1.1 设计 复合水凝胶的制备及相关表征,体外细胞学实验及体内实验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2023年6月至2024年6月在青岛大学附属医院完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 主要材料 小鼠成纤维细胞L929(中国科学院上海生命科学研究院细胞资源中心);A型明胶、CCK-8 试剂盒(索莱宝,中国);甲基丙烯酸酐(麦克林,中国);金黄色葡萄球菌(ATCC,ATCC43300);大肠杆菌(ATCC,ATCC35218);DMEM培养基、PBS、胰酶、胎牛血清(Gibco,美国);低速离心机(湘仪,中国);苯基(2,4,6-三甲基苯甲酰基)磷酸锂盐(引昌,上海);Ⅱ型胶原酶(Phygene,中国);超净工作台(东联哈尔,中国);超声波振荡器(昆山超声仪器,中国);倒置荧光显微镜(Nikon,日本);全波长酶标仪(BioTek,美国);紫外光源(405 nm,天斗照明,中国);数显恒温水浴锅(三洋,日本);小动物麻醉机(R500IE,瑞沃德,中国);冷冻干燥机(叶拓,上海);核磁共振谱仪(Bruker Avance,400 MHz,德国);扫描电子显微镜(Hitachi,日本);分光光度计(Thermo,美国)。
1.3.2 实验动物 雌性SD大鼠14只,8 周龄,体质量250-280 g,购自北京斯贝福实验动物有限公司,许可证号:SCXK (京)2019-0010。动物购进后在青岛大学附属医院动物实验中心常规适应性饲养2周,温度(22±2) ℃、湿度40%-60%,12 h光/暗循环,自由进食。所有动物实验均符合《青岛大学动物实验伦理学评价》和《国家机构实验动物护理和使用卫生指南》的规定,动物实验已通过青岛大学附属医院实验动物福利伦理委员会批准(批件号:AHQU-MAL2023032)。
1.4 方法
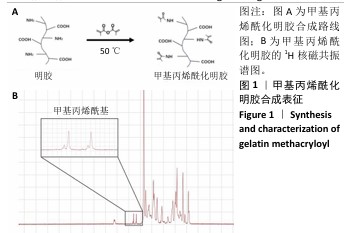
1.4.1 GelMA的合成 将5 g A型明胶溶解在50 mL PBS中,制备100 g/L的凝胶前体溶液。向凝胶前体溶液中逐滴添加8 mL甲基丙烯酸酐,避光条件下于50 ℃水浴中加热1 h。将凝胶前体溶液放入分子质量截留为3 500 Da的透析袋中,透析液使用去离子水,每24 h更换一次水以去除未反应的单体,透析2周。经过冷冻干燥(-40 ℃,48 h)获得GelMA固体。
1.4.2 GelMA的表征 将制干燥的GelMA固体样品溶解在适量的D2O中,转移至核磁共振谱仪样品管中,启动测量程序,开始收集光谱数据。该程序将自动扫描和积分信号,以生成质子光谱。
1.4.3 i-PRF制备 取5只SD大鼠,吸入异氟烷麻醉后取眶后静脉血5 mL,立即将含有静脉血的离心管放入台式离心机中,室温下700 r/min离心3 min,离心后整个血液分离为2层,所需的i-PRF位于上层的黄色液体中,小心地将离心管从离心机中取出,使用1 mL注射器小心提取上层的黄色液体,并转移至无菌离心管中。
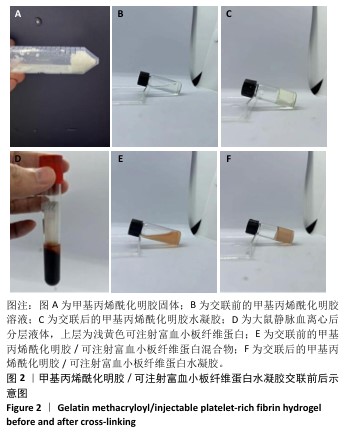
1.4.4 水凝胶的合成 将干燥的GelMA溶解在无菌PBS中,制备50 g/L GelMA溶液;加入光引发剂苯基(2,4,6-三甲基苯甲酰基)磷酸锂盐后,在室温下搅拌10 min以充分混合。将所得溶液注入直径为10 mm、高度为3 mm的圆柱形聚四氟乙烯模具中,使用405 nm紫外光源,强度为
10 mW/cm²,照射并光聚合30 s,形成GelMA水凝胶。同样制备50 g/L GelMA溶液,向溶液中加入光引发剂苯基(2,4,6-三甲基苯甲酰基)磷酸锂盐,将等体积的i-PRF混入GelMA溶液中,使用405 nm紫外光源,强度为10 mW/cm²,照射并光聚合30 s,形成GelMA/i-PRF水凝胶。
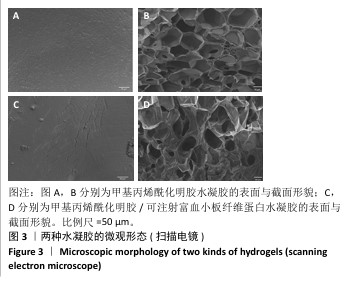
1.4.5 水凝胶的形态结构表征 将GelMA、GelMA/i-PRF水凝胶材料修剪至适当大小,约2 mm×2 mm,冷冻干燥(-40 ℃,48 h)后放置于样品台上,表面镀金,使用扫描电镜观察表面和横截面形态结构,通过Image J(NIH,美国)软件对孔径进行定量测量。
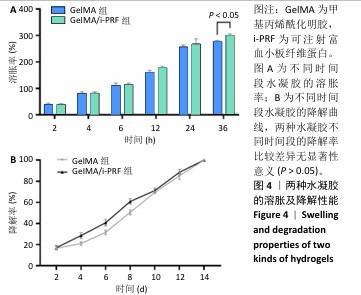
1.4.6 水凝胶的溶胀特性测试 将GelMA、GelMA/i-PRF水凝胶制备为直径10 mm、高度3 mm的圆柱形,采用质量法检测水凝胶的膨胀特性。使用分析天平称量样品的初始质量(m0)。将水凝胶样品浸入37 ℃的PBS中,确保水位覆盖水凝胶顶部。在预定的时间点(2,4,6,12,24,36 h)取出样品,用滤纸吸去表面水分,记录质量(mn)。实验重复3次。
溶胀率=(mn-m0)/m0×100%。
1.4.7 水凝胶的体外降解性能测试 将GelMA、GelMA/i-PRF水凝胶制备为直径10 mm、高度3 mm的圆柱形,采用质量法检测水凝胶的降解性能。将水凝胶样品浸入37 ℃的PBS中持续24 h以达到膨胀平衡,记录水凝胶的初始质量(m0)。将水凝胶样品放入预先准备好的Ⅱ型胶原酶(2 U/mL)-PBS中,在预定的时间点(2,4,6,8,10,12,14 d)取出水凝胶,用不含胶原酶的PBS冲洗,吸干水分,称质量(mn)。实验重复3次。
降解率 =(mn-m0)/m0×100%
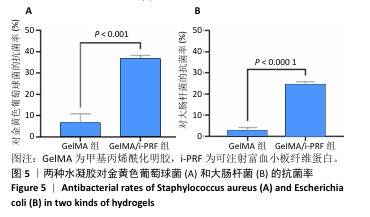
1.4.8 水凝胶的抗菌实验 金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌在37 ℃下于赖氨酸培养基(LB)中培养2 h,菌液浓度为4.0×10⁴ CFU/mL。将200 μL金黄色葡萄球菌(或大肠杆菌)悬液分别涂布于GelMA、GelMA/i-PRF水凝胶表面,在37 ℃下孵育10 h,以单独培养的细菌悬液为对照组,无水凝胶无菌液孔为空白组。使用分光光度计在600 nm波长处测量吸光度(A)值,计算菌率。
抗菌率(%)=(对照组A值-样品组A值)/(对照组A值-空白组A值)×100%。
1.4.9 水凝胶对L929细胞增殖活性与迁移能力的影响
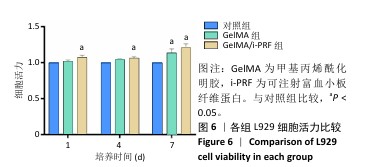
实验分组:将50 μL的GelMA、GelMA/i-PRF凝胶前体溶液分别加入96孔板的每个孔底部,使用405 nm紫外光源对每种溶液进行光凝胶化。将5代以内的L929细胞分别接种到两种水凝胶表面,细胞密度为5×103/孔,以单独培养的细胞为对照,置于37 ℃、体积分数5%CO2培养箱内培养。每个样品设置3组平行对照组。
CCK-8实验:培养第1,4,7天,取出96孔板,每孔中添加10 μL CCK-8溶液和90 μL DMEM培养基,置于37 ℃的避光孵育1 h,在450 nm波长处测量各组A值。
细胞活力(%)=(样品组A值-空白组A值)/(对照组A值-空白组A值)×100%。空白组为不含细胞仅含培养基的孔。
活/死细胞染色:培养第4天将板从培养箱中取出,进行活/死细胞染色,置于倒置荧光显微镜下观察并拍照。使用Image J软件分析绿色荧光与红色荧光数量。
细胞活力=绿色荧光数量/红色荧光数量
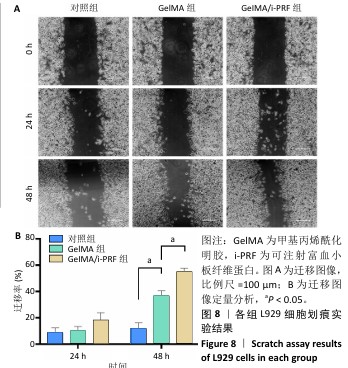
细胞划痕实验:将5代以内L929细胞分别接种到涂有GelMA、GelMA/i-PRF水凝胶的6孔板中,细胞密度为5×105/孔,置于37 ℃、体积分数5%CO2培养箱内孵育过夜。待细胞贴壁并达到汇合后,用PBS轻轻清洗,使用一根10 μL的移液管枪头在每个孔中垂直划出划痕,模拟细胞迁移过程,然后在孔中添加无血清DMEM培养基。在0,24,48 h,使用倒置显微镜观察并拍照,利用Image J软件分析细胞迁移率。
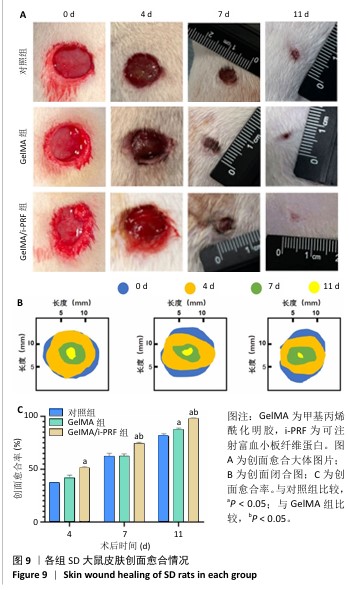
1.4.10 水凝胶修复大鼠皮肤创面实验 大鼠在动物设施中适应性喂养一两周。取9只大鼠,吸入异氟烷麻醉后对背部剃毛和消毒,使用眼科剪刀在大鼠背部创建直径约10 mm的全层皮肤创面,随机分3组干预,每组3只:对照组创面注射PBS(与水凝胶体积相同),另2组创面分别注射GelMA水凝胶、GelMA/i-PRF水凝胶,水凝胶为直径10 mm、高3 mm的圆柱体,使用标准纱布覆盖水凝胶并用医用胶带固定纱布。术后大鼠单笼饲养,不使用抗生素或其他药物。术后第0,4,7,11天拍摄创面区域的照片并进行记录,使用Image J软件计算创面愈合率。
创面愈合率=(第0天创面面积-第n天创面面积)/第0天创面面积×100%
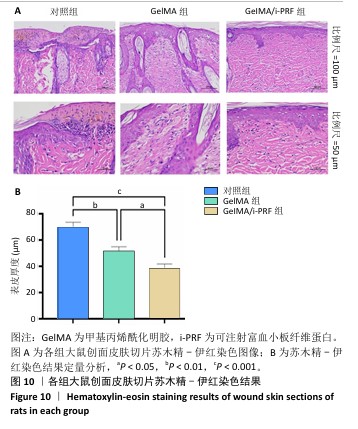
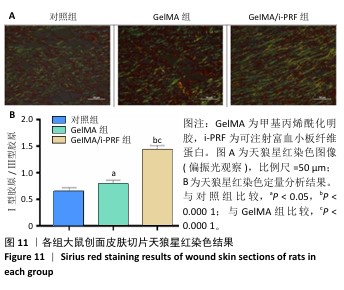
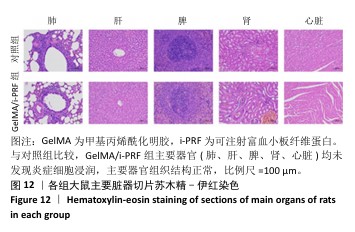
组织病理学染色:术后11 d,麻醉状态下处死大鼠并收集创伤区域及其周围约10 mm的组织,使用体积分数10%中性甲醛溶液固定24 h,二甲苯透明化处后嵌入石蜡中,使用微切片机将组织切成5 μm厚的切片,分别进行苏木精-伊红染色和天狼星红染色。在苏木精-伊红染色图像中,使用Image J软件分析表皮厚度。在天狼星红染色图像中,使用Image J软件分析红色荧光强度(Ⅰ型胶原)与绿色荧光强度(Ⅲ型胶原),确定新生皮肤组织此成熟度。新生皮肤组织的成熟度为红色荧光强度/绿色荧光强度。取出各组大鼠的心脏、肝脏、脾脏、肺和肾脏,进行苏木精-伊红染色。
1.5 主要观察指标 两种水凝胶的理化性质、抗菌性能、细胞相容性以及促进大鼠皮肤缺损愈合的作用。
1.6 统计学分析 结果数据以x±s呈现,数据分析使用Origin 8.0软件(Origin Lab,Los Angeles,CA,USA)。通过单因素方差分析(ANOVA)评估数据之间的统计差异,并进行Tukey HSD检验。P < 0.05认为差异有显著性意义。该文统计学方法已经青岛大学附属医院生物统计学专家审核。