Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (34): 5562-5568.doi: 10.12307/2022.469
Previous Articles Next Articles
Understanding of periodontal biomaterials based on the concept of bone homeostasis control and the effects on bone formation
Li Maoxue, Ding Yi, Guo Shujuan
- State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Department of Periodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2021-03-27Accepted:2021-05-09Online:2022-12-08Published:2022-04-16 -
Contact:Guo Shujuan, MD, Associate professor, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Department of Periodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Li Maoxue, Master candidate, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Department of Periodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:Applied Basic Research Project of Sichuan Science and Technology Department, No. 2020YJ0242 (to DY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Maoxue, Ding Yi, Guo Shujuan. Understanding of periodontal biomaterials based on the concept of bone homeostasis control and the effects on bone formation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5562-5568.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
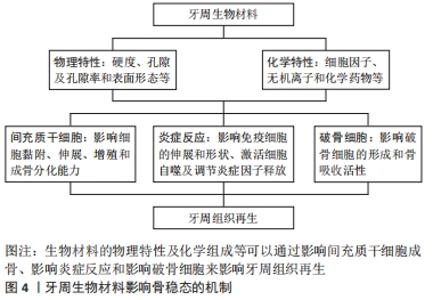
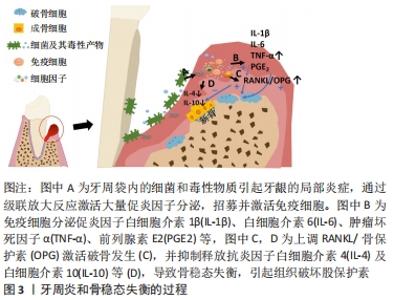
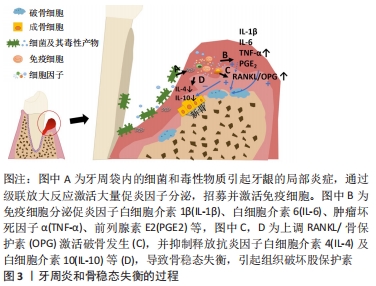
此图为牙周炎骨稳态失衡的过程,局部存在的致病微生物引起牙龈的局部炎症,从而过度激活免疫反应,触发组织破坏。 当疾病进展时,宿主和微生物会释放多种蛋白酶裂解蛋白质,并通过级联放大反应激活宿主体内免疫细胞产生大量细胞因子如白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、前列腺素E2和肿瘤坏死因子α等,它们可以通过调节RANKL/RANK/骨保护素轴,直接或间接地促进破骨细胞形成,刺激骨吸收,并抑制抗炎因子释放,使得成骨细胞的分化也受到抑制,导致最后的骨破坏[9-10]。RANKL/RANK/骨保护素轴是骨代谢过程中重要的调节途径之一,RANKL相对表达的增加或骨保护素的减少可以使骨稳态平衡向破骨方向发生倾斜[11]。与牙周健康者相比,RANKL在牙周炎患者中的表达上调,而骨保护素表达下调,导致RANKL/骨保护素比值升高,且此比例的异常在糖尿病患者和吸烟者中更为明显[12-13]。而研究证据表明,降低炎症和破骨细胞的活性有利于治疗牙周炎并恢复牙周组织稳态,促进骨形成[14]。 2.2 牙周生物材料对骨稳态调节的影响 临床上用于牙周组织再生治疗的材料主要是屏障膜和骨移植物,起着屏障与支架的作用,为具有再生能力的细胞提供一个相对稳定的空间,但诱导骨再生的能力有限[5],理解牙周生物材料影响骨稳态调节的机制,有助于开发新一代牙周再生材料。生物材料与机体的相互作用较为复杂,材料自身的物理结构、化学组分及机械性能等特性不仅对细胞黏附、增殖与分化行为产生作用,还可能影响着局部细胞因子释放和信号通路的激活,并引起机体骨稳态调节的变化[15-16],见图4。"
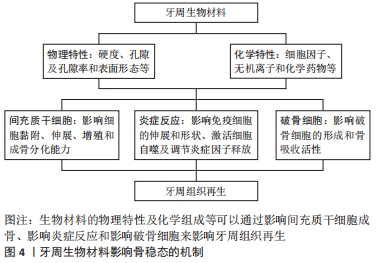
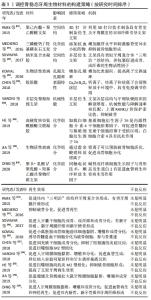
2.2.1 材料物理特性与结构的作用 材料物理特性与结构对间充质干细胞的影响:骨再生过程中,生物材料的硬度、孔径与孔隙率及表面形貌等物理特征会对细胞的生物学功能和组织生成产生影响[17]。一般来说,间充质干细胞倾向于在硬度相近的材料上黏附、增殖与分化为特定表型[18],LIU等[19]的实验发现在6-135 kPa范围内,牙周膜干细胞的增殖与成骨分化能力随基质硬度的增加而增加,Notch途径或许是基质硬度影响牙周膜。材料的孔径大小影响长入材料的细胞类型,小孔径不利于骨细胞长入[20];高孔隙率有利于营养交换及生物活性因子吸附,但会牺牲材料的力学性能影响成骨[21]。此外,材料的表面形态也可以调节间充质干细胞黏附、增殖和细胞形态,例如在亚微米尺度,随着钛种植体表面粗糙度增加,成骨细胞的分化能力增强[22];在排列整齐的纤维表面,细胞可以呈现出沿纤维排列方向的拉长形状,在无序的纤维表面细胞呈不规则的细胞形态,目前已经证明纤维的取向可以有效调节细胞反应,模拟骨骼的各向异性组织结构[23]。 有学者利用等离子体电解氧化技术在钛表面沉积富含钙、磷、银的二氧化钛涂层[24],在保持正常生物功能的同时提高钛表面的多孔性、润湿性、粗糙度、显微硬度和摩擦系数,此材料表现出良好的生物相容性和骨整合能力。 材料物理特性与结构对炎症反应的影响:生物材料的物理特性不仅可以直接影响间充质干细胞的黏附、伸展与增殖,还可以通过诱导局部免疫反应调控炎症来影响骨再生 [22, 25]。比如说材料孔径大小影响巨噬细胞的伸展和形状,进而激活细胞自噬,调节炎症反应并释放成骨因子[25];材料的表面粗糙度也影响着巨噬细胞反应,并调节细胞因子(如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素4及白细胞介素10)的释放,随着表面粗糙度的增加,巨噬细胞有向M1表型极化的趋势[22]。Bio-Gide胶原膜是临床上引导组织再生术常用的屏障膜,生物相容性好,陈泽涛课题组发现Bio-Gide胶原膜的光滑面与粗糙面在植入体内表现出不同的应答效果[26],与光滑表面相比,BioGide胶原膜的粗糙面对促炎因子的上调作用更明显,这可能与WNT5a/Ca2+途径的激活有关,而这种促炎作用不利于骨再生。 材料物理特性与结构对破骨发生的影响:骨再生过程中,破骨发生对骨重建起着至关重要作用。牙周组织工程中,关于生物材料与破骨发生的研究相对较少,而在骨组织工程研究中发现生物材料的组成、结晶度、粗糙度及表面特性等对破骨细胞有显著影响 [27-28]。例如,纳米级羟基磷灰石与羟基磷灰石相比,可以延迟破骨样细胞的形成,并抑制其活性。介孔生物活性玻璃与传统的溶胶-凝胶生物活性玻璃相比,具有高度有序的介孔结构、高孔隙率和高比表面积,能与外界快速地进行离子交换,具有良好的生物相容性和抑制破骨发生的能力,有研究发现在介孔生物活性玻璃粉末质量浓度达到1 g/L时,成骨肉瘤细胞的形态和细胞周期都没有显著的改变,虽然不抑制破骨细胞的形成,但破骨细胞的骨吸收能力降低[29]。 然而,材料的理化特性对于间充质干细胞、炎症反应和破骨发生的影响是动态变化的,例如高硬度的谷氨酰胺转氨酶交联凝胶可以促进间充质细胞的成骨向分化,但同时也会引起巨噬细胞向M1型极化,影响最终的成骨效果[30]。BioGide胶原膜的粗糙面可增强骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,但粗糙面同时具有较高的促炎作用,其介导的骨免疫微环境不利于成骨细胞分化,会影响最终的成骨效果[26]。 2.2.2 材料化学组分对骨稳态调节的影响 材料的生物化学组分是另一项影响骨再生的关键因素,牙周硬组织再生和矿化过程中,某些细胞因子、无机离子和化学药物等不仅可以直接促进牙周矿化组织的形成,还能影响局部免疫炎症和破骨形成。 细胞因子:在牙周硬组织再生与矿化过程中,细胞因子参与了调控细胞增殖、分化、免疫应答及细胞间的相互作用等事件。据报道,与牙周硬组织再生关系密切的生长因子有骨形态发生蛋白、成纤维细胞生长因子、内皮细胞生长因子等,它们可诱导基质矿化,参与骨形成与骨重建,体外实验和动物实验均已被证明具有很好的效果[31]。大量数据还支持炎症也是骨再生的重要组成部分,抗炎细胞因子如白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10及碱性成纤维细胞生长因子等具有调节炎症或抗破骨细胞形成的功能,利用其修饰材料可以减轻材料的异物反应、降低破骨细胞形成,达到促进骨再生的目的[32-33]。而其他细胞因子如白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6及肿瘤坏死因子α等与过度炎症浸润、较高的RANKL/骨保护素比值及异常活跃的破骨细胞有关,抑制这些炎症因子的释放也是减轻炎症与抑制破骨生成的有效方法[7]。此外,P物质、基质衍生因子1α、粒细胞集落刺激因子等生物活性因子被报道有招募“内源性干细胞归巢”的作用,可以吸引干细胞到达目的位置发挥特定的生物功能,也可以修饰材料改善成骨效果[34]。 无机离子:无机离子可以显著改善材料的机械性能与抗菌活性[35],可以直接促进间充质细胞分化为成骨细胞[36],促进成骨相关蛋白的表达与生物矿化[37],释放到环境中还会影响到局部免疫炎症反应和破骨形成,可作为生物活性离子修饰材料。例如,钛金属是口腔中应用最为广泛的金属材料之一,具有出色的骨整合能力[24];锌离子可以增加抗炎细胞因子白细胞介素10的释放,减少肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β的表达[38];钙离子参与非经典Wnt信号通路Wnt5A/Ca2+,从而调节免疫反应[39];锶离子可以抑制破骨细胞形成与成熟,有利于骨再生[40]。但无机离子对细胞具有一定的毒性,因此还需要大量实验研究如何选择合适的负载方式、离子浓度和缓释类型,以提高无机离子的生物安全性和生物相容性。 化学药物:化学药物也是促进骨再生的常见介质,目前与牙周硬组织形成相关研究较多的药物有四环素族抗生素、他汀类药物、抗血小板类药物、双膦酸盐及促炎症消退介质等,它们已被证明通过不同的机制调节成骨细胞分化,还具有调节宿主免疫炎症反应和破骨细胞形成的能力,可以抑制骨丧失,促进牙周硬组织再生[14,41-42]。四环素族抗生素是牙周治疗中常用抗生素之一,具有抗菌和免疫调节的作用,系统评价证明局部应用于四环素族抗生素,不仅可以辅助治疗牙周炎,还可以抑制骨丧失和促进骨形成[43]。促炎症消退介质是一类抑制炎症细胞募集、干扰巨噬细胞吞噬、同时促进巨噬细胞M2型极化的内源性分子。研究发现促炎症消退介质可以降低RANKL的生成,维持RANKL/骨保护素的比值有利于骨生成,并促进牙周炎小动物模型的骨再生[14,44]。 2.3 调控骨稳态牙周生物材料的构建策略 理想的牙周再生材料不仅要求具有良好的生物相容性,还应能调控人体骨稳态平衡,促进硬组织再生。技术的发展使得控制生物材料的理化特性主动调节细胞行为已成为可能,一些学者从调控牙周组织骨稳态方向着手设计骨修复材料以提高材料的骨再生效果[45-54]。主要方式有改良生物材料物理特性和生化组分,激活成骨细胞和牙周膜干细胞成骨向分化,并调控牙周局部炎症与抑制破骨细胞形成来提高材料的成骨效果,见表1。"


2.3.1 修饰材料的理化特性 由于生物材料自身的组成、结构等特点会直接影响到细胞行为和组织形成,所以最常见的调控骨稳态生物材料的构建策略即优化材料的理化特性。为解决传统生物活性玻璃孔隙少、细胞渗透率低等问题,KOWAL等[45]学者开发了一种由70%的二氧化硅与30%的氧化钙混合组成的新一代生物活性玻璃,这种材料具有高度多孔的特点,孔隙大小从纳米到微米级不等,不仅提高了材料的比表面积,促进物质交换,还为细胞植入提供了良好的环境,体外实验结果显示多孔支架对成骨细胞分化和破骨细胞形成均具有一定作用,表明这种材料可以支持骨再生过程中的动态修复。 材料的表面修饰和涂层可以改善材料的表面结构和理化成分,调节不同的受体结合与信号传导,为细胞黏附、生长和功能稳定提供良好的微环境,从而调控细胞反应和局部炎症。为了改善BioGide胶原膜粗糙面较高的炎症反应对骨再生的不利影响,陈泽涛课题组利用脉冲激光沉积技术在BioGide胶原膜粗糙面上涂布了一层Ca2ZnSi2O7涂层[26],实验结果证明涂层不仅增强了间充质干细胞的成骨分化,其中的钙离子、锌离子和硅离子在巨噬细胞和膜相互作用期间还以缓慢释放的方式释放到周围环境中,改变了局部炎症细胞因子表达谱并上调成骨因子的表达,抑制促炎因子释放,成功地调节了粗糙面所介导的免疫微环境,提高了Bio-Gide胶原膜的骨再生效果。因此,可以优化材料的理化性能,促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化,调控炎症反应并抑制破骨发生,来提高成骨效果。 2.3.2 添加化学介质/生物活性因子 与单纯应用材料相比,添加了化学介质/生物活性因子的材料表现出更好的骨稳态调节能力,可获得更好的骨再生效果。例如,为解决高硬度的谷氨酰胺转氨酶交联凝胶引起巨噬细胞向M1型极化不利于硬组织再生的问题,有研究引入白细胞介素4和基质细胞衍生因子1α在高硬度谷氨酰胺转氨酶交联凝胶调节巨噬细胞极化并促进内源性干细胞募集[33],组织学结果显示同时含有白细胞介素4和基质细胞衍生因子1α的谷氨酰胺转氨酶交联凝胶在附着获得、骨、牙周膜和牙骨质再生方面均获得了更满意的效果。抗血小板药物氯吡格雷是通过二磷酸腺苷受体产生抑制血小板激活的作用,有实验报道二磷酸腺苷受体在破骨细胞的分化和功能发挥中起着关键作用,MEDIERO等[42]将抗血小板药物氯吡格雷和替格瑞洛添加入3D打印可吸收三磷酸钙/羟基磷灰石支架时,结果表明其促进骨再生的能力明显强于支架本身,并与生长因子骨形态发生蛋白2相似。锶离子对预防破骨细胞活化和促进成骨细胞分化具有直接作用,JIA等[46]开发了一种可以释放锶离子的介孔生物活性玻璃支架,实验证明了与单独的介孔生物活性玻璃支架相比,锶离子的介孔生物活性玻璃支架具有促进牙周再生的能力。由此可见,添加化学介质/生物活性因子可以作为抑制破骨吸收和促进骨形成新方法,改善材料的骨稳态调节能力并促进牙周再生。 然而,牙周组织再生过程是一个由多种因子参与的多时相多序列事件,单一的组分或许难以取得良好的效果,缓释/控释系统或许更贴近于牙周硬组织形成过程。有研究证明与单独应用碱性成纤维细胞生长因子、骨形态发生蛋白2或同时应用碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和骨形态发生蛋白2相比,顺序释放碱性成纤维细胞生长因子与骨形态发生蛋白2可以显著促进牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化[47]。有研究进而利用同轴电纺超组装技术制备了一种具有核/壳结构的聚(L-乳酸)/聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物纤维支架[47],它可以按顺序快速释放碱性成纤维细胞生长因子与缓慢释放骨形态发生蛋白2,实验结果显示该支架能有效触发干细胞向缺损部位的募集,促进牙槽骨的形成、牙周膜和牙骨质的再生。因此,未来的研究可以多注重于缓释/控释系统的开发,以合理有效地释放细胞因子和药物,更有效地促进牙周硬组织再生。 2.3.3 多层仿生材料 牙周组织是牙骨质-牙周膜-牙槽骨3种组织在结构与功能上形成的多层复合体,每种组织的特性差异较大,有学者根据牙周复合体各层次的特性,设计了模拟牙周复合体“三明治”结构的多层仿生支架,并结合特定的生物活性因子促进牙周膜干细胞成骨分化与抑制破骨形成,取得了更有效的骨再生效果[48-50]。SOWMYA等[49]构建了类似牙骨质-牙周膜-牙槽骨结构的纳米多层复合水凝胶仿生支架材料,将生物活性分子包裹在支架的不同层次,分别诱导组织再生,释药曲线表明生长因子释放持续时间长达14 d,体内外实验也均表现出良好的成牙本质、成纤维和成骨分化潜力。VARONI等[50]以不同分子量壳聚糖为原料制作与牙周软硬组织的解剖厚度、机械性能与降解速率相匹配的多层仿生支架。该支架由3部分组成,分别是厚而坚硬的多孔骨层,薄且柔软的多孔牙龈层及纤维定向排列的微通道牙周膜层。体外实验表明该支架可促进人牙周膜干细胞成骨向分化,表现为碱性磷酸酶活性增强、钙沉积增强和骨钙素表达上调;而接种成骨细胞的支架部分表现为高水平的骨保护素,接种人牙周膜成纤维细胞的部分表现为高水平RANKL,提示支架可能通过RANK/RANKL/骨保护素途径调节牙周组织各部分新骨形成与破骨发生。 2.3.4 3D打印材料 3D打印技术可以设计具有特定空间结构的支架材料,为特异性地调节细胞行为和炎症发展提供了必要的基础。依据牙骨质-牙周膜-牙槽骨的“三明治”结构,利用3D打印技术将细胞、材料及生长因子等按照各自的空间排列进行打印,可以促进牙周软硬组织的再生[51]。PARK等[52]制作了3D打印聚己内酯-聚乙醇酸双相纤维引导支架,分别对应牙周组织的骨室与牙周膜室,并模拟了牙周组织微环境,将支架与人牙本质片结合植入裸鼠皮下异位培养中,实验观察到了成功的骨再生和牙周复合体再生,尤其是形成了与牙本质切片垂直或倾斜的纤维组织。3D打印材料应用于临床上牙周局部骨缺损的案例也有报道,RASPERINI等[53]通过锥束CT扫描患者的局部缺损后,利用3D打印技术制造具有高适应性(适合率为82%-87%)的可吸收纤维引导支架,虽然首例3D打印材料的临床试验结果在14个月时出现了材料暴露等问题,但其意义仍然值得肯定。目前3D打印材料的开发也多注重材料的成骨性能,对骨稳态调控的研究相对较少。未来研究可利用3D打印技术精确控制材料的物理性能、细胞排列和活性因子的释放,设计不仅与患者牙周缺损的结构相相匹配,还能精确调控骨稳态平衡的再生材料,促进个性化医疗发展,从而更好地促进牙周组织再生。"

| [1] SIDDIQUI JA, PARTRIDGE NC. Physiological bone remodeling: systemic regulation and growth factor involvement. Physiology. 2016;31(3):233-245. [2] DIEKWISCH TGH. Periodontal homeostasis: from vienna to texas-a century of periodontal research in the spirit of bernhard gottlieb. Stem Cells Dev. 2019;28(15):961-962. [3] LUAN X, ZHOU X, TROMBETTA-ESILVA J, et al. MicroRNAs and periodontal homeostasis. J Dent Res. 2017;96(5):491-500. [4] SLOTS J. Periodontitis: facts, fallacies and the future. Periodontol 2000. 2017;75(1):7-23. [5] SALLUM EA, RIBEIRO FV, RUIZ KS, et al. Experimental and clinical studies on regenerative periodontal therapy. Periodontol 2000. 2019;79(1):22-55. [6] KLOPFLEISCH R, JUNG F. The pathology of the foreign body reaction against biomaterials. J. Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(3):927-940. [7] GRUBER R. Osteoimmunology: inflammatory osteolysis and regeneration of the alveolar bone. J Clin Periodontol. 2019;46 Suppl 21:52-69. [8] GRAVES DT, LI J, COCHRAN DL. Inflammation and uncoupling as mechanisms of periodontal bone loss. J. Dent. Res. 2011;90(2):143-153. [9] HIENZ SA, PALIWAL S, IVANOVSKI S. Mechanisms of bone resorption in periodontitis. J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:615486. [10] KATO H, TAGUCHI Y, TOMINAGA K, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis LPS inhibits osteoblastic differentiation and promotes pro-inflammatory cytokine production in human periodontal ligament stem cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2014;59(2):167-175. [11] UDAGAWA N, KOIDE M, NAKAMURA M, et al. Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021; 39(1):19-26. [12] MOGI M, OTOGOTO J, OTA N, et al. Differential expression of RANKL and osteoprotegerin in gingival crevicular fluid of patients with periodontitis. J Dent Res. 2004;83(2):166-169. [13] POLAK D, SHAPIRA L. An update on the evidence for pathogenic mechanisms that may link periodontitis and diabetes. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45(2):150-166. [14] HASTURK H, KANTARCI A, GOGUET-SURMENIAN E, et al. Resolvin E1 regulates inflammation at the cellular and tissue level and restores tissue homeostasis in vivo. J Immunol. 2007;179(10):7021-7029. [15] CHEN ZT, KLEIN T, MURRAY RZ, et al. Osteoimmunomodulation for the development of advanced bone biomaterials. Mater Today. 2016; 19(6):304-321. [16] LI Y, XIAO Y, LIU C. The horizon of materiobiology: a perspective on material-guided cell behaviors and tissue engineering. Chem Rev. 2017; 117(5):4376-4421. [17] XIAO D, ZHANG J, ZHANG C, et al. The role of calcium phosphate surface structure in osteogenesis and the mechanisms involved. Acta Biomater. 2020;106:22-33. [18] ENGLER AJ, SEN S, SWEENEY HL, et al. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell. 2006;126(4):677-689. [19] LIU N, ZHOU M, ZHANG Q, et al. Effect of substrate stiffness on proliferation and differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells. Cell Prolif. 2018;51(5):e12478. [20] PAMULA E, BACAKOVA L, FILOVA E, et al. The influence of pore size on colonization of poly (L-lactide-glycolide) scaffolds with human osteoblast-like MG 63 cells in vitro. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19(1): 425-435. [21] OKAMOTO M, DOHI Y, OHGUSHI H, et al. Influence of the porosity of hydroxyapatite ceramics on in vitro and in vivo bone formation by cultured rat bone marrow stromal cells. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2006; 17(4):327-336. [22] LI X, HUANG Q, ELKHOOLY TA, et al. Effects of titanium surface roughness on the mediation of osteogenesis via modulating the immune response of macrophages. Biomed Mater. 2018;13(4):045013. [23] HE M, WANG Q, XIE L, et al. Hierarchically multi-functionalized graded membrane with enhanced bone regeneration and self-defensive antibacterial characteristics for guided bone regeneration. Chem Eng J. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125542. [24] THUKKARAM M, CORYN R, ASADIAN M, et al. Fabrication of microporous coatings on titanium implants with improved mechanical, antibacterial, and cell-interactive properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(27):30155-30169. [25] CHEN Z, NI S, HAN S, et al. Nanoporous microstructures mediate osteogenesis by modulating the osteo-immune response of macrophages. Nanoscale. 2017;9(2):706-718. [26] CHEN Z, CHEN L, LIU R, et al. The osteoimmunomodulatory property of a barrier collagen membrane and its manipulation via coating nanometer-sized bioactive glass to improve guided bone regeneration. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(5):1007-1019. [27] DETSCH R, BOCCACCINI AR. The role of osteoclasts in bone tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(10):1133-1149. [28] GERMAINI MM, DETSCH R, GRUNEWALD A, et al. Osteoblast and osteoclast responses to A/B type carbonate-substituted hydroxyapatite ceramics for bone regeneration. Biomed Mater. 2017;12(3):035008. [29] GOMEZ-CEREZO N, CASARRUBIOS L, MORALES I, et al. Effects of a mesoporous bioactive glass on osteoblasts, osteoclasts and macrophages. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;528:309-320. [30] HE XT, WU RX, XU XY, et al. Macrophage involvement affects matrix stiffness-related influences on cell osteogenesis under three-dimensional culture conditions. Acta Biomater. 2018;71:132-147. [31] GIANNOBILE WV, BERGLUNDH T, AL-NAWAS B, et al. Biological factors involved in alveolar bone regeneration: consensus report of working group 1 of the 15(th) european workshop on periodontology on bone regeneration. J Clin Periodontol. 2019;46 Suppl 21:6-11. [32] FUJIHARA C, KANAI Y, MASUMOTO R, et al. Fibroblast growth factor-2 inhibits CD40-mediated periodontal inflammation. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234(5):7149-7160. [33] HE XT, LI X, XIA Y, et al. Building capacity for macrophage modulation and stem cell recruitment in high-stiffness hydrogels for complex periodontal regeneration: experimental studies in vitro and in rats. Acta Biomater. 2019;88:162-180. [34] PACELLI S, BASU S, WHITLOW J, et al. Strategies to develop endogenous stem cell-recruiting bioactive materials for tissue repair and regeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;120:50-70. [35] SEHGAL RR, CARVALHO E, BANERJEE R. Mechanically stiff, zinc cross-linked nanocomposite scaffolds with improved osteostimulation and antibacterial properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(22): 13735-13747. [36] URIBE P, JOHANSSON A, JUGDAOHSINGH R, et al. Soluble silica stimulates osteogenic differentiation and gap junction communication in human dental follicle cells. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):9923. [37] LIU X, HE X, JIN D, et al. A biodegradable multifunctional nanofibrous membrane for periodontal tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2020; 108:207-222. [38] VON BULOW V, RINK L, HAASE H. Zinc-mediated inhibition of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity and expression suppresses TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta production in monocytes by elevation of guanosine 3’,5’-cyclic monophosphate. J Immunol. 2005;175(7):4697-4705. [39] DE A. Wnt/Ca2+ signaling pathway: a brief overview. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2011;43(10):745-756. [40] LOURENCO AH, TORRES AL, VASCONCELOS DP, et al. Osteogenic, anti-osteoclastogenic and immunomodulatory properties of a strontium-releasing hybrid scaffold for bone repair. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;99:1289-1303. [41] ZOHAR R, NEMCOVSKY CE, KEBUDI E, et al. Tetracycline impregnation delays collagen membrane degradation in vivo. J Periodontol. 2004; 75(8):1096-1101. [42] MEDIERO A, WILDER T, REDDY VS, et al. Ticagrelor regulates osteoblast and osteoclast function and promotes bone formation in vivo via an adenosine-dependent mechanism. FASEB J. 2016;30(11):3887-3900. [43] WANG B, SHAO J, FU J, et al. Topical host-modulating therapy for periodontal regeneration:a systematic review and meta-analysis. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2019;25(6):526-543. [44] EL KHOLY K, FREIRE M, CHEN T, et al. Resolvin E1 promotes bone preservation under inflammatory conditions. Front Immunol. 2018;9: 1300. [45] KOWAL TJ, HAHN NC, EIDER S, et al. New bioactive glass scaffolds with exceptional qualities for bone tissue regeneration: response of osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Biomed Mater. 2018;13(2):025005. [46] JIA X, MIRON RJ, YIN C, et al. HnRNPL inhibits the osteogenic differentiation of PDLCs stimulated by SrCl2 through repressing Setd2. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(4):2667-2677. [47] KANG W, LIANG Q, DU L, et al. Sequential application of bFGF and BMP-2 facilitates osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells. J Periodontal Res. 2019;54(4):424-434. [48] SHAH AT, ZAHID S, IKRAM F, et al. Tri-layered functionally graded membrane for potential application in periodontal regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;103:109812. [49] SOWMYA S, MONY U, JAYACHANDRAN P, et al. Tri-Layered Nanocomposite Hydrogel Scaffold for the Concurrent Regeneration of Cementum, Periodontal Ligament, and Alveolar Bone. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201601251. [50] VARONI EM, VIJAYAKUMAR S, CANCIANI E, et al. Chitosan-based trilayer scaffold for multitissue periodontal regeneration. J Dent Res. 2018;97(3):303-311. [51] 田卫东. 基于干细胞的牙功能组织模块用于牙及其支持组织再生[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2017,52(10):588-593. [52] PARK C, KIM K, LEE Y, et al. 3-D printing fabrication for periodontal complex regeneration; bone-pdl-cementum regeneration platform developments. Tissue Eng Pt A. 2015;21:S341-S342. [53] RASPERINI G, PILIPCHUK SP, FLANAGAN CL, et al. 3D-printed bioresorbable scaffold for periodontal repair. J Dent Res. 2015;94(9 Suppl):153S-157S. [54] DING T, LI J, ZHANG X, et al. Super-assembled core/shell fibrous frameworks with dual growth factors for in situ cementum-ligament-bone complex regeneration. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(9):2459-2471. [55] GAIHRE B, JAYASURIYA AC. Comparative investigation of porous nano-hydroxyapaptite/chitosan, nano-zirconia/chitosan and novel nano-calcium zirconate/chitosan composite scaffolds for their potential applications in bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;91:330-339. [56] LAUSCH AJ, CHONG LC, ULUDAG H, et al. Multiphasic collagen scaffolds for engineered tissue interfaces. Adv Funct Mater. 2018. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201804730. [57] GUNATILLAKE PA, ADHIKARI R. Biodegradable synthetic polymers for tissue engineering. Eur Cell Mater. 2003;5:1-16. [58] SAWADKAR P, MOHANAKRISHNAN J, RAJASEKAR P, et al. A Synergistic relationship between polycaprolactone and natural polymers enhances the physical properties and biological activity of scaffolds. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(12):13587-13597. [59] LIAN M, SUN B, QIAO Z, et al. Bi-layered electrospun nanofibrous membrane with osteogenic and antibacterial properties for guided bone regeneration. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;176:219-229. [60] GURBUZ S, DEMIRTAS TT, YUKSEL E, et al. Multi-layered functional membranes for periodontal regeneration: preparation and characterization. Mater Lett. 2016;178:256-259. [61] HU Y, CAI K, LUO Z, et al. Layer-by-layer assembly of beta-estradiol loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles on titanium substrates and its implication for bone homeostasis. Adv Mater. 2010;22(37):4146-4150. |
| [1] | LIU Danni, SUN Guanghua, ZHOU Guijuan, LIU Hongya, ZHOU Jun, TAN Jinqu, HUANG Xiarong, PENG Ting, FENG Wei-bin, LUO Fu. Effect of electroacupuncture on apoptosis of neurons in cerebral cortex of rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury at "Shuigou" and "Baihui" points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [2] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [3] | Jiang Huanchang, Zhang Zhaofei, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing, Yang Xiaodong, Liu Zhixiang. Comparison of advantages between unilateral multidirectional curved and straight vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [4] | Xue Yadong, Zhou Xinshe, Pei Lijia, Meng Fanyu, Li Jian, Wang Jinzi . Reconstruction of Paprosky III type acetabular defect by autogenous iliac bone block combined with titanium plate: providing a strong initial fixation for the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [5] | Li Wei, Zhu Hanmin, Wang Xin, Gao Xue, Cui Jing, Liu Yuxin, Huang Shuming. Effect of Zuogui Wan on bone morphogenetic protein 2 signaling pathway in ovariectomized osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1173-1179. |
| [6] | Xiang Xinjian, Liu Fang, Wu Liangliang, Jia Daping, Tao Yue, Zhao Zhengnan, Zhao Yu. High-dose vitamin C promotes the survival of autologous fat transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1242-1246. |
| [7] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [8] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [9] | Wu Bingshuang, Wang Zhi, Tang Yi, Tang Xiaoyu, Li Qi. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: from enthesis to tendon-to-bone healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1293-1298. |
| [10] | Hu Wei, Xie Xingqi, Tu Guanjun. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 992-998. |
| [11] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [12] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [13] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [14] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [15] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||