Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (14): 2223-2230.doi: 10.12307/2022.487
Previous Articles Next Articles
Visualization analysis on research progress and hotspots of exercise therapy for sarcopenia in older adults in recent decade
Wang Susu1, Li Lifeng2, Zhang Yimin2
- 1School of Sports Human Science, 2Laboratory of the Ministry of Sports and Physical Health Education, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China
-
Received:2021-03-16Revised:2021-03-17Accepted:2021-04-23Online:2022-05-18Published:2021-12-21 -
Contact:Zhang Yimin, PhD, Professor, Laboratory of the Ministry of Sports and Physical Health Education, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China -
About author:Wang Susu, Master candidate, School of Sports Human Science, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China -
Supported by:the National Key Research & Development Program of China, No. SQ2018YFC200013 (to ZYM [project participant])
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Susu, Li Lifeng, Zhang Yimin. Visualization analysis on research progress and hotspots of exercise therapy for sarcopenia in older adults in recent decade[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2223-2230.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

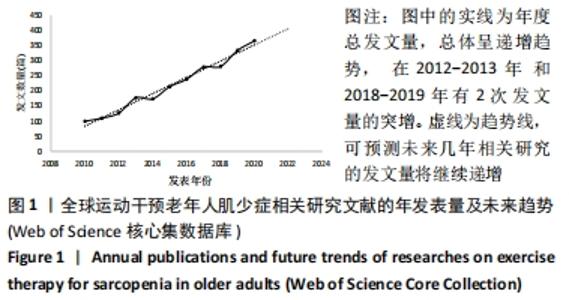
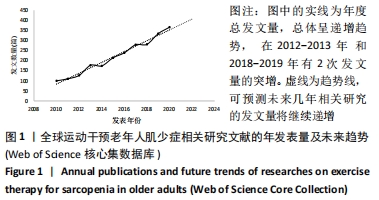
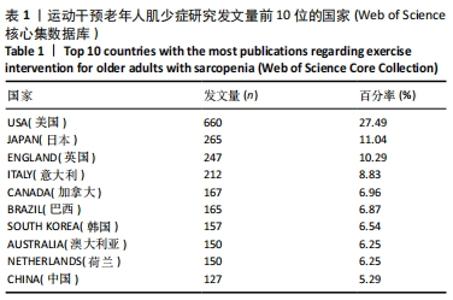
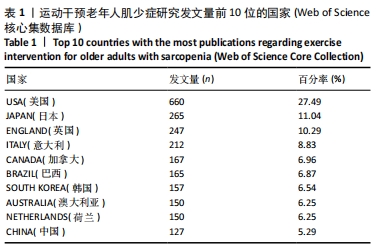
文献发表数量前10位的国家在北美洲、亚洲、欧洲、南美洲和大洋洲都有分布,可见运动干预老年人肌少症的相关研究覆盖地域范围之广,也提示肌少症运动干预的相关问题如箭在弦,亟需解决。 2.1.3 发文机构及合作分析 选择Institution(机构)作为节点类型实现共现分析,见图2。共现分析可定量地研究纳入的内容,直观展示节点出现的频率等基本特征和发展演变的规律,从而了解有关领域研究的现状和发展趋势。生成的图谱中共有395个节点,表明参与运动干预老年人肌少症研究的机构分布广泛,由图中密集的连线可知研究机构之间有密切的合作。总体来看,运动干预老年人肌少症领域发文的主力军是世界各地的高校,其中发文量前6的机构分别为:荷兰的马斯特里赫特大学(53篇),意大利的圣心天主教大学(47篇),加拿大的麦克马斯特大学(47篇),美国的塔夫茨大学(41篇),澳大利亚的墨尔本大学(41篇),英国的南安普顿大学(37篇)。中介中心性的大小反映该节点对整个网络的重要性。中心性排名前3的机构分别为美国的塔夫茨大学(0.19),荷兰的马斯特里赫特大学(0.11),意大利的圣心天主教大学(0.08)。"


2.1.4 文献作者群体分析 通过对作者科学合作网络进行分析,可以展现该领域内核心作者群及合作关系,见图3。具有高中介中心性的作者通常是连接不同学术团队的关键枢纽[12]。发表论文数量最多以及中介中心性最高的作者均为Van Loon,Luc JC (41篇,0.15)。此外具有高发文量和高中心性的作者还有Phillips,Stuart M(29篇,0.09)和Landi, Francesco(27篇,0.10)。结合图2,3可知,国际上分别形成了以荷兰马斯特里赫特大学Van Loon、加拿大麦克马斯特大学Phillips和意大利圣心天主教大学Landi等为核心的学术团队群。从作者共现网络来看,发文作者跨地域和跨机构合作不明显。"


2.2 运动干预老年人肌少症的研究热点及演变趋势 某一学术领域内多位学者在某一时间里共同关注和参与的一个或多个学术话题,可被视为该领域学术研究的热点[12]。利用CiteSpace软件,通过确定高频关键词和对关键文献进行聚类分析可以表述运动干预老年人肌少症研究的前沿热点,而关键词的突现、共现时区图以及共被引文献的时间线图可以反映研究主题在时间上的发展动向及演化趋势。 2.2.1 关键词共现分析 节点类型选择“Keyword”,以1年的时间切片为基础,每一个时间切片选取Top50的信息,即在每年中出现频次排名能占前50位的关键词才会被纳入生成共词网络时区图,见图4。时区图将同年首次出现的关键词汇集到同一时间的相同时区里,从而更清楚地展示了某知识领域的时间层次以及演进过程,图4标出了运动干预老年人肌少症相关研究的高频关键词及其出现频次。"


具体分析如下(括号内为该关键词出现的频次):肌少症与衰弱(288次)、肥胖(239次)、炎症(98次)、骨质疏松(88次)、代谢综合征(60次)、抑郁症(29次)、认知功能障碍(24次)、脑卒中(15次)、糖尿病(15次)、2型糖尿病(7次)等的发生风险有关,甚至与某些疾病的预后(17次)有关。双盲(96次)和随机对照试验(76次)等界定了研究方法,肌肉力量(732次)、身体成分(543次)、步行速度(20次)等是运动干预老年人肌少症研究的热点观察指标,身体活动不足(505次)、营养不良(59次)、衰老(31次)、久坐(4次)等是老年人肌少症的主要危险因素,增加抗阻运动(284次)或力量训练(35次)、营养补充(85次)尤其是蛋白质补充(79次)以及维生素D的摄入(19次)可有效干预老年人肌少症。肌少症的定义(72次)、预测因素(60次)、诊断(60次)、康复(60次)及干预(56次)是老年人肌少症研究领域的研究热点内容,学者们在不断探索的过程中也形成了一些共识(92次),并给出了一些建议(52次)和指南(17次)。 2.2.2 关键词突现分析 对关键词进行突现分析,突现最短持续时间设置为3年,突现性较高的分析词是某个时期内频次变化率高的词,能够挖掘研究热点,反映研究趋势。表2列出了近10年的关键词突现术语。"
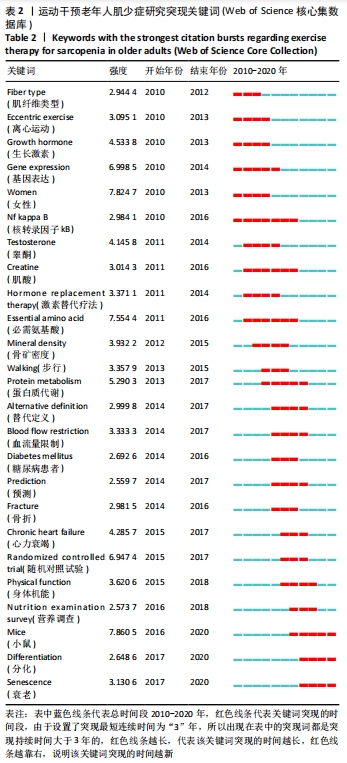

突现分析可通过对词频进行考察,从而探测到某段时间内频率变化幅度最大的词,通常所探测到的突发性词是该研究这段时期的热点内容[12]。 2010-2014年关键词突现分析:这段时间对运动干预老年人肌少症的相关研究主要在组织工程的基因表达层面开展,生长激素、睾酮、激素替代疗法等关键词的突现表明这一阶段以肌少症运动干预过程中的身体激素变化为研究热点。另外,研究表明肌少症会并发炎症和骨矿密度降低,核转录因子kB在细胞的炎症反应以及免疫应答过程中起着重要作用。早期运动干预老年人肌少症的研究对象主要集中在老年女性[13],并开始关注其运动干预过程中老年人的蛋白质代谢情况及营养补给。 2015-2020年关键词突现分析:糖尿病患者、骨折和心力衰竭等关键词的突现表明近几年运动干预老年人肌少症研究的热点对象为肌少症并发其他疾病的患者[14-17],随机对照试验是主要的研究方法,动物研究的成果也更多地应用在运动干预老年人肌少症的研究当中。抗阻训练干预肌少症对阻力强度有要求,因为若想要改善肌少症患者骨骼肌的肌凝蛋白的分布,达到提高肌肉力量、延缓肌肉功能下降的目的,就需要大幅度激活快肌纤维,但低强度的训练刺激达不到。大强度抗阻虽然可以满足大幅激活快肌纤维的目的,可大运动强度容易对肌少症老年人心血管造成压力,还有运动系统损伤的风险。因此这一时期血量流限制(blood flow restriction,BFR)在运动干预肌少症的研究中变得时髦,即使用加压设备对上臂或大腿等运动环节进行施压,以减少流向该环节的血液,有研究提出BFR结合低强度抗阻训练或耐力训练来达到预期效果[18],使得在较低强度下运动时,也能有效激发肌肉肥大适应并增加肌力,且不会对心血管造成额外的压力。有证据表明,对33位年龄(64.04±3.81)岁的老年人分组进行12周的BFR结合低强度抗阻力运动(LRT-BFR)和高强度抗阻力训练(HRT)后,虽然后者在肌肉绝对力量上较前者有一定优势,但综合股四头肌横截面面积和力量增长两方面来看,LRT-BFR可作为HRT的有效替代训练方法,并且更为安全[19]。此外,BRANDNER等[20]还报道了LRT-BFR训练对减少肌肉延迟性酸痛有一定效果。 2.2.3 运动干预老年人肌少症研究知识基础和前沿主题分析 采用对数似然率算法(LLR)提取聚类标签,从关键词中提取名词性术语对聚类进行命名,以每2年作为时间切片,将合成的网络采取时间线视图展示,见图5。"

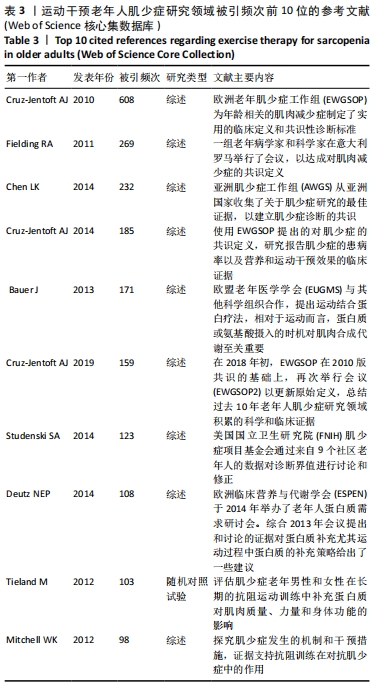
图5显示各个聚类的时间跨度不同,有些聚类目前仍是活跃聚类,如聚类#0和#5。但有些研究主题持续时间相对较短,如聚类#8。各个聚类之间的连线较多,呈现较强的关联度。最近几年仍在活跃的大型聚类蕴含着该研究领域的新兴趋势,代表着研究的前沿方向或尚未解决的科学主题[12]。 结合聚类成员大小和聚类内参考文献的平均引用时间,以下重点介绍5个主要聚类的研究主题: 聚类0:平均引用时间为2016年,属于新兴聚类。该聚类研究慢性炎症对老年人肌少症与衰老的影响、致病机制等。慢性炎症通过导致氧化损伤、DNA损伤、干细胞衰老等加速人体组织器官的衰老。过氧化氢和羟自由基(OH-)、超氧化物银离子(O2-)等活性氧簇经常会攻击细胞致细胞受氧化损伤[21],老年人体内的活性氧经常清除不及时,可能致Ca2+转运过程出现问题,进而造成骨骼肌细胞功能受损[22],这种损伤会促进细胞分泌更多促炎因子,反过来加剧氧化损伤,诱导更多活性氧。错误复制、环境刺激致基因损伤导致的DNA损伤是细胞衰老的主要原因。而高活性氧水平是DNA损伤的重要环境因素,因此慢性炎症会增加DNA受损的概率[23]。此外,慢性炎症微环境存在大量促炎因子,会导致干细胞的再生功能下降,分化功能受损。活动量不足更易出现肥胖,会增加促炎症因子,导致更多的肌肉脂肪化,进一步加重肌肉量的减少[24]。 聚类1:平均引用时间为2011年,该聚类时间较早,主要的研究内容为氨基酸和蛋白质补充对肌肉和骨骼健康的影响。支链氨基酸由3种必需氨基酸组成:亮氨酸,异亮氨酸和缬氨酸。由于这3种氨基酸具有独特的性质,研究人员认为支链氨基酸,特别是亮氨酸,能增加瘦肌肉组织和促进身体恢复[25]。TIELAND等[26]对62名衰弱并发肌少症老年人群[(78±1)岁]进行每周2次,共24周的渐进性抗阻训练,在长期的抗阻运动训练中补充蛋白质,观察干预对肌肉质量、力量和身体功能的影响,结果发现蛋白质组的瘦体质量显著增加了,而安慰剂组则没有明显变化,但两组的肌肉力量和身体功能都有显著提高。此外,欧洲临床营养与代谢学会还于2014年举办了老年人蛋白质需求研讨会[27],在此次会议上针对收集到的研究证据对蛋白质的补充策略给出了一些建议。 聚类2:平均引用时间为2014年,该聚类主要解释了抗阻训练对老年人肌少症实现显著疗效的机制。随年龄增长,骨骼肌纤维逐渐失去适应变化环境的能力,包括自噬活性不足和自噬功能异常[28]。抗阻训练较其他训练方式可有效提高老年人肌肉功能和质量[29],主要是因为抗阻训练有激活PI3K/Akt/mTOR通路、mTOR/ULK1介导的自噬通路的功效[30],以此可以增加肌肉毛细血管的数量,从而提高肌肉耗氧量,最终诱导更多的肌肉蛋白质合成,达到优化骨骼肌功能的作用。虽然有氧运动不会对肌肉质量和力量的增长产生显著影响,但是长期坚持有氧耐力运动,机体能够通过激活腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶,来上调γ辅激活物1α,以增强骨骼肌内线粒体的生物合成和功能,这有助于增强骨骼肌中的自噬水平[31],从而提高肌肉蛋白质的降解速度,降解过程中产生的能量底物,可供肌肉收缩或代谢所需[32]。然而,过多的有氧运动可能会对骨骼肌细胞的自噬过程起到过度激活作用,导致蛋白质或细胞器被过度降解,从而破坏骨骼肌的代谢稳态。因此,有氧运动干预可能对老年人肌少症的主要作用在于补偿,这种机制能够防止细胞能量底物的流失,以保持正常程度的肌肉蛋白的质量控制和代谢功能。 聚类3:平均引用时间为2012年。该聚类主要涉及运动干预老年人肌少症的流行病学研究。研究指出,65-70岁人群的肌少症患病率为13%-24%,80岁以上人群的患病率高达50%以上[33]。据估计,目前世界上约有5 000万人罹患肌少症,并且预计到2050年的时候,患此症的人数将高达5亿,该病已在2016年被列为老年人的常见疾病之 一[34-35]。亚洲国家肌少症的整体患病率在7.8%-35.3%。在中国开展的一项横断面调查研究表明,社区老人肌少症的患病率约为9.4%[36]。CHENG等发现在3 544例上海老年人群中,70岁以上的上海男性肌少症发病率为13.2%,女性为4.8%[37]。 聚类4:平均引用时间为2013年。该聚类主要开展关于老年人肌少症与衰弱的关系,衰弱是一种多维的老年综合征,其特征就是身体系统或功能的累积性下降。老年人衰弱和肌少症的身体表现十分相似,都表现为握力低和步速慢。此外,身体衰弱和肌少症的治疗方法都需要增加蛋白质摄入、维生素D的补充和体育锻炼[38-40]。被引频次前10的文献中,有4篇文献都在这个聚类里,这4篇文献都提到老年人衰弱和肌少症的密切关系,这提示在进行老年人肌少症运动干预的过程中,也可以观测衰弱疾病的相关指标,两类疾病的研究可以互相促进,共同发展。 聚类5:平均引用时间为2015年。该聚类主要涉及运动干预老年人肌少症过程中的营养策略,即蛋白质的补充,该聚类在近几年也依旧活跃,这说明营养补充和增加运动结合起来干预老年人肌少症的研究一直都有新的探讨点。适当的蛋白质补充对于维持老年人骨骼肌质量至关重要。研究发现,蛋白质摄入量高于1.2 g/(kg?d)的老年女性与未达该摄入量的老年女性相比,有着在更高的肌量和瘦体质量[41],差异有显著性意义。中国营养学会老年营养分会专家共识对老年人蛋白质摄入的推荐量为1.0-1.5 g/(kg?d)[42]。但针对老年人进行不同强度和频率运动处方的肌少症干预时,其蛋白质的补充策略还需进一步探究。 合成网络中被引频次前10位的文献见表3。被引频次反映了相应文献的学术贡献,是衡量文献重要性的重要指标。老年人肌少症运动干预领域为应用型研究,对该领域已发表文献中参考文献进行被引频次的分析,得到的高被引文献在运动干预老年人肌少症研究知识演进中具有重要作用。被引频次前10的参考文献类型基本上为综述报告,从这些文献的发表内容上看,主要为各洲老年人肌少症工作组通过会议总结各洲国家相关研究成果,从而制定的临床定义和共识性诊断标准。此外,一些机构对通过共识诊断的老年人肌少症流行病学研究进行综述,为了解该病症的患病率以及诊断标准的修订提供了数据支持。部分研究通过综述探讨老年人肌少症的患病机制以及有效的干预策略,其中肯定了运动疗法对老年人肌少症干预的价值,并且在运动结合营养的非药物干预中,运动过程中蛋白质或氨基酸摄入的时机对肌肉合成代谢至关重要,这些文献发表的内容都是该领域最重要的知识基础。"
| [1] KWON YN, YOON SS, LEE K. Sarcopenic obesity in elderly korean women: a nationwide cross-sectional study. J Bone Metab. 2018;25(1): 53-58. [2] ROSENBERG IH. Sarcopenia: origins and clinical relevance. J Nutr. 1997; 127(5 Suppl):990S-991S. [3] CRUZ JENTOFT AJ, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age and Ageing. 2019;48(1):16-31. [4] MARTONE AM, BIANCHI L, ABETE P, et al. The incidence of sarcopenia among hospitalized older patients: results from the Glisten study. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2017;8(6):907-914. [5] ISABEL L, ANDREA C, IOSIEF A, et al. Nonpharmacological interventions to treat physical frailty and sarcopenia in older patients: a systematic overview-the SENATOR Project ONTOP Series. Clin Interv Aging. 2017; 12:721-740. [6] LARA V, WENDY H, DEBRA LW. Exercise interventions in healthy older adults with sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Australas J Ageing. 2018;37(3):169-183. [7] 王岑依,梁计陵,司誉豪,等.运动通过调控线粒体质量控制改善肌少症的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2020,26(9):1066-1070. [8] BAO W, SUN Y, ZHANG T, et al. Exercise programs for muscle mass, muscle strength and physical performance in older adults with sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging Dis. 2020; 11(4):863-873. [9] 王坤,罗炯,刘立,等.老年人肌少症的成因、评估及应对[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(11):1767-1773. [10] YOO S, NO M, HEO J, et al. Role of exercise in age-related sarcopenia. J Exerc Rehabil. 2018;14(4):551-558. [11] BARAJAS-GALINDO DE, GONZÁLEZ AE, FERRERO VP, et al. Effects of physical exercise in sarcopenia. A systematic review. End Diabetes Y Nutr. 2020;68(3):159-169. [12] 李杰,陈超美.CiteSpace:科技文本挖掘及可视化[M].北京:首都经济贸易大学出版社,2017. [13] LIAO C, TSAUO J, HUANG S, et al. Effects of elastic band exercise on lean mass and physical capacity in older women with sarcopenic obesity: a randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2317. [14] TAKENAMI E, IWAMOTO S, SHIRAISHI N, et al. Effects of low-intensity resistance training on muscular function and glycemic control in older adults with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig. 2019;10(2):331-338. [15] CHANG C, WU JS, MHUIRCHEARTAIGH JN, et al. Effect of sarcopenia on clinical and surgical outcome in elderly patients with proximal femur fractures. Skeletal Radiol. 2018;47(6):771-777. [16] JIA D, CAI M, XI Y, et al. Interval exercise training increases LIF expression and prevents myocardial infarction-induced skeletal muscle atrophy in rats. Life Sci 2018;193:77-86. [17] TAYA M, AMIYA E, HATANO M, et al. High-intensity aerobic interval training can lead to improvement in skeletal muscle power among in-hospital patients with advanced heart failure. Heart Vessels. 2018; 33(7):752-759. [18] MIGUEL SC, CARLOS U. Exercise with blood flow restriction: an effective alternative for the non‐pharmaceutical treatment for muscle wasting. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2019;10(2):257-262. [19] VECHIN FC, LIBARDI CA, CONCEIÇÃO MS, et al. Comparisons between low-intensity resistance training with blood flow restriction and high-intensity resistance training on quadriceps muscle mass and strength in elderly. J Strength Cond Res. 2015;29(4):1071-1076. [20] BRANDNER CR, WARMINGTON SA. Delayed onset muscle soreness and perceived exertion after blood flow restriction exercise. J Strength Cond Res. 2017;31(11):3101-3108. [21] BEKTAS A, SCHURMAN SH, SEN R, et al. Aging, inflammation and the environment. Exp Gerontol. 2018;105:10-18. [22] CHEEMA N, HERBST A, MCKENZIE D, et al. Apoptosis and necrosis mediate skeletal muscle fiber loss in age-induced mitochondrial enzymatic abnormalities. Aging Cell. 2015;14(6):1085-1093. [23] ALLEN H, JONATHAN W, NASHWA C, et al. Latent mitochondrial DNA deletion mutations drive muscle fiber loss at old age. Aging Cell. 2016; 15(6):1132-1139. [24] VERLAAN S, ASPRAY TJ, BAUER JM, et al. Nutritional status, body composition, and quality of life in community-dwelling sarcopenic and non-sarcopenic older adults: a case-control study. Clin Nutr. 2017;36(1): 267-274. [25] Le Couteur David G, Solon-Biet Samantha M, Cogger Victoria C, et al. Branched chain amino acids, aging and age-related health. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;64:101198. [26] Tieland M, Dirks ML, van der Zwaluw N, et al. Protein supplementation increases muscle mass gain during prolonged resistance-type exercise training in frail elderly people: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2012;3(8): 713-719. [27] Deutz NEP, Bauer JM, Barazzoni R, et al. Protein intake and exercise for optimal muscle function with aging: recommendations from the ESPEN Expert Group. Clinical Nutr. 2014;33(6):929-936. [28] DAVID WR, IVA MB, KATHERINE MM, et al. Muscle-specificity of age-related changes in markers of autophagy and sphingolipid metabolism. Biogerontology. 2015;16(6):747-759. [29] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, LANDI F, SCHNEIDER SM, et al. Prevalence of and interventions for sarcopenia in ageing adults: a systematic review. Report of the International Sarcopenia Initiative (EWGSOP and IWGS). Age Ageing. 2014;43(6):748-759. [30] ZIAALDINI MM, MARZETTI E, PICCA A, et al. Biochemical pathways of sarcopenia and their modulation by physical exercise: a narrative review. Front Med. 2017. doi: 10.3389/FMED.2017.00167. [31] VITOR AL, MITSUHARU O, MEI Z, et al. Autophagy is required for exercise training‐induced skeletal muscle adaptation and improvement of physical performance. FASEB J. 2013;27(10):4184-4193. [32] MØLLER AB, VENDELBO MH, CHRISTENSEN B, et al. Physical exercise increases autophagic signaling through ULK1 in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015;118(8):971-979. [33] PING L, QIUKUI H, SHAN H, et al. Sarcopenia as a predictor of all-cause mortality among community-dwelling older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Maturitas. 2017;103:16-22. [34] CAO L, MORLEY JE. Sarcopenia Is Recognized as an Independent Condition by an International Classification of Disease, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) Code. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2016; 17(8):675-677. [35] Morley JE. Frailty and sarcopenia in elderly. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2016;128(Suppl 7):439-445. [36] YU R, LEUNG J, WOO J. Incremental predictive value of sarcopenia for incident fracture in an elderly Chinese cohort: results from the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOs) Study. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014;15(8):551-558. [37] CHENG Q, ZHU X, ZHANG X, et al. A cross-sectional study of loss of muscle mass corresponding to sarcopenia in healthy Chinese men and women: reference values, prevalence, and association with bone mass. J Bone Miner Metab. 2014;32(1):78-88. [38] STEFFL M, BOHANNON R W, SONTAKOVA L, et al. Relationship between sarcopenia and physical activity in older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Interv Aging. 2017;12:835-845. [39] DODDS R, SAYER AA. Sarcopenia and frailty: new challenges for clinical practice. Clin Med (London, England). 2016;16(5):455-458. [40] CEDERHOLM T. Overlaps between frailty and sarcopenia definitions. Nestle Nutr Inst Workshop Ser. 2015;83:65-69. [41] GENARO PDE S, PINHEIRO MDE M, SZEJNFELD VL, et al. Dietary protein intake in elderly women: association with muscle and bone mass. Nutr Clin Pract. 2015;30(2):283-289. [42] 孙建琴,张坚,常翠青,等.肌肉衰减综合征营养与运动干预中国专家共识(节录)[J].营养学报,2015,37(4):320-324. |
| [1] | Wu Min, Zhang Yeting, Wang Lu, Wang Junwei, Jin Yu, Shan Jixin, Bai Bingyi, Yuan Qiongjia. Effect of concurrent training sequences on body composition and hormone response: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1305-1312. |
| [2] | Zhao Jing, Liu Xiaobo, Zhang Yue, Zhang Jiaming, Zhong Dongling, Li Juan, Jin Rongjiang. Visualization analysis of neuromuscular electrical stimulation therapy based on CiteSpace: therapeutic effects, hot spots, and developmental trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1234-1241. |
| [3] | Shui Xiaoping, Li Chunying, Li Shunchang, Sun Junzhi, Su Quansheng . Effects of aerobic and resistance exercises on brain-derived neurotrophic factor, nuclear factor-kappa B and inflammatory cytokines in skeletal muscle of type II diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 669-675. |
| [4] | Zheng Zhenquan, Rong Jiesheng. Sarcopenia: age-related muscle mass loss and functional declines [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 792-797. |
| [5] | Zhu Zheng, Fu Changxi, Ma Wenchao, Ma Gang, Peng peng. Regulatory mechanism of aerobic exercise on cardiac remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2231-2237. |
| [6] | Li Xiaowei, Deng Chengyuan, Zhou Guijuan, Chen Xiaocui, Liao Ying. Osteosarcopenia: muscle-bone interactions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1752-1757. |
| [7] | Wang Mengting, Gu Yanping, Ren Wenbo, Qin Qian, Bai Bingyi, Liao Yuanpeng. Research hotspots of blood flow restriction training for dyskinesia based on visualization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1264-1269. |
| [8] | Chen Rong, Zeng Qing, Gong Ze, Huang Guozhi, . Different modes of blood flow restriction in the treatment of senile sarcopenia: therapeutic effects and safety factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5215-5221. |
| [9] | Fan Yinuo, Guan Zhiying, Li Weifeng, Chen Lixin, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Research status and development trend of bibliometrics and visualization analysis in the assessment of femoroacetabular impingement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 414-419. |
| [10] | Tang Shuo, Hou Decai. Constructing an animal model of femoral head necrosis: how to get closer to clinical application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(29): 4691-4696. |
| [11] | Lu Yuyun, Huang Mei, Shi Xinlei, Chen Baoyan. Bibliometric and visualization analysis of breast cancer stem cell literature from 2011 to 2020 based on Web of Science database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4001-4008. |
| [12] | Wang Zhen, Lin Haiqi, He Fei, Lin Wentao. Exercise activates skeletal muscle satellite cells: exercise prevention and treatment for age-related sarcopenia and muscle injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3752-3759. |
| [13] | Wen Zhijing, Gu Pengzhen, He Xijing, Li Jialiang, Wang Yibin, Wang Yiqun. Development of high molecular polymer polyetherketoneketone and its prospects in medical applications [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3603-3608. |
| [14] | Ren Wenbo, Liao Yuanpeng. Visualization analysis of traumatic osteoarthritis research hotspots and content based on CiteSpace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3374-3381. |
| [15] | Pan Xuan, Zhao Meng, Zhang Xiumei, Zhao Jie, Zhai Yunkai. Research and application of biological three-dimensional printing technology in the field of precision medicine: analysis of Chinese and English literature [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3382-3389. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||