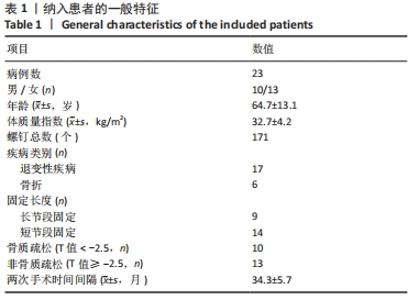
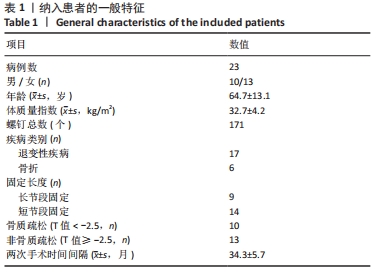
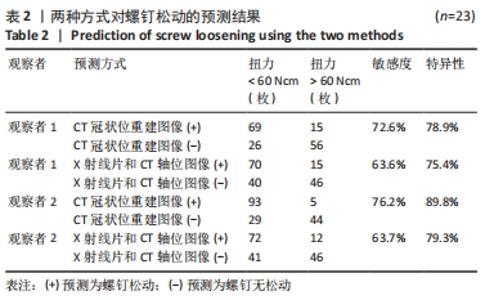
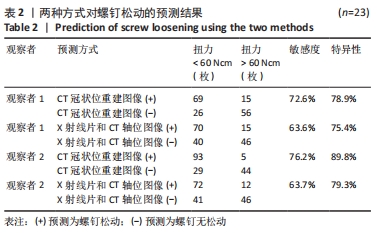
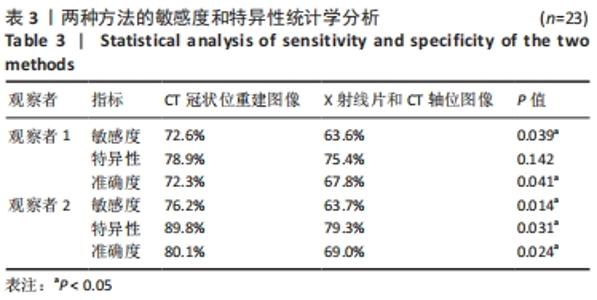
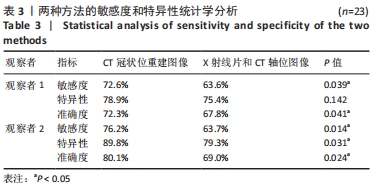
[1] KIM DH, HWANG RW, LEE GH, et al. Comparing rates of early pedicle screw loosening in posterolateral lumbar fusion with and without transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Spine J. 2020;20(9):1438-1445.
[2] UEHARA M, TAKAHASHI J, IKEGAMI S, et al. Pedicle Screw Loosening After Posterior Spinal Fusion for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis in Upper and Lower Instrumented Vertebrae Having Major Perforation. Spine. 2017;42(24):1895-1900.
[3] PEARSON HB, DOBBS CJ, GRANTHAM E, et al. Intraoperative biomechanics of lumbar pedicle screw loosening following successful arthrodesis. J Orthop Res. 2017; 35(12):2673-2681.
[4] KIM CH, JU CI, LEE SM, et al. Efficacy of Antibiotic-Loaded Cement Augmentation for Correcting Low Grade Pedicle Screw Loosening. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2021; 17(1):41-47.
[5] JARVERS JS, SCHLEIFENBAUM S, PFEIFLE C, et al. Comparison of three different screw trajectories in osteoporotic vertebrae: a biomechanical investigation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):418.
[6] SPIRIG JM, SUTTER R, GÖTSCHI T, et al. Value of standard radiographs, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging of the lumbar spine in detection of intraoperatively confirmed pedicle screw loosening-a prospective clinical trial. Spine J. 2019;19(3):461-468.
[7] ZHANG RJ, LI HM, GAO H, et al. Cortical bone trajectory screws used to save failed traditional trajectory screws in the osteoporotic lumbar spine and vice versa: a human cadaveric biomechanical study. J Neurosurg Spine. 2019;1-8.
[8] WOLF H, PAJENDA G, SARAHRUDI K. Analysis of factors predicting success and failure of treatment after type B periprosthetic humeral fractures: a case series study. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2012;38(2):177-183.
[9] SHIN SJ, LEE JH, LEE JH. Influence of Hydroxyapatite Stick on Pedicle Screw Fixation in Degenerative Lumbar Spine: Biomechanical and Radiologic Study. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(6):E819-E826.
[10] WU X, SHI J, WU J, et al. Pedicle screw loosening: the value of radiological imagings and the identification of risk factors assessed by extraction torque during screw removal surgery. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):6.
[11] WEISER L, HUBER G, SELLENSCHLOH K, et al. Insufficient stability of pedicle screws in osteoporotic vertebrae: biomechanical correlation of bone mineral density and pedicle screw fixation strength. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(11):2891-2897.
[12] ZOU D, SUN Z, ZHOU S, et al. Hounsfield units value is a better predictor of pedicle screw loosening than the T-score of DXA in patients with lumbar degenerative diseases. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(5):1105-1111.
[13] GUO HZ, TANG YC, GUO DQ, et al. Pedicle Screw Fixation in Single-Level, Double-Level, or Multilevel Posterior Lumbar Fusion for Osteoporotic Spine: A Retrospective Study with a Minimum 2-Year Follow-Up. World Neurosurg. 2020;140:e121-e128.
[14] LENG J, HAN G, ZENG Y, et al. The Effect of Paraspinal Muscle Degeneration on Distal Pedicle Screw Loosening Following Corrective Surgery for Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis. Spine. 2020;45(9):590-598.
[15] ANAND N, AGRAWAL A, RAVINSKY R, et al. The prevalence of proximal junctional kyphosis (PJK) and proximal junctional failure (PJF) in patients undergoing circumferential minimally invasive surgical (cMIS) correction for adult spinal deformity: long-term 2- to 13-year follow-up. Spine Deform. 2021;9(5):1433-1441.
[16] GUO HZ, TANG YC, LI YX, et al. The Effect and Safety of Polymethylmethacrylate-Augmented Sacral Pedicle Screws Applied in Osteoporotic Spine with Lumbosacral Degenerative Disease: A 2-Year Follow-up of 25 Patients. World Neurosurg. 2019; 121:e404-e410.
[17] HUDYANA H, MAES A, VANDENBERGHE T, et al. Accuracy of bone SPECT/CT for identifying hardware loosening in patients who underwent lumbar fusion with pedicle screws. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43(2):349-354.
[18] KAUR K, GARG A, TRIPATHI M, et al. Comparative contribution of magnetoencephalography (MEG) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) in pre-operative localization for epilepsy surgery: A prospective blinded study. Seizure. 2021;86:181-188.
[19] SAKAI Y, TAKENAKA S, MATSUO Y, et al. Hounsfield unit of screw trajectory as a predictor of pedicle screw loosening after single level lumbar interbody fusion.J Orthop Sci. 2018;23(5):734-738.
[20] GALBUSERA F, VOLKHEIMER D, REITMAIER S, et al. Pedicle screw loosening: a clinically relevant complication? Eur Spine J. 2015;24(5):1005-1016.
[21] CHOY WJ, WALSH WR, PHAN K, et al. Technical Note: Pedicle Cement Augmentation with Proximal Screw Toggle and Loosening. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(3):510-515.
[22] WILKE HJ, GRUNDLER S, OTTARDI C, et al. In vitro analysis of thoracic spinal motion segment flexibility during stepwise reduction of all functional structures.Eur Spine J. 2020;29(1):179-185.
[23] MAI Q, WAN J. Metal Artifacts Reduction in CT Scans using Convolutional Neural Network with Ground Truth Elimination. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2020; 2020:1319-1322.
|