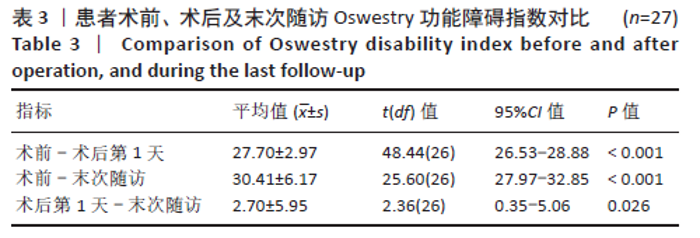
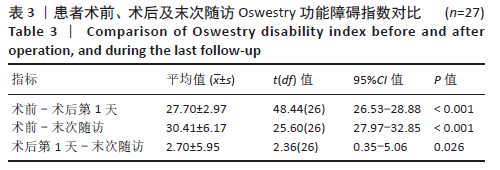
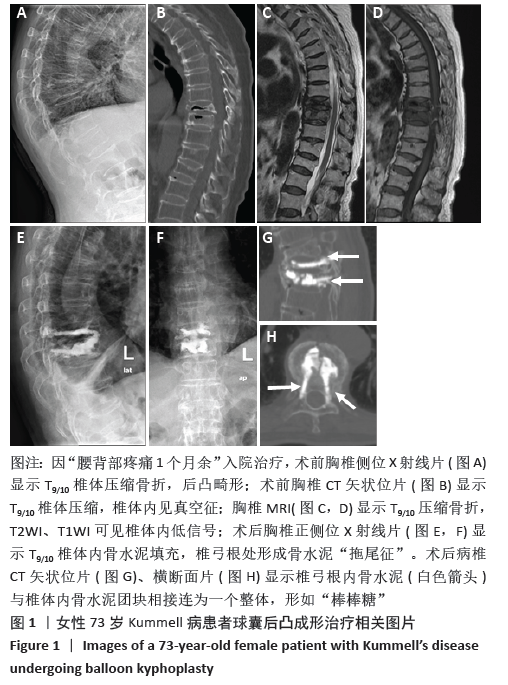
[1] YOUNG WF, BROWN D, KENDLER A, et al. Delayed post-traumatic osteonecrosis of a vertebral body (Kummell’s disease). Acta Orthop Belg. 2002;68(1):13-19.
[2] NICKELL LT, SCHUCANY WG, OPATOWSKY MJ. Kummell disease. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2013;26(3):300-301.
[3] LEE SH, KIM ES, EOH W. Cement augmented anterior reconstruction with short posterior instrumentation: a less invasive surgical option for Kummell disease with cord compression. J Clin Neurosci. 2011;18(4):509-514.
[4] 杨惠林,王根林,牛国旗,等. 骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折不愈合的诊断与治疗[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2007,27(9):682-686.
[5] WANG HS, KIM HS, JU CI, et al. Delayed bone cement displacement following balloon kyphoplasty. Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008;43(4):212-214.
[6] VAN DER SCHAAF I, FRANSEN H. Percutaneous vertebroplasty as treatment for Kummell’s disease. JBR-BTR. 2009;92(2):83-85.
[7] LI KC, WONG TU, KUNG FC, et al. Staging of Kümmell’s disease. J Musculoskelet Res. 2004;8(1):43-55.
[8] YEOM JS, KIM WJ, CHOY WS, et al. Leakage of cement in percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic compression fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85(1):83-89.
[9] YANG H, LIU H, WANG S, et al. Review of Percutaneous Kyphoplasty in China. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016; 41 Suppl 19:B52-B58.
[10] PARK JW, PARK JH, JEON HJ, et al. Kummell’s Disease Treated with Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Minimum 1 Year Follow-Up. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2017;13(2): 119-123.
[11] ZHANG J, FAN Y, HE X, et al. Is percutaneous kyphoplasty the better choice for minimally invasive treatment of neurologically intact osteoporotic Kummell’s disease? A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures. Int Orthop. 2018; 42(6):1321-1326.
[12] KONG LD, WANG P, WANG LF, et al. Comparison of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intravertebral clefts. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24 Suppl 1:S201-208.
[13] KRAUSS M, HIRSCHFELDER H, TOMANDL B, et al. Kyphosis reduction and the rate of cement leaks after vertebroplasty of intravertebral clefts. Eur Radiol. 2006;16(5):1015-1021.
[14] OH JS, DOH JW, SHIM JJ, et al. The Effectiveness of Gelfoam Technique before Percutaneous Vertebroplasy: Is It Helpful for Prevention of Cement Leakage? A Prospective Randomized Control Study. Korean J Spine. 2016;13(2):63-66.
[15] SUN HB, JING XS, LIU YZ, et al. The Optimal Volume Fraction in Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Evaluated by Pain Relief, Cement Dispersion, and Cement Leakage: A Prospective Cohort Study of 130 Patients with Painful Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture in the Thoracolumbar Vertebra. World Neurosurg. 2018; 114:e677-e688.
[16] HOPPE S, ELFIKY T, KEEL MJ, et al. Lavage prior to vertebral augmentation reduces the risk for cement leakage. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(11):3463-3469.
[17] HONG SJ, LEE S, YOON JS, et al. Analysis of intradiscal cement leakage during percutaneous vertebroplasty: multivariate study of risk factors emphasizing preoperative MR findings. J Neuroradiol. 2014;41(3):195-201.
[18] 唐永超,莫国业,张顺聪,等. 经皮椎体强化术治疗无神经症状Kümmell病的中长期疗效[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(1):38-43.
[19] OHBA T, EBATA S, CLINTON D, et al. Instability of treated vertebrae after balloon kyphoplasty causing paraparesis in osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a report of two cases. Eur Spine J. 2013;22 Suppl 3:S341-345.
[20] HUANG KY, YAN JJ, LIN RM. Histopathologic Findings of Retrieved Specimens of Vertebroplasty with Polymethylmethacrylate Cement. Spine. 2005;30: E585-588.
[21] TSAI TT, CHEN WJ, LAI PL, et al. Polymethylmethacrylate cement dislodgment following percutaneous vertebroplasty: a case report. Spine. 2003;28(22):E457-460.
[22] 李鹏,高利峰,胡军华,等. 三柱强化经皮椎体成形术治疗Ⅰ、Ⅱ期Kummell病的疗效[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2020,23(3):322-324.
[23] 邓立明,黄凯,史建刚,等. 双侧穿刺骨水泥锚定椎体成形术治疗Kummell病临床观察[J]. 山东医药,2018,58(44):64-66.
[24] 张在青,陈波. 单侧穿刺骨水泥锚定椎体后凸成形术治疗Kummell病的疗效探讨[J]. 中国临床新医学,2020,13(5):512-515.
[25] 魏桂财,郑忠,李超雄,等. 骨水泥椎弓根附近锚定技术在Kummell病椎体成形术治疗的应用体会. 2019楚天骨科高峰论坛暨第二十六届中国中西医结合骨伤科学术年会论文集,2019:434-435.
[26] 杜心如,赵玲秀,张一模,等. 胸腰椎椎弓根内径的测量及其临床意义[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2001,11(3):162-164.
|