Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (27): 4333-4337.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2799
Previous Articles Next Articles
T2-mapping quantitative imaging technique based on sequence optimization in the ankle talus osteochondral injury
Li Wei1, Chu Zhanfei2, Yu Zechen2, Yu Jinghong1, Jia Yanbo3, Wang Zongbo1
- 1Department of Imaging, 3Department of Sports Medical Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2Siemens Healthineers Co., Ltd., Shanghai 201318, China
-
Received:2020-01-18Revised:2020-01-20Accepted:2020-03-04Online:2020-09-28Published:2020-09-09 -
Contact:Yu Jinghong, Chief physician, Department of Imaging, Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Li Wei, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Imaging, Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, No. 2018MS08024; the Science and Technology Program of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region of China, No. 2019GG053
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Wei, Chu Zhanfei, Yu Zechen, Yu Jinghong, Jia Yanbo, Wang Zongbo. T2-mapping quantitative imaging technique based on sequence optimization in the ankle talus osteochondral injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(27): 4333-4337.
share this article
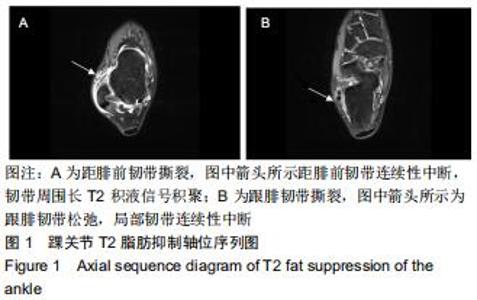
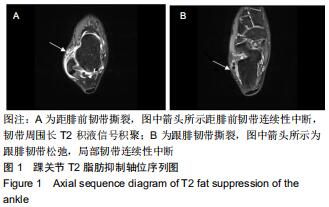
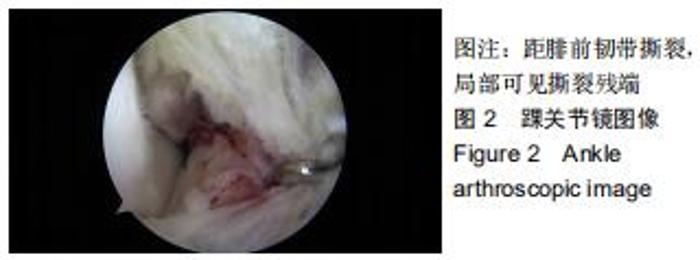
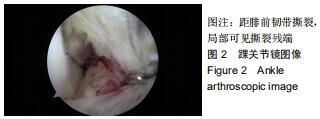
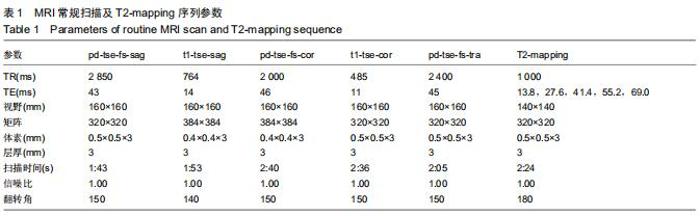
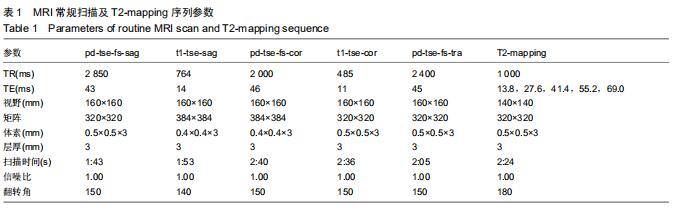
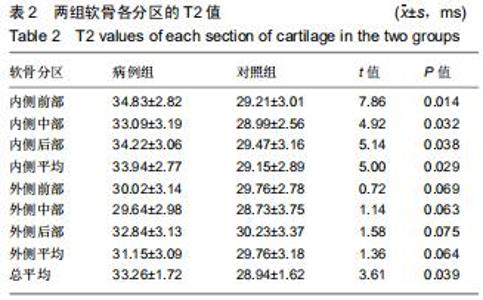
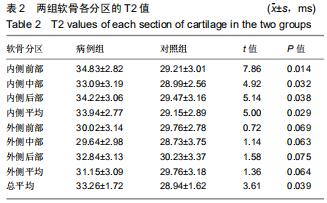
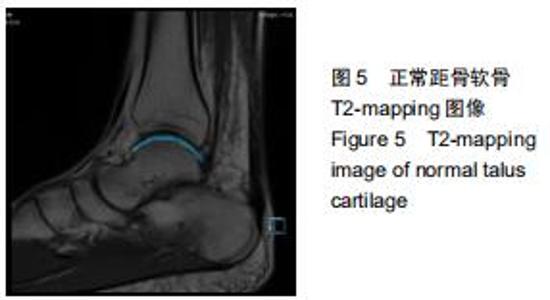
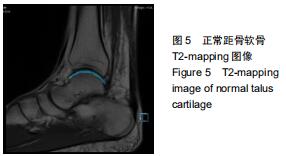
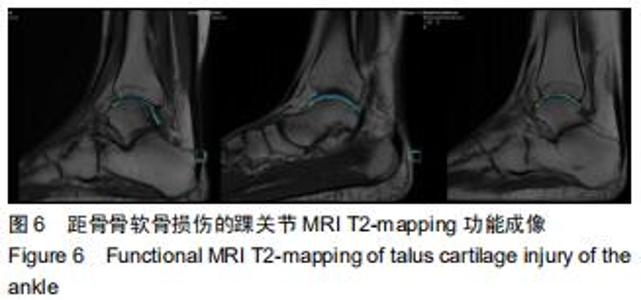
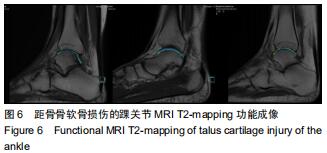
由2名高年资骨肌影像诊断医师诊断病例组韧带损伤程度及踝关节其他可能病变,严格执行纳入标准。绘制T2-mapping图:T2-mapping伪彩图(图3)由西门子Syngo VIA VB10软件处理融合,色阶选择后处理软件自带关节功能成像专用色阶Perfusion。距骨软骨6分区如下:选取踝关节冠状位距骨显示最佳层面,距骨滑车关节面各1/2定义为距骨内、外侧,各包含连续层面3-5个;选取踝关节矢状位,距骨内侧前、中、后部为距骨滑车曲面的前、中、后各1/3;距骨外侧前、中、后部为距骨滑车曲面的前、中、后各1/3。每个分区随机测量1个T2值(图4)测量大小:>1.00 mm2,测量形状:圆形感兴趣区(ROI)。内外侧分区共计6个T2值,距骨软骨内侧区平均T2值为内侧前、中、后部T2平均值;距骨软骨外侧区平均T2值为外侧前、中、后部T2平均值。总平均值为内、外侧6个区域T2值的平均值。 "
由2名高年资骨肌影像诊断医师诊断病例组韧带损伤程度及踝关节其他可能病变,严格执行纳入标准。绘制T2-mapping图:T2-mapping伪彩图(图3)由西门子Syngo VIA VB10软件处理融合,色阶选择后处理软件自带关节功能成像专用色阶Perfusion。距骨软骨6分区如下:选取踝关节冠状位距骨显示最佳层面,距骨滑车关节面各1/2定义为距骨内、外侧,各包含连续层面3-5个;选取踝关节矢状位,距骨内侧前、中、后部为距骨滑车曲面的前、中、后各1/3;距骨外侧前、中、后部为距骨滑车曲面的前、中、后各1/3。每个分区随机测量1个T2值(图4)测量大小:>1.00 mm2,测量形状:圆形感兴趣区(ROI)。内外侧分区共计6个T2值,距骨软骨内侧区平均T2值为内侧前、中、后部T2平均值;距骨软骨外侧区平均T2值为外侧前、中、后部T2平均值。总平均值为内、外侧6个区域T2值的平均值。"
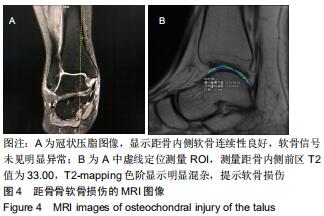
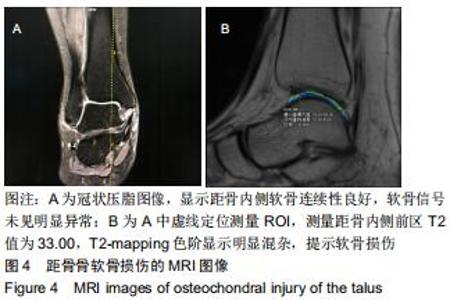
|
[1] GERSTNER GJ. Chronic ankle instability.Foot Ankle Clin. 2012; 17(3): 389-398.
[2] CAPUTO AM, LEE JY, SPRITZER CE, et al. In Vivo Kinematics of the Tibiotalar Joint After Lateral Ankle Instability.Am J Sports Med. 2009; 37(11):2241-2248.
[3] 戴海飞,余斌,张凯瑞,等.踝关节周围韧带损伤对距骨稳定性影响的有限元分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(2):121-124.
[4] KOVALESKI JE, HEITMAN RJ, GURCHIEK LR, et al. Joint Stability Characteristics of the Ankle Complex After Lateral Ligamentous Injury, Part I: A Laboratory Comparison Using Arthrometric Measurement.J Athl Train.2014;49(2):192-197.
[5] HIROSE K, MURAKAMI G, MINOWA T, et al. Lateral ligament injury of the ankle and associated articular cartilage degeneration in the talocrural joint: anatomic study using elderly cadavers.J Orthop Sci.2004;9(1):37-43.
[6] 卢昌怀,余斌,陈辉强,等.正常步态下距骨三维有限元模型的建立及应力分析[J].南方医科大学学报,2010,30(10):2273-2276.
[7] RINGLEB SI, UDUPA JK, SIEGLER S, et al. The effect of ankle ligament damage and surgical reconstructions on the mechanics of the ankle and subtalar joints revealed by three-dimensional stress MRI.J Orthop Res. 2005;23(4):743-749.
[8] 刘清华,余斌,庄岩.足踝部数字化研究的现状及浅析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(10):998-998.
[9] KRIPS R, DIJK CNV, HALASI T, et al. Long-Term Outcome of Anatomical Reconstruction Versus Tenodesis for the Treatment of Chronic Anterolateral Instability of the Ankle Joint: A Multicenter Study.Foot Ankle Int.2001;22(5):415-421.
[10] 张禹,刘志成,成永忠,等.旋后外旋型踝关节损伤有限元模型的建立与力学分析[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(3):36-42.
[11] HU H, YANG B, LI Y, et al. Blocking of the P2X7 receptor inhibits the activation of the MMP-13 and NF-κB pathways in the cartilage tis- sue of rats with osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Med.2016;38 (6):1922-1932
[12] HUANG X, PAN Q, MAO Z, et al. Sinapic acid inhibits the IL-1β-induced inflammation via MAPK downregulation in rat chondrocytes. Inflammation. 2018;41(2):562-568.
[13] WANG D, WENG Y, GUO S, et al. Platelet-rich plasma inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation through activation of Wnt pathway during bone remodeling.Int J Mol Med.2018;41(2):729-738.
[14] BIAN Y, WANG H, SUN S. Taurine alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress in the chondrocytes from patients with osteoarthritis.Redox Rep. 2018;23(1):118-124.
[15] SANDYA S, ACHAN MA, SUDHAKARAN PR, et al. Multiple matrix metalloproteinases in type II collagen induced arthritis. Indian J Clin Biochem.2009;24(1):42-48.
[16] JANUSZ MJ, BENDELE AM, BROWN KK.Induction of osteoarthritis in the rat by surgical tear of the meniscus:Inhibition of joint damage by a matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2002;10(10):785-791.
[17] ZWIERZCHOWSKI TJ, STASIKOWSKA-KANICKA O, DANILEWICZ M, et al. Assessment of apoptosis and MMP-1, MMP-3 and TIMP-2 expression in tibial hyaline cartilage afterviable medial meniscus transplantation in the rabbit.Arch Med Sci.2012;8(6):1108-1114.
[18] KAST RE, HALATSCH ME. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in glioblastoma: a trio of old drugs-captopril, disulfiram and nelfinavir-are inhibitors with potential as adjunctive treatments in glioblastoma.Arch Med Res.2012;43(3):243-247.
[19] KAĬLINA AN, OGORODOVA LM, CHASOVSKIKH I, et al. Indices of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1) with juvenile arthritis in children.Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk.2013;(7):36-40.
[20] 马丽艳,宋旭动,张德新,等.MMP-13 和Galectin-3 在骨性关节炎滑膜组织中的临床意义[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2013,2(5):280-284.
[21] JAZRAWI LM, ALAIA MJ, CHANG G, et al. Advances in magnetic resonance imaging of articular cartilage.J Am Acad Orthop Sur.2011; 19(7):420-429.
[22] RAYA JG, HORNG A, DIETRICH O, et al. Articular cartilage:in vivo diffusion-tensor imaging.Radiology.2012;262(2):550-559.
[23] NOTOHAMIPRODJO M, KUSCHEL B, HORNG A, et al. 3D-MRI of the ankle with optimized 3D-SPACE. Invest Radiol.2012;47(4):231-239.
[24] 富丽萍,王绍武,宋清伟,等.软骨的MR敏感序列在软骨类病变中的应用研究[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2007,5(4):12-17.
[25] 杨海涛,王仁法,李锋,等.早期髌骨软化症髌软骨磁共振T2图成像和扩散加权成像的对照研究[J].实用放射学杂志, 2008,24(3):55-57, 61.
[26] PAN JD, PIALAT JB, JOSEPH T, et al. Knee cartilage T2 characteristics and evolution in relation to morphologic abnormalities detected at 3-T MR imaging:a longitudinal study of the normal control cohort from the Osteoarthritis Initiative.Radiology.2011;261(2):507-515.
[27] PRASAD AP, NARDO L, SCHOOLER J, et al. T1ρ and T2 relaxation times predict progression of knee osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):69-76.
[28] STAHL R, LUKE A, LI XJ, et al. T1rho,T2 and focal knee cartilage abnormalities in physically active and sedentary healthy subjects versus early OA patients-a 3.0-Tesla MRI study.Eur Radio.2009;19(1):132-143.
[29] 侯进,梅颖洁,代月黎,等.兔骨性关节炎模型关节软骨的弥散张量研究[J].中国比较医学杂志,2014,24(1):1-4.
[30] TAO H, SHANG X, LU R, et al. Quantitative magnetic resonance im- aging (MRI)evaluation of cartilage repair after microfracture (MF)treatment for adult unstable osteochondritis disecans (OCD)in the ankle:corelations with clinical outcome.Eur Radiol.2014;24(8):1758-1767.
[31] GOLDITZ T, STEIB S, PFEIFER K, et al. Functional ankle instability as a risk factor for osteoarthritis:using T2-mapping to analyze early cartilage degeneration in the ankle joint of young athletes.Os- teoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(10):1377-1385.
[32] 郭秦炜,胡跃林,焦晨,等.踝关节距骨骨软骨损伤的影像学及关节镜下表现[J].中华关节外科杂志,2010,4(6):723-728.
[33] JOSEPH GB, NEVITT MC, MCCULLOCH CE, et al. Associations between molecular biomarkers and MR-based cartilage composition and knee joint morphology: data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2018;26(8):1070-1077.
[34] LI Z, WANG H, LU Y, et al. Diagnostic value of T1ρ and T2 mapping sequences of 3D fat- suppressed spoiled gradient (FS SPGR-3D) 3.0-T magnetic resonance imaging for osteoarthritis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(1):e13834.
[35] 刘国彬,张国平,任庆云,等.踝关节不同姿势下MRI检查对其周围韧带及肌腱损伤的诊断价值[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(4):598-602.
[36] 吴昆华,王天朝,梁虹,等.3.0T磁共振不同成像技术对膝关节软骨显示对比分析[J].实用放射学杂志,2014,30(6):1010-1013.
[37] 高丽香,袁慧书.T1ρ序列、MR和关节镜在膝关节软骨成像中的应用对比[J].实用放射学杂志,2018,34(2):256-259.
[38] VANTIENDEREN RJ, DUNN JC, KUSNEZOV N, et al. Osteochondral allograft transfer for treatment of osteochondral lesions of the talus: a systematic review.Arthroscopy.2017;33(1):217-222.
[39] GAO F, CHEN N, SUN W, et al. Combined therapy with shock wave and retrograde bone marrow-derived cell transplantation for osteochondral lesions of the talus.Sci Rep.2017;7(1):2106.
[40] RUNGPRAI C, TENNANT JN, GENTRY RD, et al. Management of osteochondral lesions of the talar dome.Open Orthop J.2017;11:743-761.
[41] 李延炜,洪海森,翟文亮.距骨软骨损伤的诊疗及研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2013,7(8):3510-3512.
[42] GIZA E, DELMAN C, COETZEE JC, et al. Arthroscopic treatment of talus osteochondral lesions with particulated juvenile allograft cartilage.Foot Ankle Int.2014;35(10):1087-1094.
[43] 刘国彬,张国平,任庆云,雷立存,赵峰,高宏阳,朱超华,李亚光.踝关节不同姿势下MRI检查对其周围韧带及肌腱损伤的诊断价值:单中心、诊断性试验[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(4):598-602. |
| [1] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Huang Youyi, Yuan Wei. Application of 3D printing technology in fracture and deformity of foot and ankle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 438-442. |
| [3] | Yi Meizhi, Luo Guanghua, Xiao Yawen, Hu Rong, Chen Xiaolong, Zhao Heng. MRI findings of anatomical variations of the talus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3888-3893. |
| [4] | Peng Chao, Liu Yunpeng, Hua Guojun, Yang Jiaji, Wang Xingliang, Wang Xiaolong. Imaging evaluation of the hip-knee-ankle angle and osteoarthritis progression before and after partial meniscectomy for degenerative medial meniscus posterior root tear [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3368-3373. |
| [5] | Bai Xiaotian, Huo Hongfeng. Biomechanical evaluation of foot and ankle function: constructing static and dynamic indexes of the foot [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2747-2754. |
| [6] | He Shaobo, Liu Jichao, Yang Lifeng, Ding Yongfeng, Li Wujian. Finite element analysis of transposition of posterior tibial tendon for foot drop [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2334-2340. |
| [7] | Chen Xiaolong, Zhao Heng, Hu Rong, Luo Guanghua, Liu Jincai . Correlation of infrapatellar fat pad edema with trochlear and patellofemoral joint morphology: MRI evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2410-2415. |
| [8] | Wang Lei, Qi Rong, Li Jia, Qiu Zhixue, Wang Kai, Suo Nanangxiu. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis and elastic nail system in the treatment of distal tibiofibular fracture in adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1864-1868. |
| [9] | Zhang Yicen, Wang Peixin, Liu Zhicheng. Ultrasound-guided injection of hyaluronic acid and corticosteroid for treating plantar fasciitis: evaluation of pain, fascia thickness and ankle-foot function [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1670-1674. |
| [10] | Han Xinguang, Yin Zhijiang, Wang Xiangcheng, Yang Chenyu, Shang Jian. Effectiveness and safety of modified sliding chute bone graft plus hollow screw fixation for tibiotalar joint fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 839-842. |
| [11] | Bao Chunyu, Yan Mingming. Biomechanical characteristics of ankle joint in volleyball players during stop-jump [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 662-666. |
| [12] | Weng Shiyang, Wu Kai, Lin Jian, Huang Yinjun, Wang Qiugen, Huang Jianhua. Double-strand suture anchor in the treatment of tibiofibular syndesmosis injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5332-5337. |
| [13] | Wang Dong, Zeng Debin, Lin Qiao, Liu Kehui. Tibiofibular syndesmosis reduction after screw fixation of ankle fracture evaluated by CT imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5349-5353. |
| [14] | Li Ying, Guan Hantian, Zhou Yu. Semantic memory impairment and neuroregulation in patients with mild cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5236-5242. |
| [15] | Wang Songbo, Ling Ming, Wang Jicheng, Liu Shizhang. Design and application status of three-component total ankle replacement prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(30): 4847-4853. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||