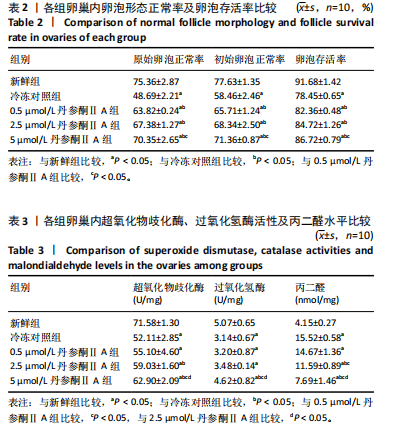
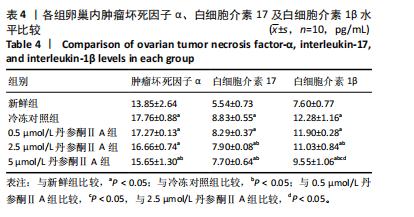
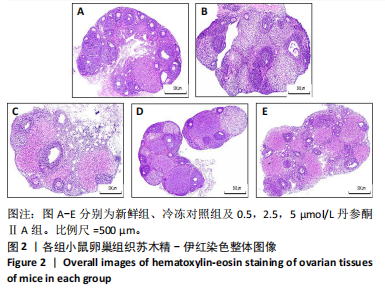
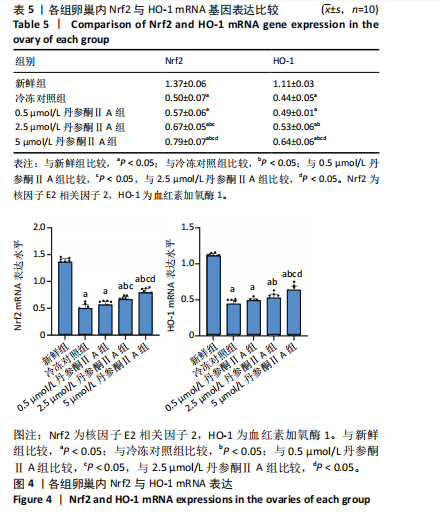
[1] 谷牧青, Pooja D,阮祥燕.女性生育力保护/保存进展[J].实用妇产科杂志,2021,37(10):721-723.
[2] COURBIERE B, ODAGESCU V, BAUDOT A, et al. Cryopreservation of the ovary by vitrification as an alternative to slow-cooling protocols. Fertil Steril. 2006;86(4 Suppl):1243-1251.
[3] WARNER RM, BROWN KS, BENSON JD, et al. Multiple cryoprotectant toxicity model for vitrification solution optimization. Cryobiology. 2022;108:1-9.
[4] 刘艳丽,申峻涵,杜姗姗,等.玻璃化冷冻和程序化冷冻人卵巢组织的效果[J].实用医学杂志,2021,37(24):3202-3207.
[5] 胡方方,李延,崔趁趁,等.人卵巢组织玻璃化冷冻及移植的影响因素分析[J].中国计划生育和妇产科,2023,15(9):20-24.
[6] MERCIER A, JOHNSON J, KALLEN AN. Prospective solutions to ovarian reserve damage during the ovarian tissue cryopreservation and transplantation procedure. FFertil Steril. 2024;122(4):565-573.
[7] SEOL SI, KANG IS, LEE JS, et al. Taurine Chloramine-Mediated Nrf2 Activation and HO-1 Induction Confer Protective Effects in Astrocytes. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024;13(2):169.
[8] MA K, WU HY, WANG SY, et al. The Keap1/Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway is involved in atrazine induced dopaminergic neurons degeneration via microglia activation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;226:112862.
[9] 杨璐恺,蒋利刚,崔妍婷,等.槲皮素在羊卵巢组织玻璃化冻存中的卵泡保护及抗氧化作用[J].山东大学学报(医学版),2020,58(9):1-7.
[10] 张珦,李惠,章宜芬,等.基于Nrf2/HO-1信号通路研究白藜芦醇在小鼠卵巢冷冻复苏中的保护作用及机制[J].广州中医药大学学报,2023,40(5):1221-1227.
[11] CHEN W, YUAN C, LU Y, et al. Tanshinone IIA Protects against Acute Pancreatitis in Mice by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress via the Nrf2/ROS Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:5390482.
[12] YOUM HW, LEE JR, LEE J, et al. Optimal vitrification protocol for mouse ovarian tissue cryopreservation: effect of cryoprotective agents and in vitro culture on vitrified-warmed ovarian tissue survival. Hum Reprod. 2014;29(4):720-730.
[13] GOUGEON A. Dynamics of follicular growth in the human: a model from preliminaryresults . Hum Reprod. 1986;1(2):81-87.
[14] KOMETAS M, CHRISTMAN GM, KRAMER J, et al. Methods of Ovarian Tissue Cryopreservation: Is Vitrification Superior to Slow Freezing?-Ovarian Tissue Freezing Methods. Reprod Sci. 2021;28(12):3291-3302.
[15] RAMOS L, GALBINSKI S, NACUL A, et al. Detailed Morphological Analysis of Cryoinjury in Human Ovarian Tissue Following Vitrification or Slow Freezing. Reprod Sci. 2022,29(8):2374-2381.
[16] 屈媛,王婷,付慧婕,等.丹参有效成分及药理作用研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2024,26(9):172-176.
[17] FANG ZY, ZHANG M, LIU JN, et al. Tanshinone IIA: A Review of its Anticancer Effects. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:611087.
[18] SHERAWAT K, MEHAN S. Tanshinone-IIA mediated neuroprotection by modulating neuronal pathways. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023;396(8):1647-1667.
[19] ROTH A, ZHAO P, SOUKUP ST, et al. Chemical Stability and Bioactivity of tanshinone I, tanshinone IIA, cryptotanshinone and dihydrotanshinone in in vitro test systems. Toxicol Lett. 2023;375:21-28.
[20] CARPI S, QUARTA S, DOCCINI S, et al. Tanshinone IIA and Cryptotanshinone Counteract Inflammation by Regulating Gene and miRNA Expression in Human SGBS Adipocytes. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(7):1029.
[21] YANG C, MU Y, LI S, et al. Tanshinone IIA: a Chinese herbal ingredient for the treatment of atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1321880.
[22] 秦文秀,许军峰,杨婷,等.丹参酮ⅡA治疗缺血性脑卒中后神经损伤的信号通路研究进展[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2023,28(6): 705-713.
[23] 杨芳,高素文,刘旋,等.丹参酮ⅡA通过调控p38MAPK/NF-κB信号通路减轻糖尿病雄性大鼠生殖损伤实验研究[J].陕西医学杂志, 2024,53(5):610-615.
[24] 姚兴凤,陆清芳,许常龙.抗氧化剂在卵巢组织玻璃化冷冻保存中的研究进展[J].中国妇幼保健,2024,39(5):958-961.
[25] NAJAFI A, ASADI E, BENSON JD. Comparative effects of a calcium chelator (BAPTA-AM) and melatonin on cryopreservation-induced oxidative stress and damage in ovarian tissue. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1): 22911.
[26] 李扬璐,阮祥燕,程姣姣,等.抗氧化剂联合应用优化人卵巢组织冻融效果的研究[J].首都医科大学学报,2021,42(4):526-532.
[27] SHIROMA ME, DAMOUS LL, COTRIM FP, et al. Pretreatment with melatonin improves ovarian tissue cryopreservation for transplantation. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021;19(1):17.
[28] ÑAUPAS L, BRITO D, DE SOUZA SS, et al. Alpha Lipoic Acid Supplementation Improves Ovarian Tissue Vitrification Outcome: An Alternative to Preserve the Ovarian Function of Morada Nova Ewe. Reprod Sci. 2021;28(11):3109-3122.
[29] 张海云,韩伟东,刘海梅,等.丹参酮ⅡA对急性肺损伤小鼠炎症因子和氧化应激水平的影响[J].解剖学研究,2020,42(6):491-495.
[30] 蒋丽,芮燕君,戴佳琪,等.丹参酮IIA对过氧化氢诱导的人晶状体上皮细胞凋亡和氧化应激的影响[J]. 眼科新进展,2021,41(9):838-842.
[31] 蒋诗敏,张珂嘉,周泰,等.丹参酮ⅡA抑制氧化应激减轻人脐静脉内皮细胞损伤[J].徐州医科大学学报,2021,41(4):235-240.
[32] 杨恒,张晶,罗明建,等.丹参酮Ⅱ_A磺酸钠注射液联合奥拉西坦对卒中后认知障碍患者认知功能、血清炎性因子和氧化应激指标的影响[J].药物评价研究,2021,44(7):1478-1482.
[33] 黄约诺,叶威,郑青秀,等.丹参酮ⅡA对脓毒症肺损伤大鼠氧化应激的影响[J].浙江临床医学,2022,24(10):1430-1432.
[34] 李洁,毛宇,蒋可欣,等.丹参酮ⅡA通过改善线粒体功能和氧化应激减轻大鼠认知障碍[J].华东理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021, 47(1):48-57.
[35] LI Y, HU Y, ZHU S, et al. Protective Effects of Reduced Glutathione and Ulinastatin on Xeno-transplanted Human Ovarian Tissue Against Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury. Cell Transplant. 2021;30: 963689721997151.
[36] 丁维,钟立仁,张海波,等.丹参酮ⅡA磺酸钠对高脂血症勃起功能障碍大鼠 Nrf2/HO-1通路及勃起功能的影响[J].陕西中医,2020, 41(11):1520-1523+1538.
[37] 耿银萍,程志杰,郝艳超,等.丹参酮IIA上调Nrf2/HO-1信号通路减轻海马神经元氧糖剥夺/复糖复氧损伤[J].微循环学杂志,2024, 34(2):12-18.
[38] 秦智,周敏.丹参酮Ⅱ_A通过Nrf2信号通路抑制肝组织铁死亡对非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠肝脏的保护作用[J].中国中药杂志,2024, 49(6):1611-1620.
[39] FU K, FENG C, SHAO L, et al. Tanshinone IIA exhibits anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects in LPS-stimulated bovine endometrial epithelial cells by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Res Vet Sci. 2021;136:220-226.
[40] LI H, WU M, GUO C, et al. Tanshinone IIA Regulates Keap1/Nrf2 Signal Pathway by Activating Sestrin2 to Restrain Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am J Chin Med. 2022;50(8):2125-2151. |