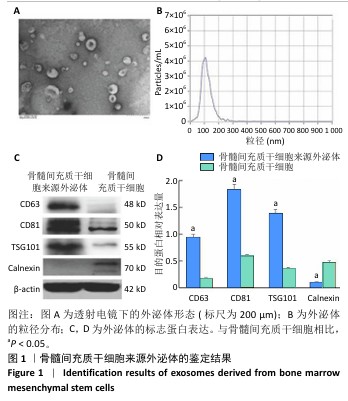
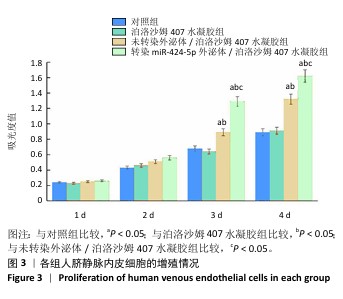
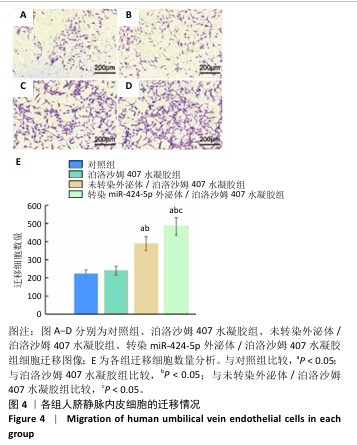
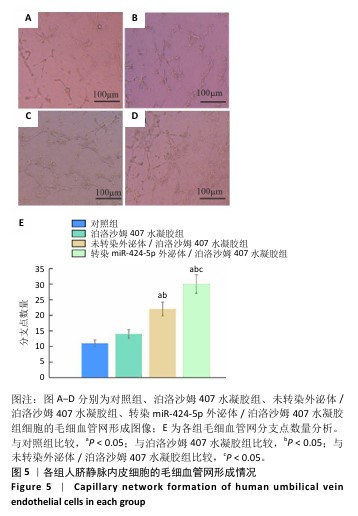
[1] CÁNOVAS R, DAEMS E, LANGLEY AR, et al. Are aptamer-based biosensing approaches a good choice for female fertility monitoring? A comprehensive review. Biosens Bioelectron. 2023;220:114881.
[2] SHAHVEGHAR ASL Z, PARASTOUEI K, ESKANDARI E. The effects of N-acetylcysteine on ovulation and sex hormones profile in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Nutr. 2023;130(2):202-210.
[3] MOUSTAFA SM, GARNEAU AS, GOODMAN LR. Elusive effect of endometrial thickness: through thick and thin. Fertil Steril. 2021;115(1):89-90.
[4] ERSAHIN SS, ERSAHIN A. Endometrial injury concurrent with hysteroscopy increases the expression of Leukaemia inhibitory factor: a preliminary study. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2022;20(1):11.
[5] ZHU X, CHEN S, ZHANG P, et al. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor promotes endometrial repair after injury by regulating macrophages in mice. J Reprod Immunol. 2023;160:104156.
[6] LIN J, WANG Z, HUANG J, et al. Microenvironment-Protected Exosome-Hydrogel for Facilitating Endometrial Regeneration, Fertility Restoration, and Live Birth of Offspring. Small. 2021;17(11):e2007235.
[7] DOODY KJ. Infertility Treatment Now and in the Future. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2021;48(4):801-812.
[8] WU H, CHE J, ZHENG W, et al. Novel biallelic ASTL variants are associated with polyspermy and female infertility: A successful live birth following ICSI treatment. Gene. 2023;887:147745.
[9] ZHANG H, XU D, LI Y, et al. Organoid Transplantation Can Improve Reproductive Prognosis by Promoting Endometrial Repair in Mice. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18(6):2627-2638.
[10] ZHANG D, DU Q, LI C, et al. Functionalized human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and injectable HA/Gel hydrogel synergy in endometrial repair and fertility recovery. Acta Biomater. 2023;167:205-218.
[11] LAI JJ, CHAU ZL, CHEN SY, et al. Exosome Processing and Characterization Approaches for Research and Technology Development. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(15):e2103222.
[12] ZHANG X, XU Y, MA L, et al. Essential roles of exosome and circRNA_101093 on ferroptosis desensitization in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2022;42(4):287-313.
[13] LIU H, ZHANG X, ZHANG M, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Repair Uterine Injury by Targeting Transforming Growth Factor-beta Signaling. ACS Nano. 2024;18(4):3509-3519.
[14] QI J, ZHANG X, ZHANG S, et al. P65 mediated UBR4 in exosomes derived from menstrual blood stromal cells to reduce endometrial fibrosis by regulating YAP Ubiquitination. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):305.
[15] ZHU Q, TANG S, ZHU Y, et al. Exosomes Derived From CTF1-Modified Bone Marrow Stem Cells Promote Endometrial Regeneration and Restore Fertility. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:868734.
[16] TENG F, ZHANG JX, CHANG QM, et al. LncRNA MYLK-AS1 facilitates tumor progression and angiogenesis by targeting miR-424-5p/E2F7 axis and activating VEGFR-2 signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):235.
[17] GHOSH G, SUBRAMANIAN IV, ADHIKARI N, et al. Hypoxia-induced microRNA-424 expression in human endothelial cells regulates HIF-α isoforms and promotes angiogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2010;120(11): 4141-4454.
[18] XIONG Z, HU Y, JIANG M, et al. Hypoxic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosomes promote angiogenesis and enhance endometrial injury repair through the miR-424-5p-mediated DLL4/Notch signaling pathway. PeerJ. 2024;12:e16953.
[19] WU Y, GU S, COBB JM, et al. E2-Loaded Microcapsules and Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Injectable Scaffolds for Endometrial Regeneration Application. Tissue Eng Part A. 2024;30(3-4):115-130.
[20] WU F, LEI N, YANG S, et al. Treatment strategies for intrauterine adhesion: focus on the exosomes and hydrogels. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11: 1264006.
[21] ZARRINTAJ P, JOUYANDEH M, REZA GANJALI M, et al. Thermo-sensitive polymers in medicine: a review. Eur Polym J. 2019;117:402-423.
[22] YANG J, CHEN Z, PAN D, et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Combined Pluronic F127 Hydrogel Promote Chronic Diabetic Wound Healing and Complete Skin Regeneration. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:5911-5926.
[23] BORGES R, KAI KC, LIMA CA, et al. Bioactive glass/poloxamer 407 hydrogel composite as a drug delivery system: The interplay between glass dissolution and drug release kinetics. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;206:111934.
[24] ZHAO Y, LIU X, PENG X, et al. A poloxamer/hyaluronic acid/chitosan-based thermosensitive hydrogel that releases dihydromyricetin to promote wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;216:475-486.
[25] 韩晓燕,纳涛,张可华,等.人间充质干细胞生物学有效性的质量评价[J].中国新药杂志,2018,27(21):2511-2518.
[26] 熊正花,刘贝贝,杨琳娟,等.低氧处理骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体对宫腔粘连模型大鼠的疗效研究[J].中华妇产科杂志,2023,58(12): 911-921.
[27] 陈美婷,肖邦,朱怡卿,等.骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体对成年大鼠子宫内膜细胞铁死亡的改善作用及其机制[J].山东医药,2022,62(12):35-39.
[28] LI J, PAN Y, YANG J, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-primed mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote M2 macrophage polarization via Galectin-1 and modify intrauterine adhesion on a novel murine model. Front Immunol. 2022;13:945234.
[29] YAO Y, CHEN R, WANG G, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells reverse EMT via TGF-beta1/Smad pathway and promote repair of damaged endometrium. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):225.
[30] 孙晓清,崔照领,刘晓旭.子宫内膜异位症患者血清LncRNANEAT1,miR-424-5p水平表达与临床分期及不孕诊断的相关研究[J].现代检验医学杂志,2024,39(5):54-57,74.
[31] 冯佳梅,万华,高晴倩,等.LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1调节miR-424-5p/PSAT1轴对乳腺癌恶性进展的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2024,24(14): 2606-2612,2625.
[32] 曹浪,李雪,周善璧,等.miRNA-424 (322)-5p通过激活Raf/MEK/ERK通路促进大鼠角膜新生血管形成[J].第三军医大学学报,2021,43(17): 1650-1657.
[33] VIMALRAJ S, SARAVANAN S, RAGHUNANDHAKUMAR S, et al. Melatonin regulates tumor angiogenesis via miR-424-5p/VEGFA signaling pathway in osteosarcoma. Life Sci. 2020;256:118011.
[34] KHAN I, BHARDWAJ M, SHUKLA S, et al. Carvacrol encapsulated nanocarrier/ nanoemulsion abrogates angiogenesis by downregulating COX-2, VEGF and CD31 in vitro and in vivo in a lung adenocarcinoma model. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;181:612-622.
[35] LUBAHN DB, MOYER JS, GOLDING TS, et al. Alteration of reproductive function but not prenatal sexual development after insertional disruption of the mouse estrogen receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90(23): 11162-11166.
[36] DEY SK, LIM H, DAS SK, et al. Molecular cues to implantation. Endocr Rev. 2004;25(3):341-273.
[37] SONG H, LIM H, DAS SK, et al. Dysregulation of EGF family of growth factors and COX-2 in the uterus during the preattachment and attachment reactions of the blastocyst with the luminal epithelium correlates with implantation failure in LIF-deficient mice. Mol Endocrinol. 2000;14(8):1147-1161. |