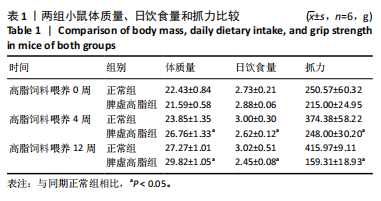
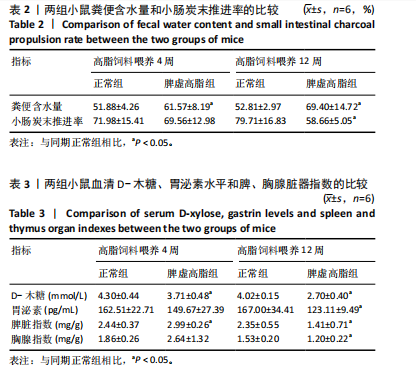
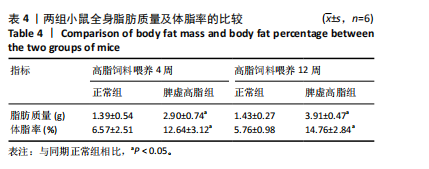
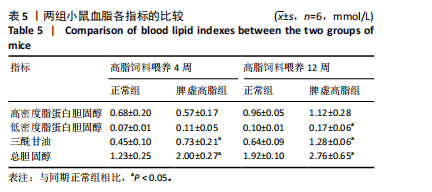
[1] 王增武,刘静,李建军,等.中国血脂管理指南(2023年)[J].中国循环杂志, 2023,38(3):237-271.
[2] 诸骏仁,高润霖,赵水平,等.中国成人血脂异常防治指南(2016年修订版)[J].中国循环杂志,2016,31(10):937-953.
[3] SONG PK, MAN QQ, LI H, et al. Trends in lipids level and dyslipidemia among Chinese adults,2002-2015. Biomed Environ Sci. 2019;32(8):559-570.
[4] 国家卫生健康委员会疾病预防控制局.中国居民营养与慢性病状况报告2020[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2020.
[5] TAKAOKA M, ZHAO X, LIM HY, et al. Early intermittent hyperlipidaemia alters tissue macrophages to fuel atherosclerosis. Nature. 2024;634(8033):457-465.
[6] WRIGHT J, SUBRAMANIAN S. Therapy for Hyperlipidemia. Med Clin North Am. 2024;108(5):881-894.
[7] LEE MK, HAN K, KIM B, et al. Cumulative exposure to hypertriglyceridemia and risk of type 2 diabetes in young adults. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2024;208:111109.
[8] WELSH A, HAMMAD M, PIÑA IL, et al. Obesity and cardiovascular health. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2024;31(8):1026-1035.
[9] CHENG D, ZHANG M, ZHENG Y, et al. α-Ketoglutarate prevents hyperlipidemia-induced fatty liver mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress by activating the AMPK-pgc-1α/Nrf2 pathway. Redox Biol. 2024;74:103230.
[10] 郑贵力,王煦,王绵之.王绵之教授治疗高脂血症学术思想及经验[J].北京中医药大学学报,2000,23(2):48-50.
[11] 贾连群,杨关林,张哲,等.从“脾主运化”理论探讨膏脂转输与胆固醇逆向转运[J].中医杂志,2013,54(20):1793-1795.
[12] 张琦,隋国媛,宋囡,等.香砂六君子汤对脾虚高脂血症大鼠肝脏内质网应激/PERK/SREBP1c途径及甘油三酯合成的影响及机制[J].时珍国医国药, 2024,35(3):545-550.
[13] 翟亚荣,孟嘉伟,张琦,等.基于肠源性高密度脂蛋白调控脂多糖介导Kupffer-肝细胞Cross-Talk探讨脾虚膏脂转输障碍的分子生物学基础[J].中华中医药学刊,2023,41(2):75-77.
[14] 中国脾虚人群白皮书2023年[C]//上海艾瑞市场咨询有限公司.2023艾瑞咨询4月研究报告会论文集.[出版者不详],2023:61.
[15] 安冬青,吴宗贵,梁春,等.血脂异常中西医结合诊疗专家共识[J].中国全科医学,2017,20(3):262-269.
[16] 冷雪,李阳.TMAO对脾虚高脂血症大鼠脂代谢的影响及香砂六君子汤的干预作用[J].中国实验动物学报,2023,31(10):1261-1270.
[17] 王杰,宋囡,隋国媛,等.香砂六君子汤对脾虚高脂血症大鼠肠道菌群及肝脏脂质沉积的防治作用机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2023,38(5):2264-2269.
[18] SUN S, GUO H, SHANG E, et al. Lipidomics study of Liujunzi decoction in hyperlipidemia rats with spleen deficiency based on UPLC-Q-TOF/MS. Heliyon. 2024;10(11):e31710.
[19] 李芹,张会永,周鹤,等.基于S1PR1/PI3K/Akt/eNOS信号通路探究健脾化痰方对高脂血症脾虚痰浊小猪血管内皮的保护机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2021, 36(8):4564-4567.
[20] 李芹,张会永,周鹤,等.健脾化痰方对高脂血症脾虚痰浊证模型小型猪血管内皮功能的影响[J].中医杂志,2020,61(10):886-889+895.
[21] 高心雪,高佳新,朱建宇,等.聚苯乙烯微塑料对小鼠生长发育和肝脏脂质代谢的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(29):4634-4638.
[22] 王圆圆,杨晓桐,陈伟.白玉菇多糖发酵乳对小鼠肠道微生物的影响及抗氧化作用[J].中国食品学报,2023,23(4):127-135.
[23] 段雨婷,张越,黄佳静,等.茯苓不同部位水提物对脾虚模型小鼠健脾作用的研究[J].安徽中医药大学学报,2023,42(2):68-73.
[24] 王珑静,张瑾,罗婕,等.齐墩果酸对脾虚水湿内停模型小鼠异常水液代谢的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2023,29(4):77-85.
[25] 李思怡,麦伟栅,林琨洋,等.健脾化瘀解毒方调控AKT/p38蛋白磷酸化改善胃癌前病变小鼠脾虚证研究[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2022, 24(12):4953-4959.
[26] 张永龙,马唯刚,钱星羽,等.脾虚证实验动物模型构建及评价方法的研究述评[J].中国实验动物学报,2024,32(3):385-396.
[27] 侯红平,张广平,彭博,等.不同周期的高脂血症大鼠模型的相关指标变化分析[J].实验动物科学,2023,40(6):67-72.
[28] 彭高强,文颖娟,陈茉,等.基于“壮火食气”探讨痰-瘀-脾与高脂血症关系[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2021,41(6):967-971.
[29] 雷萍,韩晓伟,徐铭,等.灰树花多糖对白念珠菌肠道感染脾虚小鼠TLR2/MyD88/NF-κB通路基因早期转录的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2019,37(12): 2933-2937.
[30] 任蓁,刘思莹,代培方,等.益气养阴方对高脂血症模型小鼠AMPK/SREBP-1c通路相关基因及蛋白的影响[J].时珍国医国药,2023,34(10):2342-2346.
[31] 任珊,丁琳,李清禹,等.白藜芦醇对高脂饮食诱导小鼠高脂血症的作用机制研究[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2022,38(2):137-141.
[32] 李静,贾连群,李宁,等.一种新型小动物脾虚高脂血症模型的建立[J].时珍国医国药,2015,26(2):503-505.
[33] 段新屹,兰昀羲,沈龙宇,等.异功散中陈皮对脾虚大鼠MTL分泌和人参皂苷Rb1药动学影响及PK-PD相关性分析[J].时珍国医国药,2024,35(7): 1781-1786.
[34] 于涵川,孟杨杨,王恩康,等.补中益气汤经肠道菌群的调控改善脾虚证的作用机制研究[J].中国中药杂志,2024,49(4):1028-1043.
[35] 王楷,侯雨君,宋玮,等.泄泻中医证候动物模型研究进展[J].中国实验动物学报,2021,29(6):823-829.
[36] 刘洋,刘旭东,刘文俊,等.基于脾气虚的脾阳虚大鼠模型的复制方法及评价标准研究[J].中国医学创新,2016,13(3):25-28.
[37] 肥胖症中医诊疗方案专家共识[J].北京中医药大学学报,2022,45(8):786-794.
[38] 卢梦雄,黄金科,王一帆,等.高乳糖饮食叠加水平台法脾虚证模型研究与评价[J].世界中医药,2022,17(21):3033-3038.
[39] 谢慧臣,冉云,张云,等.生品与麸炒苍术对脾虚证大鼠小肠吸收转运相关蛋白载体的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2023,29(14):47-56.
[40] 葛士宁,樊薛津,张涵彧,等.基于PI3K/Akt通路探讨滋阴润肠法治疗慢传输型便秘机制[J].天津中医药,2024,41(8):1023-1029.
[41] 李哲,王继红,孙瑞,等.从小肠炭末推进率观察摩法的补泻效应[J].长春中医药大学学报,2022,38(3):273-277.
[42] LI WJ, LI L, ZHEN WY, et al. Ganodermaatrum polysaccharide ameliorates ROS generation and apoptosis in spleen and thymus of immunosuppressed mic. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017;99:199-208.
[43] SHI K, QU L, LIN X, et al. Deep-fried AtractylodisRhizomaprotectagainst spleen deficiency-induced diarrhea through regulating intestinal inflammatory response and gut microbiota. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;21(1):124.
[44] 郝洪丹,刘冠慧,李琴,等.加味理中汤方对脾虚泄泻小鼠疗效、免疫及肠道菌群的影响[J].黑龙江畜牧兽医,2024(10):81-88.
[45] 高丽君,王继红,黄泽芳,等.一指禅手法对脾虚型家兔小肠推进率的影响研究[J].辽宁中医杂志,2022,49(5):10-12.
[46] 何枭,杜鹏,周小雪,等.复方木香保健酒对脾虚大鼠的影响[J].重庆师范大学学报(自然科学版),2023,40(4):143-153.
[47] 李冰,张淑玲,范会织.健脾益气方对脾虚小鼠胃肠动力、血清淀粉酶、GAS及血浆MTL的影响[J].临床医学研究与实践,2024,9(8):1-4.
[48] 卢梦雄,薛红,张北华,等.脾虚证动物模型研究述评[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2024,26(3):652-658.
[49] 李伟强,李发炘,黎杰轩,等.游泳运动对高脂血症大鼠的改善作用[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(6):1312-1315.
[50] 路晓荣,杨亚军,马宁,等.高脂饲料诱导SD大鼠高脂血症模型的建立及评估[J].中兽医医药杂志,2020,39(6):8-12.
[51] 付满玲,姚淮育,胡月,等.高脂血症大鼠模型制备方法的探索性研究[J].中国医学工程,2020,28(5):1-5. |