, Zhang Shaojie, Liu Yanan, Duo Lan, Li Ziyu. Feasibility of axial transpedicle screw internal fixation in children aged 1 to 6 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1383-1387. |
| [6] | Li Canhui, Wu Zhengjie, Zeng Yanhui, He Yinghao, Situ Xiaopeng, Du Xuelian, Hong Shi, He Jiaxiong. Advantage and disadvantage of robot-assisted sacroiliac screw placement and traditional fluoroscopy in orthopedic surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1434-1438. |
| [7] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [8] | Lü Yiyan, Li Hanbing, Ma Xiaoqing, Zhang Han, Zhang Yuhang, Li Genlin. Establishment and characteristic analysis of interior heat and diabetes mouse model using compound factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1187-1193. |
| [9] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [10] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [11] | Li Shuo, Su Peng, Zhang Li, Wu Qiulong, Hu Xiangyu, Lai Yuliang. Positive effect of supracondylar femoral osteotomy on the correction of knee varus based on three-dimensional reconstruction and finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 858-863. |
| [12] | Wei Bing, Chang Shan. Finite element analysis of different angles of nail placement in sagittal plane of spinal fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 864-869. |
| [13] | Song Yuxin, Zhang Tongtong, Niu Jianxiong, Wang Zengping, Wen Jie, Zhang Qunli, Xue Wen, Liu Lin. Precise screw placement of 3D printing model and orthopedic robot in spinal deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 904-907. |
| [14] | Yang Jun, Yang Qun, Zhang Rui, Jiang Chang. A novel slidable pedicle screw-rod system for lumbar tuberculosis: promoting bone graft fusion by producing stress stimulation to fused segment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 914-918. |
| [15] | Guo Xiaohui, Song Xizheng, Xiang Hanrui, Kang Zhaorong, Li Daming, Kang Yu, Hu Jun, Sheng Kai. External spinal fixation elastic stress in the treatment of jumping spinal fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 919-923. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||