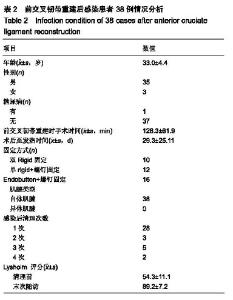
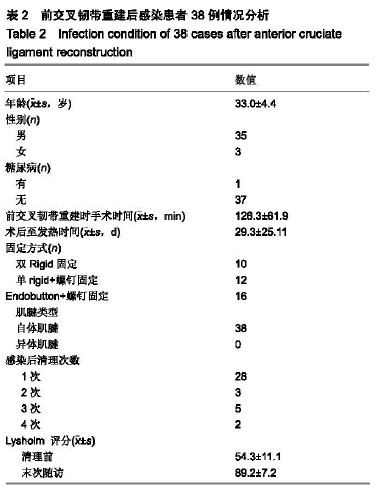
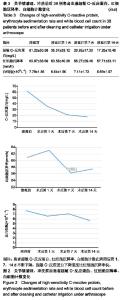
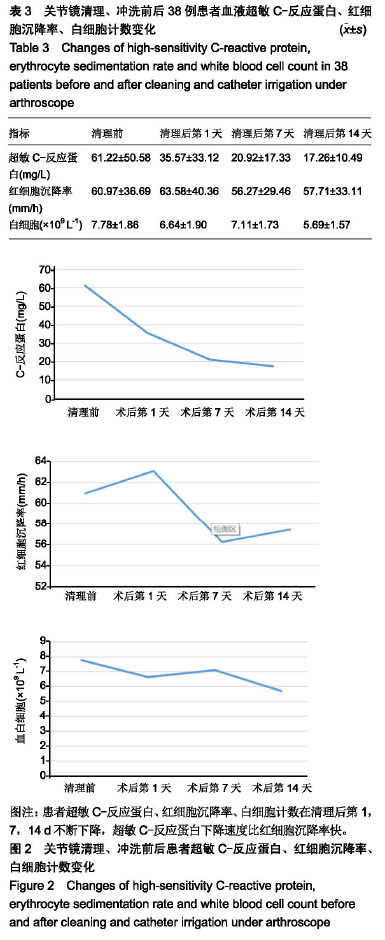
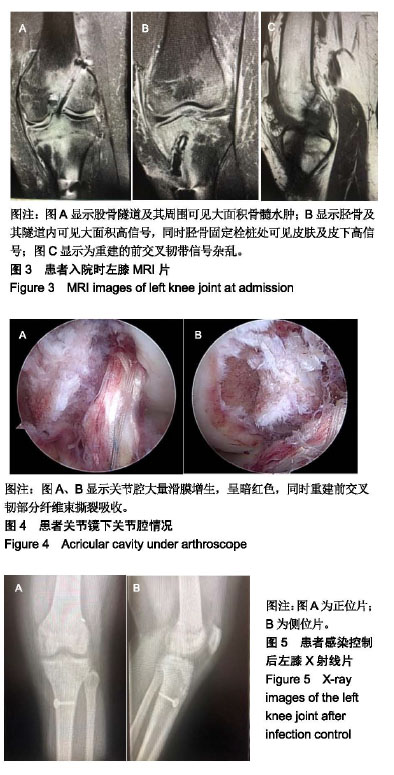
| [1]Sadeqi M,Klouche S,Bohu Y,et al.Progression of the Psychological ACL RSI Score and Return to Sport After Anterior CruciateLigament Reconstruction: A Prospective 2-Year Follow-up Study From the French ProspectiveAnterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Cohort Study (FAST). Orthop J Sports Med.2018;6(12):1-6.[2]宋斌,李卫平,陈仲,等.前交叉韧带重建术后早期感染的治疗[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2014, 33(4):292-296.[3]Waterman BR,Arroyo W,Cotter EJ,et al.Septic Arthritis After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Clinical and Functional Outcomes Based on Graft Retention or Removal. Orthop J Sports Med. 2018;6(3):2325967118758626. [4]Saper M,Stephenson K,Heisey M.Arthroscopic irrigation and debridement in the treatment of septic arthritis after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.Arthroscopy. 2014;30: 747-754.[5]Calvo R,Figueroa D,Anastasiadis Z,et al.Septic arthritis in ACL reconstruction surgery with hamstring autografts.Eleven years of experience.Knee.2014;21:717-720.[6]Cadet ER, Makhni EC, Mehran N,et al.Management of septic arthritis following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: A review of current practices and recommendations.J Am AcadOrthop Surg.2013;21: 647-656.[7]杨松杰,张清旭,陈绪彪,等.关节镜下膝交叉韧带重建中自体与异体肌腱移植物的疗效比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(34): 5513-5518.[8]Dekker TJ,Godin JA,Dale KM,et al.Return to Sport After Pediatric Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction and Its Effect on Subsequent Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(11):897-904.[9]Gupta AK,Moorman CR.Nocardia nova infection afterprimary anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with tibialis anterior allograft.Am J Sports Med.2010;38(7):1483-1486.[10]Nakayama H,Yagi M,Yoshiya S,et al.Micro- organismcolonization and intraoperative contamination in patientsundergoing arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligamentreconstruction.Arthroscopy. 2012;28(5):667-671.[11]Tuman J,Diduch DR,Baumfeld JA,et al.Joint infection unique tohamstring tendon harvester used during anterior cruciate ligamentreconstruction surgery.Arthroscopy. 2008;24(5): 618-620.[12]Schollin-Borg M, Michaëlsson K, Rahme H. Presentation, outcome, and cause of septic arthritis after anterior cruciateligament reconstruction:a case control study. Arthroscopy.2003;19(9):941-947.[13]Katz LM,Battaglia TC,Patino P,et al.A retrospectivecomparison of the incidence of bacterial infection followinganterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with autograft versus allograft.Arthroscopy. 2008;24(12): 1330-1335.[14]Maletis GB,Inacio MC,Reynolds S,et al.Incidence of postoperative anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction infections: graft choice makes a difference.Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(8):1780-1785.[15]Greenberg DD,Robertson M,Vallurupalli S,et al. Allograftcompared with autograft infection rates in primary anteriorcruciate ligament reconstruction.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2010;92(14):2402-2408.[16]Barker JU,Drakos MC,Maak TG,et al. Effect of graft selection on the incidence of postoperative infection in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(2): 281-286.[17]Murphy MV, Du DT, Hua W,et al.Risk Factors for Surgical SiteInfections Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol.2016; 37(7): 827-833.[18]Yazdi H, Moradi A, Herbort M.The effect of gentamicin inirrigating solutions on articular infection prophylaxis duringarthroscopic ACL reconstruction.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2014;134(2):257-261.[19]Pérez-Prieto D, Torres-Claramunt R, Gelber PE, et al. Autograftsoaking in vancomycin reduces the risk of infection afteranterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Knee Surg SportsTraumatolArthrosc.2016;24(9):2724-2728.[20]Vertullo CJ, Quick M, Jones A,et al.A surgical technique usingpresoaked vancomycin hamstring grafts to decrease the riskof infection after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy. 2012;28(3):337-342.[21]刘玉杰.关注前交叉韧带重建术后影响疗效的因素与对策[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(11): 883-885.[22]Matava MJ,Evans TA,Wright RW,et al.Septic arthritis of theknee following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: results of a survey of sports medicine fellowship directors. Arthroscopy. 1998;14(7):717-725.[23]陈拿云,敖英芳.前交叉韧带重建术后关节感染的风险因素?病理?诊断和治疗研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志. 2019,38(1): 54-60.[24]赵阳, 张春礼.关节镜下自体肌腱移植重建前交叉韧带术后并发症的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2015,4(5):422-426.[25]Riordan T,Doyle D,Tabaqchali S.Synovial fluid lactic acid measurement in the diagnosis and management of septic arthritis. J Clin Pathol. 1982;35(4):390-394.[26]徐长明,杨 乐,胡传亮,等.前交叉韧带重建后的感染[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(5):938-944.[27]Kim SJ ,Postigo R,Koo S,et al.Infection After Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Orthopedics. 2014;37(7):477.[28]Kim YM,Joo YB.Clinical Presentation of Staphylococcusepidermidis Septic Arthritis Following Anterior CruciateLigament Reconstruction.Knee Surg Relat Res. 2012;24(1):46-51.[29]Viola R, Marzano N, Vianello R. An unusual epidemic ofStaphylococcus-negative infections involving anterior cruciateligament reconstruction with salvage of the graft andfunction. Arthroscopy.2000. 16(2):173-177.[30]Wang C,Ao YF,Wang JQ,et al.Diagnosis and management of septic arthritis after arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction]. Zhonghua Waike Zazhi.2008;46(10): 745-748.[31]Gianotti SM,Marshall SW, Hume PA,et al.Incidence of anterior cruciate ligament injury and other knee ligament injuries: a national population-based study. J Sci Med Sport. 2009;12(6): 622-627.[32]Torres-Claramunt R, Pelfort X, Erquicia J, et al. Kneejointinfection after ACL reconstruction: prevalence, managementand functional outcomes. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(12):2844-2849.[33]Odio CM,Ramirez T,Arias G,et al.Double blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of dexamethasone therapy for hematogenous septic arthritis in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003;22(10):883-889.[34]Philipp S, Martin S, Micha I , et al. Septic Arthritis After Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Evaluation of an Arthroscopic Graft-Retaining Treatment Protocol.Am J Sports Med.2015; 43(12):3005-3012.[35]Abdelaziz A,Radwan YA,Rizk A.Multiple arthroscopic debridement and graft retention in septic knee arthritis after ACL reconstruction: a prospective case-control study. Int Orthop. 2014;38(1):73-82.[36]Pogorzelski J,Themessl A,Achtnich A,et al.Septic Arthritis After Anterior CruciateLigamentReconstruction;How Important Is Graft Salvage?Am J Sports Med.2018;46(10): 2376-2383.[37]Wang C,Lee YH,Siebold R.Recommendations for the management of septic arthritis after ACL reconstruction.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(9):2136-2144. |