中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (2): 489-498.doi: 10.12307/2025.892
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
活性微生态水凝胶促进皮肤创面的愈合
黄新旭,张 鑫,王 剑
- 口腔疾病研究国家重点实验室,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,四川大学华西口腔医院修复科,四川省成都市 610041
-
收稿日期:2024-08-28接受日期:2024-10-26出版日期:2026-01-18发布日期:2025-07-02 -
通讯作者:王剑,博士,教授,口腔疾病研究国家重点实验室,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,四川大学华西口腔医院修复科,四川省成都市 610041 -
作者简介:黄新旭,女,2001年生,四川省泸州市人,汉族,四川大学华西口腔医学院在读八年制博士,主要从事生物材料基础科学研究。 -
基金资助:四川省科技计划项目(2023NSFSC2000),项目名称:基于贻贝仿生双层GTR膜的制备及其促进软硬组织再生的应用和基础研究,项目负责人:王剑;国家自然科学基金项目(82271034),项目名称:兼具优良空间维持力和湿粘接性的仿生双层GTR膜的构建及其促进软硬组织再生的机制研究,项目负责人:王剑
Living microecological hydrogels promote skin wound healing
Huang Xinxu, Zhang Xin, Wang Jian
- State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-08-28Accepted:2024-10-26Online:2026-01-18Published:2025-07-02 -
Contact:Huang Xinxu, Doctoral candidate, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Wang Jian, MD, Professor, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Plan Project, No. 2023NSFSC2000 (to WJ); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82271034 (to WJ)
摘要:
文题释义:
活性微生态水凝胶:是指负载了活性生物的水凝胶,活性生物在水凝胶中形成微生态,进行迁移、增殖、分泌、释放等生物行为。水凝胶为活性生物提供良好的生存环境,保证生物在复杂环境下的生理活性。活性生物通过各种生物行为赋予水凝胶生物特性,使其能够响应复杂的外界环境及环境变化,扩大了水凝胶的应用场景。
细胞外基质:是由细胞分泌并释放的生物大分子物质组成的纤维状物质,构成细胞外环境的特殊结构,是细胞增殖、迁移、代谢、功能和分化的基础。细胞外基质既可以作为一种独立的结构为细胞生存活动提供适宜的场所,也可以作为细胞外活动的调节器,参与细胞外信号传导和活性物质的调节转运等。
背景:活性微生态水凝胶是创面敷料研究领域的一大热点,受到广泛关注。
目的:概述活性微生态水凝胶的基本特点与优势,综述近年来各种活性微生态水凝胶在皮肤创面修复中的应用进展。
方法:以“cell,probiotics,phage,chlorella,algae,living microecological,hydrogel,skin,wound healing,wound repair”为英文检索词,以“细胞,益生菌,噬菌体,小球藻,微藻,活性微生态,水凝胶,皮肤,伤口愈合,伤口修复”为中文检索词,在Web of Science、PubMed、中国知网及万方数据库进行文献检索,文献检索时限为各数据库建库至2024年。按照排除和纳入标准筛选纳入文献,最终纳入108篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:活性微生态水凝胶具有良好的生物相容性,能为负载的生物提供适宜的生存环境,并在活性生物与皮肤创面之间发挥屏障作用,避免潜在威胁。相较于传统伤口敷料,活性微生态水凝胶的作用是可持续可更新的,生物调节能使创面处微环境保持相对稳定的状态,可以长时间为创面愈合提供适宜条件,减少频繁更换敷料给皮肤创面造成的额外创伤。相较于直接使用活性生物促进皮肤创面愈合,活性微生态水凝胶能提高生物的存活率,保障其发挥生物调节作用。活性微生态水凝胶主要是通过调控创面愈合进程中“炎症”和“增殖”这两阶段来促进皮肤创面愈合。现有的活性微生态水凝胶主要负载细胞、益生菌、微藻、噬菌体这几类生物,赋予了水凝胶不同的生物特性,使其通过释放创面愈合所需物质或者改善创面环境等促进皮肤创面愈合,具有较大的应用潜力。为进一步扩大活性微生态水凝胶的实际临床运用,未来还需要进一步深入把控水凝胶中活性生物的生物安全风险,避免潜在的生物威胁,并需要研究更能适应人体皮肤创面复杂变化且能负载活性生物的水凝胶基质。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7368-5694(黄新旭);https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5137-0330(王剑)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
黄新旭, 张 鑫, 王 剑. 活性微生态水凝胶促进皮肤创面的愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 489-498.
Huang Xinxu, Zhang Xin, Wang Jian. Living microecological hydrogels promote skin wound healing[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 489-498.
2.1.1 活性微生态水凝胶的基本特点 活性微生态水凝胶需要为负载在其中的活性生物提供适宜的生存环境,所以应该具有良好的生物相容性,并允许营养物质和氧气等通过[16-17]。在负载活性生物时,为了避免生物在凝胶化过程中受损,水凝胶凝胶化所需条件不应对生物的生存和生理活动造成不良影响。所以,活性微生态水凝胶通常选用天然聚合物作为凝胶基础成分,包括海藻酸盐、壳聚糖、透明质酸、纤维素、明胶及其改性产物等[18-19]。一方面,天然聚合物本身相容性好,一般不会影响生物活性[20];另一方面,天然聚合物水凝胶的凝胶化过程大多数是简单、快速、易行的[21]。而许多人工合成聚合物来源的水凝胶(如聚丙烯酰胺、聚乙烯醇、聚丙烯酸水凝胶等),在未交联时其前驱液毒性较大,生物相容性差,活性生物难以在前驱液中生存,并且这些水凝胶的凝胶化过程通常需要较高温度和较长时间,也会导致生物活性的降低或丧失[22-23]。虽然这类水凝胶在交联后的生物相容性有所提高,允许在其表面接种活性生物,但接种于水凝胶表面的生物往往仅分布在水凝胶表层,分布不均匀[24]。以上原因导致人工合成聚合物来源的水凝胶体系难以稳定负载活性生物,所以,这类水凝胶较少用于活性微生态水凝胶领域。应用于皮肤创面修复时,活性微生态水凝胶还应形成物理屏障[25],既要消除复杂创面环境对负载生物活性的不良影响,又要避免负载生物溢出引起机体的免疫反应和形成潜在的威胁[26-27],最终才能利用其活性成分持续促进皮肤创面愈合。
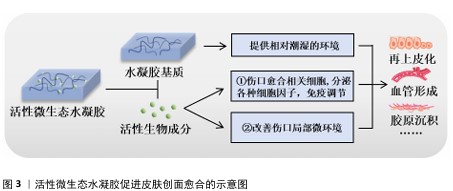
2.1.2 活性微生态水凝胶在皮肤创面愈合中发挥的作用及优势 皮肤创面愈合是一个非常复杂的生物过程,通常由止血、炎症、增殖、重塑4个阶段组成,这4个阶段的顺利完成是创面愈合的必要条件[28]。活性微生态水凝胶主要通过调控“炎症”和“增殖”这两阶段来促进皮肤创面愈合[29],其发挥的具体作用见图3。
水凝胶作为活性生物的载体,其优秀的保水能力能提供相对潮湿的环境,软化创面,促进生长因子、表皮细胞因子和抗炎细胞因子等因子的迁移,从而加速皮肤创面再上皮化的进程[30-31]。根据活性微生态水凝胶负载的生物种类不同,其促进皮肤创面愈合的作用机制又可大致分为2种:一是直接负载创面愈合相关细胞,如人皮肤成纤维细胞、人脐静脉内皮细胞、脂肪来源干细胞、间充质干细胞等[32-35],它们能够持续分泌创面愈合所需的生长因子、旁分泌因子,如血管内皮生长因子 A、成纤维细胞生长因子2、肝细胞生长因子等[36-38],部分研究显示细胞因子主要通过激活Janus激酶/信号转导和转录激活因子通路,并通过诱导细胞的增殖、分化和生长来促进血管形成和再上皮化等,最终促进创面愈合[39-40];二是改善创面局部微环境,如改善缺氧、感染、高糖等情况,使巨噬细胞转变为抗炎的M2型,减轻炎症反应,促进细胞增殖、血管形成、胶原沉积等过程,最终促进创面愈合[41-42]。
活性微生态水凝胶因其生物特性具有许多独特优势[43-44]。由不同原因造成的皮肤创面愈合周期也不同,其中由感染、糖尿病、烧伤、缺血等引起的慢性皮肤创面,需要2周甚至更长时间才能愈合[45-46]。与其他水凝胶敷料相比,活性微生态水凝胶的优势在于生物增殖、迁移、分泌、释放等行为是可持续、可更新的,这样的生物调节能使创面处的微环境保持相对稳定的状态,可以长时间为皮肤创面愈合提供适宜条件,减少频繁更换敷料给创面造成的额外创伤[47-48]。而与直接应用活性生物促进皮肤创面愈合相比,水凝胶的应用能维持活性生物稳定的生物行为,解决了由于创面处缺氧、细菌感染、活性氧水平高等不利因素导致生物存活率低的问题[49-50]。水凝胶还可以保护活性生物不被机体免疫系统破坏,同时又防止其逃逸到皮肤创面环境中引起潜在的威胁[51]。
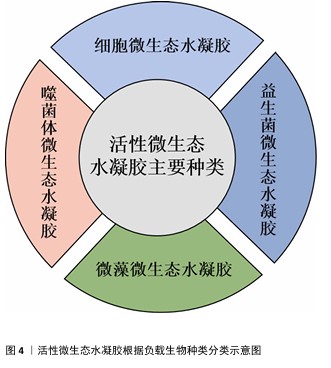
2.2 活性微生态水凝胶在皮肤创面修复中的应用进展 活性微生态水凝胶中的活性生物是此类敷料发挥作用的核心,也是研究的重点,细胞、益生菌、藻类、噬菌体是现有研究中应用较多的活性生物成分。该文按照生物种类对活性微生态水凝胶进行分类,见图4,详细介绍其在皮肤创面修复中的应用进展。
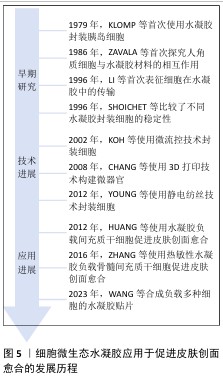
2.2.1 细胞微生态水凝胶 细胞疗法是一种前景广阔的新型治疗方法[52]。许多细胞能持续分泌生长因子,例如胰岛素样生长因子、肝细胞生长因子、转化生长因子β1和血管内皮生长因子等,促进血运重建和再上皮化等[53-54],同时这些细胞还参与干细胞生存微环境的形成,诱导机体内源性干细胞分化,有助于将创面环境从促炎环境转变为促再生环境[55],因此,细胞疗法被广泛应用于皮肤创面的治疗[56-57]。但由于不良的创面环境以及机体对外源细胞可能产生的免疫反应,直接递送的细胞活性和数量会在短时间内大幅度下降,治疗效率低下[58-59]。将细胞负载于能模拟细胞外基质的水凝胶中,是解决细胞存活问题以及潜在免疫排斥的有效方法[60-61]。利用水凝胶负载细胞促进皮肤创面愈合已有很长的发展历程,见图5。
水凝胶能为所负载的细胞提供良好的生存环境[62]。WU等[63]采用微流控水凝胶技术将脂肪来源干细胞封装到甲基丙烯酰化透明质酸与纤连蛋白分子链偶联合成的水凝胶微球中,微载体具有较大的表面积,能使干细胞在其中充分生长、增殖和分化,同时与单纯用甲基丙烯酰化透明质酸负载脂肪来源干细胞相比,纤连蛋白-甲基丙烯酰化透明质酸微载体水凝胶添加了细胞外基质中重要的功能蛋白,使细胞能更好地黏附在水凝胶的网络结构上,进而稳定地发挥生物功能。在糖尿病小鼠皮肤创面愈合实验中,与直接注射脂肪来源干细胞组相比,纤连蛋白-甲基丙烯酰化透明质酸A@脂肪来源干细胞组显示出更快的皮肤组织再生速率,表明纤连蛋白-甲基丙烯酰化透明质酸@脂肪来源干细胞可以通过模拟干细胞的生存微环境增强血管生成和胶原沉积,促进组织再生,从而加速糖尿病皮肤创面的愈合。
水凝胶的特殊结构能对负载细胞的生物功能进行主动调节。ZHENG等[64]将间充质干细胞封装于丝素蛋白纳米纤维水凝胶微粒中,丝素蛋白纳米纤维在该细胞微生态水凝胶中定向排列,能主动调节干细胞的旁分泌并模拟干细胞的生存微环境,使干细胞在治疗部位长期发挥作用;在动物体内实验中,该水凝胶体系通过调节免疫行为和血管化进程,促进毛囊再生,实现了皮肤的无瘢痕修复。细胞微生态水凝胶还能分层模拟皮肤结构和功能[65]。WANG等[66]将人皮肤成纤维细胞和人脐静脉内皮细胞细胞片与甲基丙烯酰化明胶、海藻酸钠仿生水凝胶贴片结合形成细胞片水凝胶CSH,CSH中的人皮肤成纤维细胞层模拟皮肤表皮,人脐静脉内皮细胞层模拟皮肤真皮,细胞在水凝胶内保持了优异的增殖活性和迁移能力,同时还保持了良好的细胞间连接,解决了细胞片在应用中易卷曲、折叠的问题;此外,CSH水凝胶被植入到全层皮肤缺损模型中,第2天创面愈合率达到(60.00±6.26)%,第10天CSH组创面处具有最厚的表皮层,其肉芽组织和真皮层包含最多的毛囊和新生血管,表明CSH水凝胶极好地模拟了表皮和真皮的结构和功能,为机体内源性细胞向内生长提供了三维支架结构和仿生微环境。文章将细胞微生态水凝胶在皮肤创面修复中的应用进展研究总结于表1。
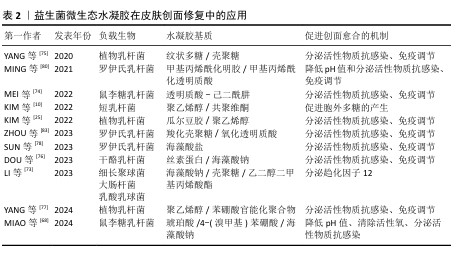
2.2.2 益生菌微生态水凝胶 益生菌是指对宿主有益的微生物,主要包括乳杆菌属和双歧杆菌属[67-68],这些益生菌能够通过分泌抗菌物质或竞争生存资源对抗病原体[69],能用于治疗感染皮肤创面[70-71]。与抗生素相比,益生菌对耐药菌(如铜绿假单胞菌、耐药金黄色葡萄球菌)有更好的治疗效果[72]。另外,益生菌通常还能引发创面处的免疫调节,促进抗炎微环境的形成;一些经过基因编辑的工程化益生菌还可分泌细胞因子等促进创面的血运重建和再上皮化等[73]。目前,乳杆菌属益生菌在皮肤创面修复领域应用最多[74-77]。
益生菌在直接用于感染皮肤创面时会遭受机体免疫系统的攻击,创面处的理化环境也对益生菌的生存提出较大的挑战[78-79]。为了解决这些问题,MING等[80]将罗伊氏乳杆菌封装于甲基丙烯酰化透明质酸中形成含菌水凝胶微球,再将微球封装于甲基丙烯酰化透明质酸水凝胶中形成LRHA水凝胶,结果显示罗伊氏乳杆菌在LRHA水凝胶中具有较好的增殖活性,解决了益生菌在免疫系统攻击下和在不良创面环境中难以生存的问题,同时LRHA水凝胶对多种细菌表现出优异的抗菌性能,其抗菌能力与罗伊氏乳杆菌分泌的乳酸和氘蛋白有关;含菌微球浸出液培养结果显示,含菌水凝胶微球能有效防止细菌的外溢,避免了潜在的感染风险;在金黄色葡萄球菌感染的皮肤创面愈合实验中,LRHA水凝胶组创面愈合过程中未发现黄色脓液,在第10天创面即完全闭合,并且与正常皮肤无异,证明了LRHA水凝胶卓越的体内抗感染能力以及促进皮肤创面愈合的能力。
但在应对复杂感染皮肤创面时,抗生素仍是目前不可或缺的治疗方式,所以有必要开发益生菌与抗生素联合应用的创面敷料,增强敷料控制感染的能力[81]。在联合应用情况下,抗生素不可避免也会对益生菌的活性造成影响,影响敷料的抗菌能力[82],为此,ZHOU等[83]开发了一种具有自屏蔽能力的益生菌,由单宁酸和铁离子螯合后在罗伊氏乳杆菌表面形成纳米保护层,从而发挥屏蔽作用,自屏蔽益生菌进一步被负载于羧化壳聚糖/氧化透明质酸可注射水凝胶中,水凝胶通过逐层覆盖益生菌表面的金属-多酚复合物和发生希夫碱反应形成水凝胶网络,发挥屏蔽作用;相比于未受保护的益生菌,双层保护使益生菌能在庆大霉素环境中增殖并分泌乳酸,同抗生素一起发挥协同抗菌作用。
综上所述,将益生菌负载于水凝胶中,一方面保护了益生菌,使其能发挥良好的抗菌性能;另一方面防止益生菌外溢对创面造成潜在威胁。益生菌微生态水凝胶还能实现益生菌与抗生素的联合应用,为益生菌在皮肤创面修复中的应用提供了一种新的策略。文章将益生菌微生态水凝胶在皮肤伤口修复中的应用进展研究总结于表2。
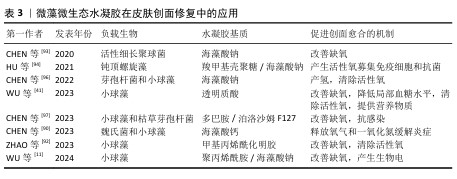
2.2.3 微藻微生态水凝胶 糖尿病患者的皮肤创面愈合是目前临床治疗的难点,由于创面周围高糖、低氧、高活性氧的环境,创面愈合的速度和质量都会大幅下降[84-85],所以开发能够改善创面愈合环境的皮肤创面敷料是研究的重点。微藻是一种光合自养生物,在光照条件下能转换光能和固定二氧化碳,并持续释放氧气[86];在无光照的情况下,微藻进行暗反应,消耗多余的葡萄糖[87];同时微藻内通常含有抗氧化剂,如叶黄素、胡萝卜素、虾青素等[88-89],可以消耗活性氧来促进组织再生[90-91]。水凝胶能为微藻的存活提供合适的环境,使微藻持续发挥生物功能,改善目前传统氧疗方法中氧气浓度不稳定、氧气维持时间不足等问题;同时微藻通过消耗葡萄糖、活性氧,为糖尿病患者的皮肤创面愈合提供适宜条件[92-94]。因此,微藻在糖尿病皮肤创面修复领域具有广阔应用前景[95]。
目前,微藻负载于水凝胶主要分为单一负载和与细菌一同构成共生群体负载。KANG等[91]开发了一种单一负载雨生红球藻的程序化微藻(HEA@Gel)水凝胶,通过调节光强度,HEA@Gel水凝胶可以程序化执行多种功能,如抗菌、供氧、活性氧清除和免疫调节;在强光下,HEA@Gel水凝胶利用高效光热转换在创面表面发挥杀菌消毒作用;在弱光下,HEA@Gel水凝胶通过光合作用持续产氧改善创面低氧环境;持续光照后,依靠雨生红球藻中累积的虾青素清除多余的活性氧,并通过外泌体分泌虾青素囊泡引导巨噬细胞M1型向M2型转化。所以,HEA@Gel水凝胶在创面修复应用中可以增强细胞增殖和迁移,促进新血管生成、胶原沉积,从而促进糖尿病感染皮肤创面的愈合。
CHEN等[96]开发了一种共生群体负载的芽孢杆菌-小球藻凝胶贴片,在芽孢杆菌的作用下,小球藻依靠光合作用中电子转移效率降低而产生氢气,氢气作为还原剂具有极好的活性氧清除作用,能降低创面处的氧化应激和炎症水平。CHEN等[97]开发了一种同时封装小球藻和枯草芽孢杆菌的活性微生态水凝胶LMH,通过小球藻实现了持续的氧气输送,通过枯草芽孢杆菌分泌抗菌剂和竞争作用实现抗菌,以促进慢性皮肤创面愈合。此类负载多种生物的水凝胶,既可以同时发挥每种生物在创面愈合中的调控作用,生物共生群体之间又能相互影响,形成新的物质或者发挥协同作用,使活性微生态水凝胶具有更强的修复皮肤创面的能力。文章将微藻微生态水凝胶在皮肤创面修复中的应用进展研究总结于表3。
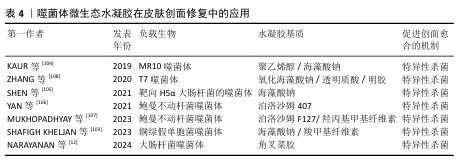
2.2.4 噬菌体微生态水凝胶 感染的皮肤创面通常伴有出血、炎症等,延长了创面愈合过程[98]。抗生素是治疗感染皮肤创面的常用方法,但近年来抗生素的广泛使用导致了耐药菌的出现,而噬菌体治疗是应对耐药菌感染的有效方法之一[99]。噬菌体疗法具有高特异性、低毒性,能够特异性杀死目标菌种,而不破坏创面环境的正常菌群生态和人体细胞[100];同时,噬菌体还可以破坏细菌生物膜或防止细菌生物膜形成,进一步发挥强有力的抗菌作用[101]。
目前用于递送噬菌体的材料主要包括乳膏、脂质体、纳米颗粒、水凝胶等[102],其中水凝胶由于具有良好的生物相容性、生物降解性和无毒性等特点被广泛应用于递送噬菌体,并进一步用于促进感染皮肤创面的愈合[103-104]。
噬菌体用于特异性识别宿主细菌的噬菌体尾部容易与其他物质发生化学反应而失效,同时,噬菌体具有酸、碱、热敏感性,因此在噬菌体微生态水凝胶中,水凝胶应使用不与噬菌体尾部发生反应的成分,还要具有温和的凝胶化条件,才能保持噬菌体的活性和功能。SHEN等[105]使用3D打印的方法将噬菌体负载于海藻酸盐水凝胶当中,3D打印过程时间短,pH值、温度等条件能够保持在适合噬菌体存活的范围。噬菌体是通过物理作用包埋在水凝胶中,表面不与水凝胶形成化学连接,保证了噬菌体尾部对宿主细菌的特异性识别,噬菌体从水凝胶中释放后能立即与细菌发生相互作用。
噬菌体微生态水凝胶还应具有长期储存稳定性,保持噬菌体持续的裂解活性,才能在皮肤创面愈合整个过程中发挥抗菌作用[106]。MUKHOPADHYAY等[107]将噬菌体和黏菌素负载于由羟丙基甲基纤维素和泊洛沙姆F127形成的水凝胶中,在4 ℃下储存9个月后,该水凝胶中的噬菌体仍具有良好的裂解活性。ZHANG等[108]开发了一种包裹酸性成纤维细胞生长因子和噬菌体的可注射水凝胶ABgel,ABgel能持续释放噬菌体,并且在储存7 d后仍然表现出与新鲜ABgel相同的抗菌活性;皮肤全层创面愈合实验结果显示,与不含噬菌体组相比,ABgel治疗组7 d后创面完全闭合,创面处几乎未检测到细菌,也未观察到明显的炎症。这些研究结果证明了噬菌体微生态水凝胶作为创面敷料促进感染皮肤创面愈合的巨大潜力。文章将噬菌体微生态水凝胶在皮肤创面修复中的应用进展研究总结于表4。
| [1] GRAVITZ L. Skin. Nature. 2018;563(7732): S83. [2] TANG N, ZHENG Y, CUI D, et al. Multifunctional Dressing for Wound Diagnosis and Rehabilitation. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(22):e2101292. [3] MOEINI A, PEDRAM P, MAKVANDI P, et al. Wound healing and antimicrobial effect of active secondary metabolites in chitosan-based wound dressings: A review. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;233:115839. [4] CHEN Y, WANG X, TAO S, et al. Research advances in smart responsive-hydrogel dressings with potential clinical diabetic wound healing properties. Mil Med Res. 2023;10(1):37. [5] YANG Z, HUANG R, ZHENG B, et al. Highly Stretchable, Adhesive, Biocompatible, and Antibacterial Hydrogel Dressings for Wound Healing. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021; 8(8):2003627. [6] YANG J, LIU W, WANG W. A supramolecular hydrogel leveraging hierarchical multi-strength hydrogen-bonds hinged strategy achieving a striking adhesive-mechanical balance. Bioact Mater. 2024;43:32-47. [7] SHAKIBI R, KHAYAMIAN MA, ABADIJOO H, et al. Enhancing cell activities through integration of polyanionic alginate or hyaluronic acid derivatives with triboelectric nanogenerators. Carbohydr Polym. 2024; 346:122629. [8] YAO M, ZHANG J, GAO F, et al. New BMSC-Laden Gelatin Hydrogel Formed in Situ by Dual-Enzymatic Cross-Linking Accelerates Dermal Wound Healing. ACS Omega. 2019; 4(5):8334-8340. [9] FAYYAZBAKHSH F, KHAYAT MJ, LEU MC. 3D-Printed Gelatin-Alginate Hydrogel Dressings for Burn Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Study. Int J Bioprint. 2022; 8(4):618. [10] KIM JS, YU H, WOO MR, et al. Influence of hydrophilic polymers on mechanical property and wound recovery of hybrid bilayer wound dressing system for delivering thermally unstable probiotic. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2022;135:112696. [11] WU Y, LI M, HE R, et al. Photosynthetic live microorganism-incorporated hydrogels promote diabetic wound healing via self-powering and oxygen production. Chem Eng J. 2024;485:149545. [12] NARAYANAN KB, BHASKAR R, CHOI SM, et al. Development of carrageenan-immobilized lytic coliphage vB_Eco2571-YU1 hydrogel for topical delivery of bacteriophages in wound dressing applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;259(Pt 2):129349. [13] LIU X, INDA M E, LAI Y, et al. Engineered Living Hydrogels. Adv Mater. 2022;34(26): e2201326. [14] WANG H, HEILSHORN SC. Adaptable hydrogel networks with reversible linkages for tissue engineering. Adv Mater. 2015;27(25):3717-3736. [15] WEI X, YANG X, HAN ZP, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: a new trend for cell therapy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013;34(6):747-754. [16] LIN YH, LIU EW, LIN YJ, et al. The Synergistic Effect of Electrical Stimulation and Dermal Fibroblast Cells-Laden 3D Conductive Hydrogel for Full-Thickness Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(14):11698. [17] SELIKTAR D. Designing cell-compatible hydrogels for biomedical applications. Science. 2012;336(6085):1124-1128. [18] SPRENGER L, LU HH, TRIPPMACHER S, et al. Composite Alginate Dialdehyde-Gelatin (ADA-GEL) Hydrogel Containing Short Ribbon-Shaped Fillers for Skeletal Muscle Tissue Biofabrication. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(34):44605-44622. [19] KIM J, CHOI Y , GAL CW, et al. Enhanced Osteogenesis in 2D and 3D Culture Systems Using RGD Peptide and α-TCP Phase Transition within Alginate-Based Hydrogel. Macromol Biosci. 2024;8:e2400190. [20] WANG Z, WEI H, HUANG Y, et al. Naturally sourced hydrogels: emerging fundamental materials for next-generation healthcare sensing. Chem Soc Rev. 2023;52(9):2992-3034. [21] VERNEREY FJ, LALITHA SRIDHAR S, MURALIDHARAN A, et al. Mechanics of 3D Cell-Hydrogel Interactions: Experiments, Models, and Mechanisms. Chem Rev. 2021; 121(18):11085-11148. [22] ZHANG S, YANG L, WANG Y, et al. Development of a Stretchable and Water-Resistant Hydrogel with Antibacterial and Antioxidant Dual Functions for Wound Healing in Movable Parts. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(37):43524-43540. [23] SHAHROUSVAND M, MIRMASOUDI SS, POURMOHAMMADI-BEJARPASI Z, et al. Polyacrylic acid/ polyvinylpyrrolidone hydrogel wound dressing containing zinc oxide nanoparticles promote wound healing in a rat model of excision injury. Heliyon. 2023;9(8):e19230. [24] RAHIMI N, MOLIN DG, CLEIJ TJ, et al. Electrosensitive polyacrylic acid/fibrin hydrogel facilitates cell seeding and alignment. Biomacromolecules. 2012; 13(5):1448-1457. [25] KIM JS, KIM J, LEE SM, et al. Development of guar gum-based dual-layer wound dressing containing Lactobacillus plantarum: Rapid recovery and mechanically flexibility. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;221:1572-1579. [26] XIONG Y, LIN Z, BU P, et al. A Whole-Course-Repair System Based on Neurogenesis-Angiogenesis Crosstalk and Macrophage Reprogramming Promotes Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv Mater. 2023;35(19):e2212300. [27] QI X, CAI E, XIANG Y, et al. An Immunomodulatory Hydrogel by Hyperthermia-Assisted Self-Cascade Glucose Depletion and ROS Scavenging for Diabetic Foot Ulcer Wound Therapeutics. Adv Mater. 2023;35(48):e2306632. [28] CUI T, YU J, WANG CF, et al. Micro-Gel Ensembles for Accelerated Healing of Chronic Wound via pH Regulation. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(22):e2201254. [29] GURTNER GC, WERNER S, BARRANDON Y, et al. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature. 2008;453(7193):314-321. [30] GONG Y, WANG P, CAO R, et al. Exudate Absorbing and Antimicrobial Hydrogel Integrated with Multifunctional Curcumin-Loaded Magnesium Polyphenol Network for Facilitating Burn Wound Healing. ACS Nano. 2023;17(22):22355-22370. [31] ROH EJ, KIM DS, KIM JH, et al. Multimodal therapy strategy based on a bioactive hydrogel for repair of spinal cord injury. Biomaterials. 2023;299:122160. [32] BANKOTI K, RAMESHBABU AP, DATTA S, et al. Carbon nanodot decorated acellular dermal matrix hydrogel augments chronic wound closure. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(40): 9277-9294. [33] HAO L, ZHAO S, HAO S, et al. Functionalized gelatin-alginate based bioink with enhanced manufacturability and biomimicry for accelerating wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;240:124364. [34] KOH K, WANG J K, CHEN JXY, et al. Squid Suckerin-Spider Silk Fusion Protein Hydrogel for Delivery of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome to Chronic Wounds. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(1):e2201900. [35] ZHAO M, WANG J, ZHANG J, et al. Functionalizing multi-component bioink with platelet-rich plasma for customized in-situ bilayer bioprinting for wound healing. Mater Today Bio. 2022;16:100334. [36] HAO L, TAO X, FENG M, et al. Stepwise Multi-Cross-Linking Bioink for 3D Embedded Bioprinting to Promote Full-Thickness Wound Healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(20):24034-24046. [37] MI B, CHEN L, XIONG Y, et al. Osteoblast/Osteoclast and Immune Cocktail Therapy of an Exosome/Drug Delivery Multifunctional Hydrogel Accelerates Fracture Repair. ACS Nano. 2022;16(1):771-782. [38] PAEZ-MAYORGA J, CAPUANI S, FARINA M, et al. Enhanced In Vivo Vascularization of 3D-Printed Cell Encapsulation Device Using Platelet-Rich Plasma and Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(19): e2000670. [39] YUAN X, YANG W, FU Y, et al. Four-Arm Polymer-Guided Formation of Curcumin-Loaded Flower-Like Porous Microspheres as Injectable Cell Carriers for Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023; 12(30):e2301486. [40] ROY ME, VEILLEUX C, ANNABI B. In vitro biomaterial priming of human mesenchymal stromal/stem cells : implication of the Src/JAK/STAT3 pathway in vasculogenic mimicry. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):21444. [41] WU H, YANG P, LI A, et al. Chlorella sp.-ameliorated undesirable microenvironment promotes diabetic wound healing. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023;13(1):410-424. [42] HUANG K, LIU W, WEI W, et al. Photothermal Hydrogel Encapsulating Intelligently Bacteria-Capturing Bio-MOF for Infectious Wound Healing. ACS Nano. 2022;16(11):19491-19508. [43] ZHANG Y, ZHAO Y, AN C, et al. Material-driven immunomodulation and ECM remodeling reverse pulmonary fibrosis by local delivery of stem cell-laden microcapsules. Biomaterials. 2024;313: 122757. [44] ZHANG H, ZHOU Z, ZHANG F, et al. Hydrogel-Based 3D Bioprinting Technology for Articular Cartilage Regenerative Engineering. Gels. 2024;10(7):430. [45] FONDER MA, LAZARUS GS, COWAN DA, et al. Treating the chronic wound: A practical approach to the care of nonhealing wounds and wound care dressings. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58(2):185-206. [46] GUAN Y, NIU H, LIU Z, et al. Sustained oxygenation accelerates diabetic wound healing by promoting epithelialization and angiogenesis and decreasing inflammation. Sci Adv. 2021;7(35):EABJ0153. [47] HUANG J, YANG R, JIAO J, et al. A click chemistry-mediated all-peptide cell printing hydrogel platform for diabetic wound healing. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):7856. [48] HAFEEZ S, ALDANA AA, DUIMEL H, et al. Molecular Tuning of a Benzene-1,3,5-Tricarboxamide Supramolecular Fibrous Hydrogel Enables Control over Viscoelasticity and Creates Tunable ECM-Mimetic Hydrogels and Bioinks. Adv Mater. 2023;35(24):e2207053. [49] RAO N, AGMON G, TIERNEY MT, et al. Engineering an Injectable Muscle-Specific Microenvironment for Improved Cell Delivery Using a Nanofibrous Extracellular Matrix Hydrogel. ACS Nano. 2017;11(4): 3851-3859. [50] ZHU H, WU X, LIU R, et al. ECM-Inspired Hydrogels with ADSCs Encapsulation for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(9):e2206253. [51] XU H, LI Y, SONG J, et al. Highly active probiotic hydrogels matrixed on bacterial EPS accelerate wound healing via maintaining stable skin microbiota and reducing inflammation. Bioact Mater. 2024;35:31-44. [52] HUMES HD. Cell therapy: leveraging nature’s therapeutic potential. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14(8):2211-2213. [53] HASSAN WU, GREISER U, WANG W. Role of adipose-derived stem cells in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2014;22(3): 313-325. [54] XUE Y, ZHANG Y, ZHONG Y, et al. LNP-RNA-engineered adipose stem cells for accelerated diabetic wound healing. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):739. [55] SHI M, GAO Y, LEE L, et al. Adaptive Gelatin Microspheres Enhanced Stem Cell Delivery and Integration With Diabetic Wounds to Activate Skin Tissue Regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:813805. [56] ZHANG Y, YIN P, HUANG J, et al. Scalable and high-throughput production of an injectable platelet-rich plasma (PRP)/cell-laden microcarrier/hydrogel composite system for hair follicle tissue engineering. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):465. [57] SU L, JIA Y, FU L, et al. The emerging progress on wound dressings and their application in clinic wound management. Heliyon. 2023;9(12):e22520. [58] BURDICK JA, MAUCK RL, GERECHT S. To Serve and Protect: Hydrogels to Improve Stem Cell-Based Therapies. Cell Stem Cell. 2016;18(1):13-15. [59] FARHAT W, HASAN A, LUCIA L, et al. Hydrogels for Advanced Stem Cell Therapies: A Biomimetic Materials Approach for Enhancing Natural Tissue Function. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2019;12: 333-351. [60] SHAFIEE A, CAVALCANTI AS, SAIDY NT, et al. Convergence of 3D printed biomimetic wound dressings and adult stem cell therapy. Biomaterials. 2021;268:120558. [61] XU Q, A S, GAO Y, et al. A hybrid injectable hydrogel from hyperbranched PEG macromer as a stem cell delivery and retention platform for diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2018;75:63-74. [62] GJOREVSKI N, LUTOLF MP. Synthesis and characterization of well-defined hydrogel matrices and their application to intestinal stem cell and organoid culture. Nat Protoc. 2017;12(11): 2263-2274. [63] WU X, ZHU H, CHE J, et al. Stem cell niche-inspired microcarriers with ADSCs encapsulation for diabetic wound treatment. Bioact Mater. 2023;26:159-168. [64] ZHENG X, DING Z, CHENG W, et al. Microskin-Inspired Injectable MSC-Laden Hydrogels for Scarless Wound Healing with Hair Follicles. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(10):e2000041. [65] KANG D, LIU Z, QIAN C, et al. 3D bioprinting of a gelatin-alginate hydrogel for tissue-engineered hair follicle regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2023;165:19-30. [66] WANG H, SUN D, LIN W, et al. One-step fabrication of cell sheet-laden hydrogel for accelerated wound healing. Bioact Mater. 2023;28:420-431. [67] SUEZ J, ZMORA N, SEGAL E, et al. The pros, cons, and many unknowns of probiotics. Nat Med. 2019;25(5):716-729. [68] MIAO Y, WEI J, CHEN X, et al. Evaluation of living bacterial therapy assisted by pH/reactive oxygen species dual-responsive sodium alginate-based hydrogel for wound infections. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024; 271(Pt 2):132536. [69] ZHANG P, FAN Z, CHENG P, et al. Dynamic hydrazone crosslinked salecan/chondroitin sulfate hydrogel platform as a promising wound healing Strategy: A comparative study on antibiotic and probiotic delivery. Int J Pharm. 2024;665:124667. [70] VAN HOLM W, CARVALHO R, DELANGHE L, et al. Antimicrobial potential of known and novel probiotics on in vitro periodontitis biofilms. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2023; 9(1):3. [71] WEI Y, HAN Z, MAO X. Injectable Living Probiotic Dressing Built by Droplet-Based Microfluidics and Photo-Cross-Linking to Prevent Pathogenic Infection and Promote Wound Repair. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(4):e2302423. [72] VALDÉZ JC, PERAL MC, RACHID M, et al. Interference of Lactobacillus plantarum with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro and in infected burns: the potential use of probiotics in wound treatment. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2005;11(6):472-479. [73] LI L, YANG C, MA B, et al. Hydrogel-Encapsulated Engineered Microbial Consortium as a Photoautotrophic “Living Material” for Promoting Skin Wound Healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023; 15(5):6536-6547. [74] MEI L, ZHANG D, SHAO H, et al. Injectable and Self-Healing Probiotics-Loaded Hydrogel for Promoting Superbacteria-Infected Wound Healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(18):20538-20550. [75] YANG L, HAN Z, CHEN C, et al. Novel probiotic-bound oxidized Bletilla striata polysaccharide-chitosan composite hydrogel. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;117:111265. [76] DOU Z, LI B, WU L, et al. Probiotic-Functionalized Silk Fibroin/Sodium Alginate Scaffolds with Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Relieving Properties for Promoted Scarless Wound Healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(5):6297-6311. [77] YANG X, CHE T, TIAN S, et al. A Living Microecological Hydrogel with Microbiota Remodeling and Immune Reinstatement for Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(23):e2400856. [78] SUN Y, LIU M, TANG X, et al. Culture-Delivery Live Probiotics Dressing for Accelerated Infected Wound Healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(46): 53283-53296. [79] SUN Q, YIN S, HE Y, et al. Biomaterials and Encapsulation Techniques for Probiotics: Current Status and Future Prospects in Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023;13(15):2185. [80] MING Z, HAN L, BAO M, et al. Living Bacterial Hydrogels for Accelerated Infected Wound Healing. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(24): e2102545. [81] LEVY SB, MARSHALL B. Antibacterial resistance worldwide: causes, challenges and responses. Nat Med. 2004;10(12 Suppl): S122-129. [82] LI Z, BEHRENS AM, GINAT N, et al. Biofilm-Inspired Encapsulation of Probiotics for the Treatment of Complex Infections. Adv Mater. 2018;30(51):e1803925. [83] ZHOU C, ZOU Y, XU R, et al. Metal-phenolic self-assembly shielded probiotics in hydrogel reinforced wound healing with antibiotic treatment. Mater Horiz. 2023;10(8):3114-3123. [84] LIAKOS A, LIAKOPOULOU P, TSAPAS A. Cyclical pressurized topical wound oxygen therapy increased healing of refractory diabetic foot ulcers. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(6):JC27. [85] CAO Y, CHEN B, LIU Q, et al. Dissolvable microneedle-based wound dressing transdermally and continuously delivers anti-inflammatory and pro-angiogenic exosomes for diabetic wound treatment. Bioact Mater. 2024;42:32-51. [86] LIU H, YU S, LIU B, et al. Space-Efficient 3D Microalgae Farming with Optimized Resource Utilization for Regenerative Food. Adv Mater. 2024;36(24):e2401172. [87] ZHANG C, HAN ZY, CHEN KW, et al. In Situ Formed Microalgae-Integrated Living Hydrogel for Enhanced Tumor Starvation Therapy and Immunotherapy through Photosynthetic Oxygenation. Nano Lett. 2024;24(12):3801-3810. [88] ÇELEKLI A, ÖZBAL B, BOZKURT H. Challenges in Functional Food Products with the Incorporation of Some Microalgae. Foods. 2024;13(5):725. [89] DE ANDRADE AF, PORTO ALF, BEZERRA RP. Photosynthetic microorganisms and their bioactive molecules as new product to healing wounds. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022;106(2):497-504. [90] CHEN HH, FU FS, CHEN QW, et al. Two-Pronged Microbe Delivery of Nitric Oxide and Oxygen for Diabetic Wound Healing. Nano Lett. 2023;23(12):5595-5602. [91] KANG Y, XU L, DONG J, et al. Programmed microalgae-gel promotes chronic wound healing in diabetes. Nat Commun. 2024; 15(1):1042. [92] ZHAO E, XIAO T, TAN Y, et al. Separable Microneedles with Photosynthesis-Driven Oxygen Manufactory for Diabetic Wound Healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023; 15(6):7725-7734. [93] CHEN H, CHENG Y, TIAN J, et al. Dissolved oxygen from microalgae-gel patch promotes chronic wound healing in diabetes. Sci Adv. 2020;6(20):eaba4311. [94] HU H, ZHONG D, LI W, et al. Microalgae-based bioactive hydrogel loaded with quorum sensing inhibitor promotes infected wound healing. Nano Today. 2022; 42:101368. [95] LIU S, SHI L, LUO H, et al. Processed microalgae: green gold for tissue regeneration and repair. Theranostics. 2024;14(13):5235-5261. [96] CHEN H, GUO Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Symbiotic Algae-Bacteria Dressing for Producing Hydrogen to Accelerate Diabetic Wound Healing. Nano Lett. 2022;22(1):229-237. [97] CHEN G, WANG F, ZHANG X, et al. Living microecological hydrogels for wound healing. Sci Adv. 2023;9(21):eadg3478. [98] WANG M, LI T, TIAN J, et al. Engineering Single-Component Antibacterial Anti-inflammatory Polyitaconate-Based Hydrogel for Promoting Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus-Infected Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration. ACS Nano. 2024;18(1):395-409. [99] LYON J. Phage Therapy’s Role in Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Pathogens. JAMA. 2017;318(18):1746-1748. [100] SHIUE SJ, WU MS, CHIANG YH, et al. Bacteriophage-cocktail hydrogel dressing to prevent multiple bacterial infections and heal diabetic ulcers in mice. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2024;112(11):1846-1859. [101] AL-ISHAQ RK, SKARIAH S, BÜSSELBERG D. Bacteriophage Treatment: Critical Evaluation of Its Application on World Health Organization Priority Pathogens. Viruses. 2020;13(1):51. [102] ROTMAN SG, SUMRALL E, ZIADLOU R, et al. Local Bacteriophage Delivery for Treatment and Prevention of Bacterial Infections. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:538060. [103] SHAFIGH KHELJAN F, SHEIKHZADEH HESARI F, AMINIFAZL MS, et al. Design of Phage-Cocktail-Containing Hydrogel for the Treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Infected Wounds. Viruses. 2023;15(3):803. [104] KAUR P, GONDIL VS, CHHIBBER S. A novel wound dressing consisting of PVA-SA hybrid hydrogel membrane for topical delivery of bacteriophages and antibiotics. Int J Pharm. 2019;572:118779. [105] SHEN HY, LIU ZH, HONG JS, et al. Controlled-release of free bacteriophage nanoparticles from 3D-plotted hydrogel fibrous structure as potential antibacterial wound dressing. J Control Release. 2021;331:154-163. [106] YAN W, BANERJEE P, LIU Y, et al. Development of thermosensitive hydrogel wound dressing containing Acinetobacter baumannii phage against wound infections. Int J Pharm. 2021;602:120508. [107] MUKHOPADHYAY S, TO KKW, LIU Y, et al. A thermosensitive hydrogel formulation of phage and colistin combination for the management of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii wound infections. Biomater Sci. 2023;12(1):151-163. [108] ZHANG J, GE J, XU Y, et al. Bioactive multi-engineered hydrogel offers simultaneous promise against antibiotic resistance and wound damage. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020; 164:4466-4474. |
| [1] | 陈 灵, 毛秋华, 徐 普, 张文柏. 纳米珍珠粉水溶性基质对小鼠成纤维细胞增殖、迁移及凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 338-344. |
| [2] | 刘晓红, 赵 天, 穆云萍, 冯文金, 吕存声, 张智永, 赵子建, 李芳红. 脱细胞真皮基质水凝胶促进大鼠皮肤创面的愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 395-403. |
| [3] | 谭凤怡, 谢嘉敏, 潘振锋, 张新旭, 郑泽态, 曾祉莹, 周艳芳. 胶原蛋白联合微针治疗皮肤光老化的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 451-458. |
| [4] | 王 卓, 孙盼盼, 程焕芝, 曹婷婷. 壳聚糖在口腔软硬组织修复与再生中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 459-468. |
| [5] | 王 域, 范民杰, 郑朋飞. 多重刺激响应性水凝胶在骨损伤修复中的应用:特殊响应能力及多样性功能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 469-479. |
| [6] | 张 茜, 王福霞, 王 文, 张 坤. 纳米水凝胶复合系统特性分析及在可视化影像诊疗中的应用策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 480-488. |
水凝胶是一种高吸水材料,能够吸收创面渗出液;同时还具有良好的机械性能,能适应创面处的应力变化;具有良好的生物相容性,能够为皮肤创面愈合提供适宜的生理环境[4]。与普通创面敷料(如纱布、敷贴等)相比,水凝胶还具有生物降解能力,避免了更换敷料给皮肤创面造成的二次创伤[5]。但单一组分水凝胶能发挥的作用有限,所以有许多研究对水凝胶进行各种改性,强化水凝胶的性能、增加水凝胶的功能,提高其促进皮肤创面愈合的能力[6-7]。
活性微生态水凝胶是水凝胶的改性成果之一。因水凝胶具有三维多孔结构,允许营养物质和氧气等通过,并且富含水分,所以水凝胶能模拟细胞外基质,为活性生物提供适宜的生存环境[8]。基于该特点,水凝胶中可以加入活性生物如细胞[9]、益生菌[10]、微藻[11]、噬菌体等[12],形成活性微生态水凝胶。这种改性方式赋予了水凝胶生物活性,使其能够响应复杂的外界环境及环境变化,扩大了水凝胶的应用场景,尤其在生物医药领域[13]。水凝胶的3D网络结构固定并保护了活性生物,使这些通常培养于液体中的生物能被固定在特定部位持续发挥作用[14]。因此,负载有活性生物的活性微生态水凝胶具有成为优秀皮肤创面敷料的潜能。应用活性微生态水凝胶修复皮肤创面时,水凝胶为其中的活性生物提供适宜的生存环境,生物在其中又形成微生态,进行持续而稳定的迁移、增殖、分泌、释放等生物行为,水凝胶与活性生物之间的相互作用使整个水凝胶体系能适应创面处复杂的环境,调控创面愈合进程,从而促进皮肤创面愈合[15]。
该文首先简要概括活性微生态水凝胶的基本特点,随后阐述活性微生态水凝胶相较于其他皮肤创面敷料的优势,以及它在皮肤创面愈合过程中发挥的关键作用,最后重点综述了活性微生态水凝胶在皮肤创面修复中的应用进展。
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2024年9月进行检索。
1.1.2 文献检索时限 各数据库建库至2024年9月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 Web of Science、PubMed、中国知网和万方数据库。
1.1.4 检索途径 主题词检索、关键词检索、摘要检索和全文检索。
1.1.5 检索词 英文检索词为“cell,probiotics,phage,chlorella,algae,living microecological,hydrogel,skin,wound healing,wound repair”,中文检索词为“细胞,益生菌,噬菌体,小球藻,微藻,活性微生态,水凝胶,皮肤,伤口愈合,伤口修复”。
1.1.6 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述。
1.1.7 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.8 检索策略 以PubMed数据库为例的检索策略,见图1。
1.1.9 检索文献量 初步检索文献量为1 577篇,其中PubMed数据库519篇,Web of Science数据库1 019篇,中国知网12篇,万方数据库27篇。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①与活性微生态水凝胶促进皮肤创面愈合相关的文献;②优先纳入近5年内论点论据可靠且发表于权威专业杂志、高引用率著作的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①重复性文献;②与研究目的不相符的文献;③论点不明确及论据不充分的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估和数据提取 按照检索策略共检索文献1 577篇,阅读标题和摘要,排除无关和重复文献后余202篇。通过阅读全文进一步筛选,根据纳入标准综合考察文献实验设计是否完善、论点论据是否充分等因素,最终纳入108篇文献。文献筛选流程见图2。
3.2 该综述区别于他人他篇的特点 目前尚无综述报道各类活性微生态水凝胶在皮肤创面愈合方面的研究进展,文章着眼于活性微生态水凝胶中负载生物的生物活性,归纳总结了活性微生态水凝胶的基本特点,相较于其他创面敷料的优势以及在皮肤创面愈合过程中发挥的关键作用,具有较强的针对性。另外,该文综述了近年来负载不同活性生物的活性微生态水凝胶在皮肤创面修复中的应用进展,阐述了不同活性微生态水凝胶在应用中的特点和仍然存在的问题,反映出该类水凝胶敷料较好的临床应用潜能。
3.3 该综述的局限性 由于活性微生态水凝胶相关研究大都集中在近3年,对于负载生物的选择还比较少,目前主要有负载细胞、微藻、益生菌、噬菌体这4类生物的相关研究,但每种类型中使用的具体活性生物重合度较高,限制了文章进行同类型微生态水凝胶的横向比较。目前几乎没有文章探究各类活性微生态水凝胶促进皮肤创面愈合的具体通路,因此,该文也只根据现有研究简要地概括了该类水凝胶促进皮肤创面愈合的机制,对于深层机制的探究还需要继续完善。
3.4 该综述的重要意义 该文综述了近年来活性微生态水凝胶在促进皮肤创面愈合中的研究进展,阐明了活性微生态水凝胶在促进皮肤创面愈合领域具有广泛的应用前景,其生物活性的多样性为创面治疗带来更多可能。该综述提出了现存问题,为未来活性微生态水凝胶的进一步研究提供了理论支持和新的方向。
微生态活性水凝胶是指负载了活性生物的水凝胶,活性生物在水凝胶中形成微生态,进行迁移、增殖、分泌、释放等生物行为。该文着眼于活性微生态水凝胶中负载生物的生物活性,归纳总结了活性微生态水凝胶的基本特点,相较于其他创面敷料的优势,以及在皮肤创面愈合过程中发挥的关键作用,具有较强的针对性。同时,文章回顾了近年来负载不同活性生物的微生态水凝胶在皮肤创面修复中的应用进展,探讨了不同种类微生态水凝胶在应用中的独特特点与尚存问题,表明了该类水凝胶在促进皮肤创面愈合方面的广泛应用前景,总的来说,文章为未来活性微生态水凝胶的进一步研究提供了理论基础和新方向。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||