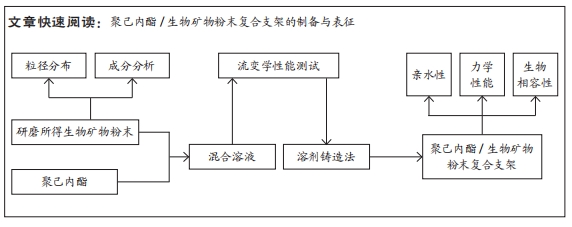
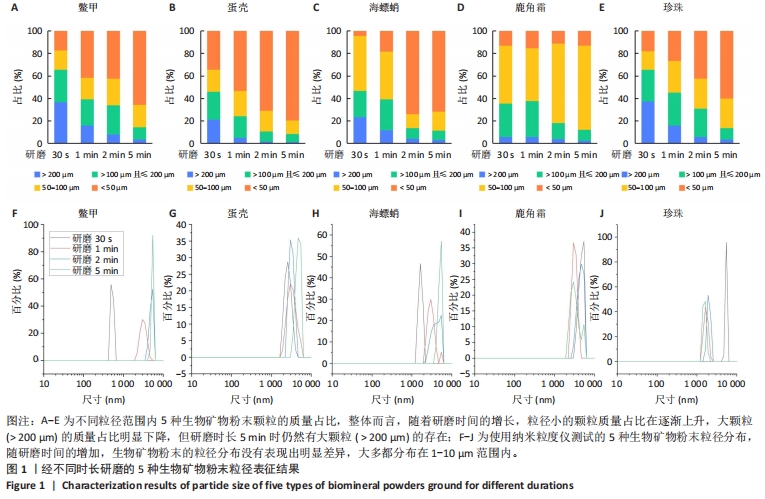
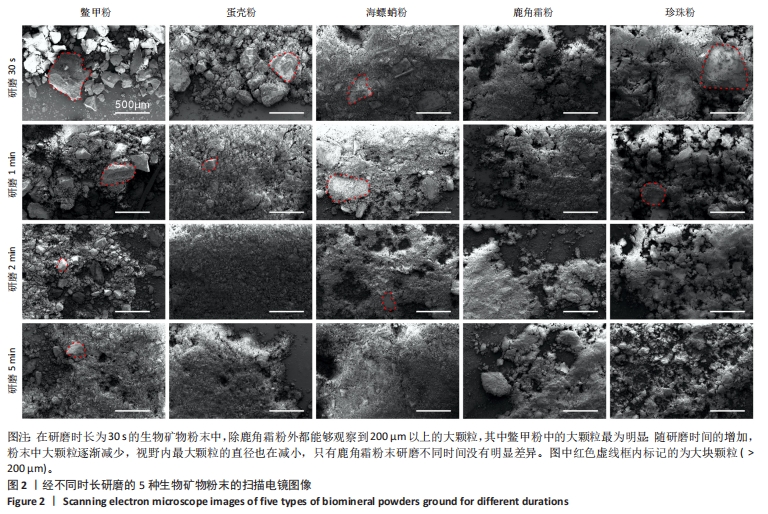
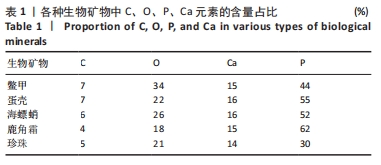
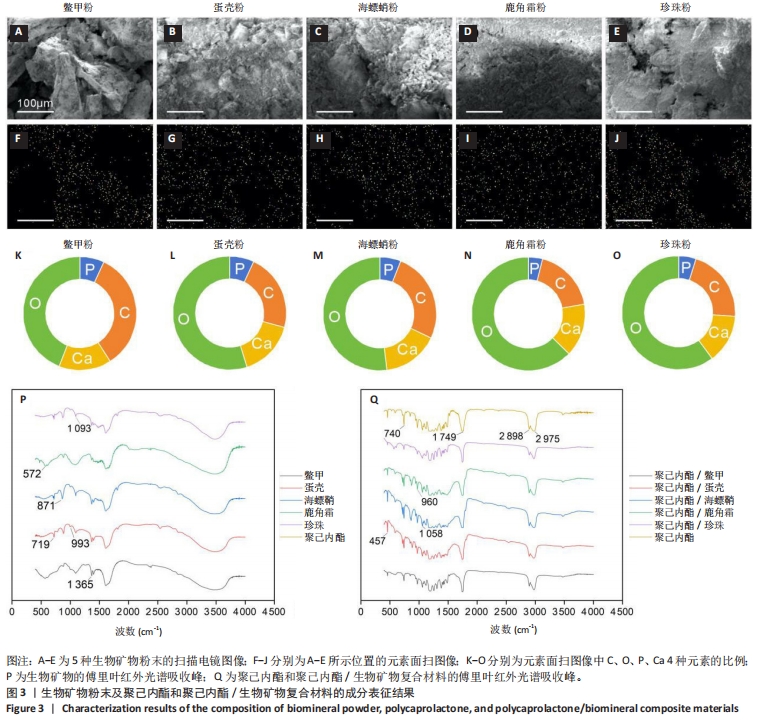
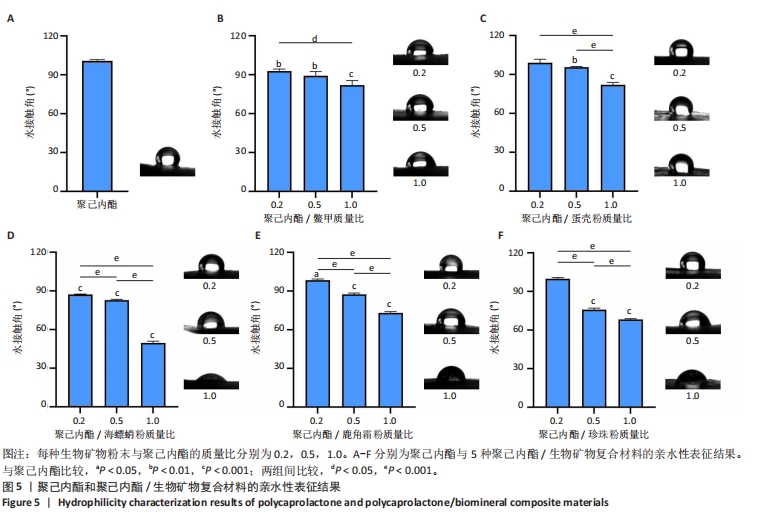
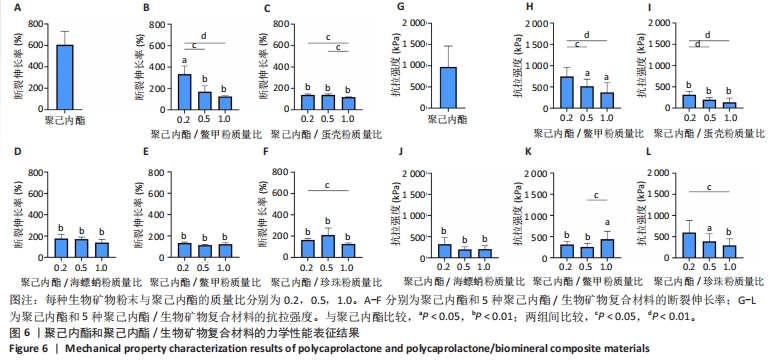
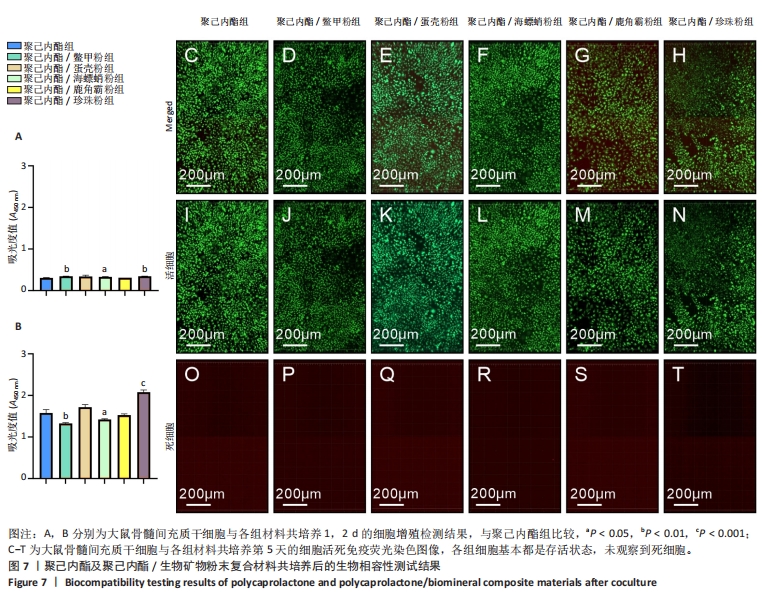
[1] COPP DH, SHIM SS. The homeostatic function of bone as a mineral reservoir. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1963;16(6):738-744.
[2] WANG W, YEUNG KW. Bone grafts and biomaterials substitutes for bone defect repair: A review. Bioact Mater. 2017;2(4):224-247.
[3] 李剑锋.生命的矿物质“银行”:骨骼[J].环球中医药,2008(2):62-63.
[4] ANNAMALAI RT, HONG X, SCHOTT NG, et al. Injectable osteogenic microtissues containing mesenchymal stromal cells conformally fill and repair critical-size defects. Biomaterials. 2019;208:32-44.
[5] 王兴,刘洪臣.自体骨移植修复种植位点骨缺损的研究进展[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2016,17(1):49-52.
[6] AZI ML, APRATO A, SANTI I, et al. Autologous bone graft in the treatment of posttraumatic bone defects: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskel Dis. 2016;17(1):465.
[7] 马武秀,程迅生.自体骨移植修复骨缺损的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(6):574-576.
[8] SHIBUYA N, JUPITER DC. Bone graft substitute: allograft and xenograft. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2015;32(1):21-34.
[9] BRACEY DN, JINNAH AH, WILLEY JS, et al. Investigating the osteoinductive potential of a decellularized xenograft bone substitute. Cells Tissues Organs. 2019;207(2):97-113.
[10] 曹国定,裴豫琦,刘军,等.骨缺损修复材料的研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2021,34(4):382-388.
[11] BLACK CR, GORIAINOV V, GIBBS D, et al. Bone tissue engineering. Curr Mol Biol Rep. 2015;1:132-140.
[12] DEC P, MODRZEJEWSKI A, PAWLIK A. Existing and novel biomaterials for bone tissue engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):529.
[13] FERRETRA AM, GENTILE P, CHIONO V, et al. Collagen for bone tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(9):3191-200.
[14] WUBNEH A, TSEKOURA EK, AYRANCI C, et al. Current state of fabrication technologies and materials for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2018;80:1-30.
[15] RODDY E, DEBAUN MR, DAOUD-GRAY A, et al. Treatment of critical-sized bone defects: clinical and tissue engineering perspectives. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2018;28(3):351-362.
[16] 秦宇星,任前贵,沈佩锋,等.组织工程技术治疗骨缺损:应用于临床还有多远?[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(29):4703-4708.
[17] TURNBULL G, CLARKE J, PICARD F, et al. 3D bioactive composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Bioact Mater. 2018;3(3):278-314.
[18] KARA A, DISTLER T, POLLEY C, et al. 3D printed gelatin/decellularized bone composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: Fabrication, characterization and cytocompatibility study. Mater Today Bio. 2022;15: 100309.
[19] 申亚杰,程雯,马晓婷,等.胶原/无机物复合支架在骨缺损修复中的研究进展[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2024,33(1):42-49.
[20] HASSANAJILI S, KARAMI-POUR A, ORYAN A, et al. Preparation and characterization of PLA/PCL/HA composite scaffolds using indirect 3D printing for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C. 2019;104: 109960.
[21] NITYA G, NAIR GT, MONY U, et al. In vitro evaluation of electrospun PCL/nanoclay composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012;23:1749-1761.
[22] RODENAS-ROCHINA J, RIBELLES JLG, LEBOURG M. Comparative study of PCL-HAp and PCL-bioglass composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013;24:1293-1308.
[23] XU M, LI Y, SUO H, et al. Fabricating a pearl/PLGA composite scaffold by the low-temperature deposition manufacturing technique for bone tissue engineering. Biofabrication. 2010;2(2):025002.
[24] NIE D, LUO Y, LI G, et al. The construction of multi-Incorporated polylactic composite nanofibrous scaffold for the potential applications in bone tissue regeneration. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021;11(9):2402.
[25] GANG F, YE W, MA C, et al. 3D printing of PLLA/biomineral composite bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(12):4280.
[26] ZHANG X, DU X, LI D, et al. Three dimensionally printed pearl powder/poly-caprolactone composite scaffolds for bone regeneration. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018;29(14):1686-1700.
[27] LIU Y, HUANG Q, FENG Q. 3D scaffold of PLLA/pearl and PLLA/nacre powder for bone regeneration. Biomed Mater. 2013;8(6):065001.
[28] DU X, YU B, PEI P, et al. 3D printing of pearl/CaSO4 composite scaffolds for bone regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(3):499-509.
[29] FENG Y, ZHU S, MEI D, et al. Application of 3D printing technology in bone tissue engineering: A review. Curr Drug Deliv. 2021;18(7):847-861.
[30] 刘嗣聪,刘宏治,殷亚然.生物可降解聚酯/生物陶瓷3D打印骨组织工程支架研究进展[J].复合材料学报,2024,41(4):1672-1693.
[31] 刚芳莉,石瑞,马春阳,等.低温冷凝沉积法3D打印骨组织工程左旋聚乳酸/珍珠粉复合支架[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(17): 2702-2707.
[32] JANG J H, CASTANO O, KIM HW. Electrospun materials as potential platforms for bone tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009; 61(12):1065-1083.
[33] GOUMA PI, RAMACHANDRAN K. Electrospinning for bone tissue engineering. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2008;2(1):1-7.
[34] NIE L, CHEN D, SUO J, et al. Physicochemical characterization and biocompatibility in vitro of biphasic calcium phosphate/polyvinyl alcohol scaffolds prepared by freeze-drying method for bone tissue engineering applications. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2012;100: 169-176.
[35] SUN W, GREGORY DA, TOMEH MA, et al. Silk fibroin as a functional biomaterial for tissue engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(3):1499.
[36] 陈佩,戴红莲.骨组织工程中天然生物衍生材料的研究进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2005,2(5):26-28.
[37] BRETT E, FLACCO J, BLACKSHEAR C, et al. Biomimetics of bone implants: the regenerative road. Biores Open Access. 2017;6(1):1-6. |