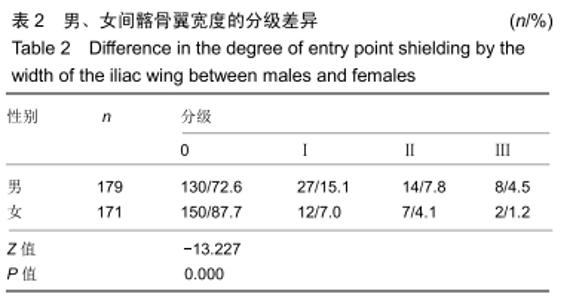
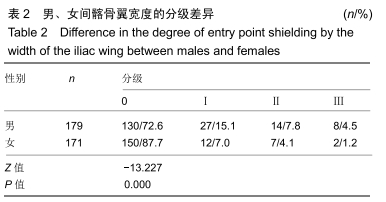
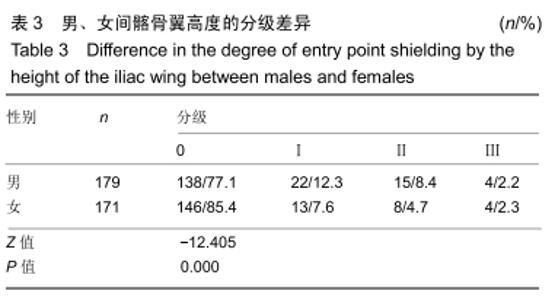
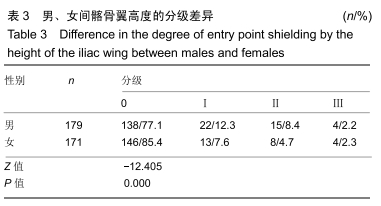
[1] CHOI KC, PARK CK. Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy for L5-S1 Disc Herniation: Consideration of the Relation between the Iliac Crest and L5-S1 Disc. Pain Physician. 2016;19(2):E301-E308.
[2] WANG YL, WANG XY, FANG BD, et al. L5-S1 disc degeneration and the anatomic parameters of the iliac crest: imaging study. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(11):2481-2487.
[3] JIN HM, BAI XQ, PAN XX, et al. Does the iliac wing influence L5 pedicle screw fixation? World Neurosurgery. 2018; 113-120.
[4] MAGERL FP. Stabilization of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine with external skeletal fixation. Clin Orthop. 1984; 189 (189):125-141.
[5] BOUCHER HH. A method of spinal fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1959;41(2):248-259.
[6] ROY-CAMILLE R, SAILLANT G, MAZEL C. Internal fixation of the lumbar spine with pedicle screw plating. ClinOrthop. 1986; 203(203):7-17.
[7] GAUTSCHI OP, BAWARJAN S, KARL S, et al. Clinically relevant complications related to pedicle screw placement in thoracolumbar surgery and their management: a literature review of 35,630 pedicle screws. Neurosurg Focus. 2011; 31(4):E1-E8.
[8] JUTTE PC, CASTELEIN RM. Complications of pedicle screws in lumbar and lumbosacral fusions in 105 consecutive primary operations. Eur Spine J. 2002;11(6):594-598.
[9] WEINSTEIN JN, RYDEVIK BL, RAUSCHNING W. Anatomic and technical considerations of pedicle screw fixation. Clin Orthop. 1992;284(284):34-46.
[10] XIN RU DU, ZHAO LX, ZHANG YM. Anatomical study of the adjacent structures to the top point of the “∧” shape crest and its relevance. Chin J Spine Spinal Cord. 2001;11(2):89-92.
[11] LAINE T, LUND T, YLIKOSKI M, et al. Accuracy of pedicle screw insertion with and without computer assistance: a randomised controlled clinical study in 100 consecutive patients. Eur Spine J. 2000;9(3):235-240.
[12] LAW M, TENCER AF, ANDERSON PA. Caudo-cephalad loading of pedicle screws: mechanisms of loosening and methods of augmentation. Spine. 1993;18(16):2438-2443.
[13] MATJAZ M, IGOR D, MATJAZ V, et al. A multi-level rapid prototyping drill guide template reduces the perforation risk of pedicle screw placement in the lumbar and sacral spine. Arch OrthopTrauma Surg. 2013;133(7):893-899.
[14] ABITBOL MM. The shapes of the female pelvis. Contributing factors. Reprod Med. 1996;41(4):242-250.
[15] ANDERSON AE, PETERS CL, TUTTLE BD, et al. Subject-specific finite element model of the pelvis: development, validation and sensitivity studies. J Biomech En. 2005;127(3):364-373.
[16] GSKATZ HE. Magnetic resonance-based serial pelvimetry:Do maternal pelvic dimensions change during pregnancy? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;194(6):1689-1694.
[17] LEHMANN KJ, WISCHNIK A, ZAHN K, et al. Do the obstetrically relevant bony pelvic measurements change? A retrospective analysis of computed tomographic pelvic x-rays. Rofo. 1992;156(5):425-428.
[18] NARUMOTO K, SUGIMURA M, SAGA K, et al. Changes in pelvic shape among Japanese pregnant women over the last 5 decades. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2015;41(11):1687-1692.
[19] SZE E, KOHLI N JR, ROAT T, et al. Computed tomography comparison of bony pelvis dimensions between women with and without genital prolapse. Obstet Gynecol. 1999;93(2): 229-232.
[20] HANDA VL, PANNU HS, GUTMAN R, et al. Architectural differences in the bony pelvis of women with and without pelvic floor disorders. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;102(6): 1283-1290.
[21] CHIN KR, KUNTZ AF, BOHLMAN HH, et al. Changes in the iliac crest-lumbar relationship from standing to prone. Spine J. 2006;6(2):185-189.
[22] DIMITRIOU R, MATALIOTAKIS GI, ANGOULES AG, et al. Complications following autologous bone graft harvesting from the iliac crest and using the RIA: a systematic review. Injury. 2011;42(5):S3-S15.
[23] LUK KD, HO HC, LEONG JC. The iliolumbar ligament. A study of its anatomy, development and clinical significance. J Bone Joint Surg. 1986;68(2):197-200.
[24] JING G, GUO L, GAO J, et al. Does a deep seated L5 vertebra position with respect to the iliac crests affect the accuracy of percutaneous pedicle screw placement at lumbosacral junction? Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2017; 18(180):1-6.
[25] SANTONI BG, HYNES RA, MCGILVRAY KC, et al. Cortical bone trajectory for lumbar pedicle screws. Spine J. 2009;9(5): 366-373.
|