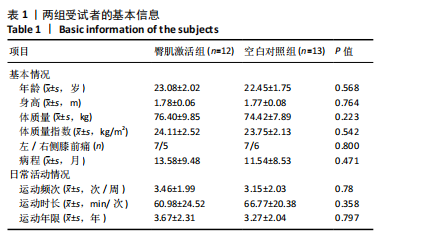
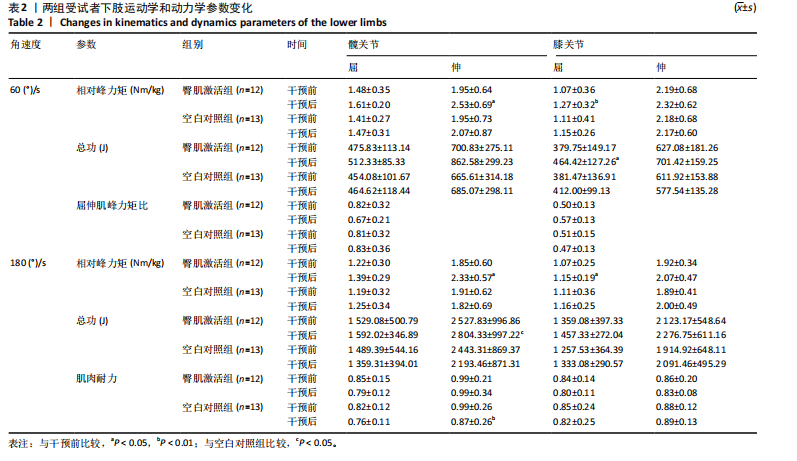
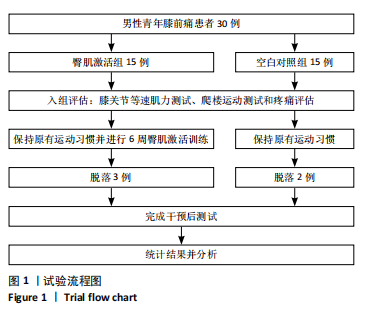
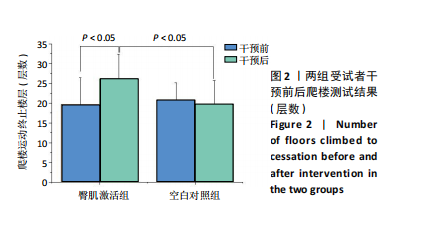
[1] CROSSLEY KM, STEFANIK JJ, SELFE J, et al. 2016 Patellofemoral pain consensus statement from the 4th International Patellofemoral Pain Research Retreat, Manchester. Part 1: Terminology, definitions, clinical examination, natural history, patellofemoral osteoarthritis and patient-reported outcome measures. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(14):839-843.
[2] COBURN SL, BARTON CJ, FILBAY SR, et al. Quality of life in individuals with patellofemoral pain: A systematic review including meta-analysis. Phys Ther Sport. 2018;33:96-108.
[3] MACLACHLAN LR, COLLINS NJ, HODGES PW, et al. Psychological and pain profiles in persons with patellofemoral pain as the primary symptom. Eur J Pain. 2020;24(6):1182-1196.
[4] DUONG V, OO WM, DING C, et al. Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Pain: A Review. JAMA. 2023;330(16):1568-1580.
[5] SMITH BE, SELFE J, THACKER D, et al. Incidence and prevalence of patellofemoral pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2018;13(1):e0190892.
[6] FERBER R, BOLGLA L, EARL-BOEHM JE, et al. Strengthening of the hip and core versus knee muscles for the treatment of patellofemoral pain: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. J Athl Train. 2015;50(4):366-377.
[7] FICK CN, GRANT C, SHEEHAN FT. Patellofemoral Pain in Adolescents: Understanding Patellofemoral Morphology and Its Relationship to Maltracking. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(2):341-350.
[8] BAZETT-JONES DM, NEAL BS, LEGG C, et al. Kinematic and Kinetic Gait Characteristics in People with Patellofemoral Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2023;53(2):519-547.
[9] FUKUDA TY, MELO WP, ZAFFALON BM, et al. Hip posterolateral musculature strengthening in sedentary women with patellofemoral pain syndrome: a randomized controlled clinical trial with 1-year follow-up. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2012;42(10):823-830.
[10] POWERS CM. The influence of altered lower-extremity kinematics on patellofemoral joint dysfunction: a theoretical perspective. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2003;33(11):639-646.
[11] XIE P, ISTVÁN B, LIANG M. The Relationship between Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome and Hip Biomechanics: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Healthcare (Basel). 2022;11(1):99.
[12] MARTINELLI N, BERGAMINI AN, BURSSENS A, et al. Does the Foot and Ankle Alignment Impact the Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Clin Med. 2022;11(8):2245.
[13] HAMSTRA-WRIGHT KL, AYDEMIR B, EARL-BOEHM J, et al. Lasting Improvement of Patient-Reported Outcomes 6 Months After Patellofemoral Pain Rehabilitation. J Sport Rehabil. 2017;26(4):223-233.
[14] 宣磊,吴建贤,潘家武.等速技术在康复医学领域中的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2019,25(7):788-792.
[15] COWAN SM, BENNELL KL, CROSSLEY KM, et al. Physical therapy alters recruitment of the vasti in patellofemoral pain syndrome. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002;34(12):1879-1885.
[16] BRITTO P, MUNIZ A, NADAL J. Electromyographic activity of the lower limb in runners with anterior knee pain while running. Res Biomed Eng. 2021; 37(5):135-142.
[17] 杨辰,曲峰,刘卉,等.髌股关节痛业余跑者性别特异的下肢生物力学特征[J].医用生物力学,2020,35(6):672-678.
[18] BOLGLA LA, MALONE TR, UMBERGER BR, et al. Comparison of hip and knee strength and neuromuscular activity in subjects with and without patellofemoral pain syndrome. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2011;6(4):285-296.
[19] MCCLINTON SM, COBIAN DG, HEIDERSCHEIT BC. Physical Therapist Management of Anterior Knee Pain. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2020; 13(6):776-787.
[20] 杨雪清,程亮.篮球运动员躯干和下肢等速肌力分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(12):1835-1840.
[21] CHENG L, CHANG S, QIAN L, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for isokinetic muscle strength around the knee joint in athletes with patellar tendinopathy. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2019;59(5):822-827.
[22] 林长地,程亮,林烯.全身振动训练对老年女性平衡能力和下肢关节肌力的影响[[J]首都体育学院学报,2015,27(6):572-576.
[23] MCCORMACK HM, HORNE DJ, SHEATHER S. Clinical applications of visual analogue scales: a critical review. Psychol Med. 1988;18(4):1007-1019.
[24] WANG L, YU G, ZHANG R, et al. Positive effects of neuromuscular exercises on pain and active range of motion in idiopathic frozen shoulder: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):50.
[25] GARCÍA-PÉREZ-DE-SEVILLA G, SÁNCHEZ-PINTO PINTO B. Effectiveness of physical exercise and neuromuscular electrical stimulation interventions for preventing and treating intensive care unit-acquired weakness: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Intensive Crit Care Nurs. 2023;74:103333.
[26] EMERY CA, OWOEYE OBA, RÄISÄNEN AM, et al. The “SHRed Injuries Basketball” Neuromuscular Training Warm-up Program Reduces Ankle and Knee Injury Rates by 36% in Youth Basketball. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2022;52(1):40-48.
[27] FARINA D, GANDEVIA S. The neural control of movement: a century of in vivo motor unit recordings is the legacy of Adrian and Bronk. J Physiol. 2024;602(2):281-295.
[28] PENG Y, WANG Z. Differential Cortical and Subcortical Activations during Different Stages of Muscle Control: A Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Brain Sci. 2024;14(4):404.
[29] ROSTRON ZP, GREEN RA, KINGSLEY M, et al. Associations Between Measures of Physical Activity and Muscle Size and Strength: A Systematic Review. Arch Rehabil Res Clin Transl. 2021;3(2):100124.
[30] DUFFEY MJ, MARTIN DF, CANNON DW, et al. Etiologic factors associated with anterior knee pain in distance runners. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000; 32(11):1825-1832.
[31] HIEMSTRA LA, KERSLAKE S, IRVING C. Anterior knee pain in the athlete. Clin Sports Med. 2014;33(3):437-459.
[32] COWAN SM, CROSSLEY KM, BENNELL KL. Altered hip and trunk muscle function in individuals with patellofemoral pain. Br J Sports Med. 2009; 43(8):584-588.
[33] POHL MB, PATEL C, WILEY JP, et al. Gait biomechanics and hip muscular strength in patients with patellofemoral osteoarthritis. Gait Posture. 2013; 37(3):440-444.
[34] WILLSON JD, PETROWITZ I, BUTLER RJ, et al. Male and female gluteal muscle activity and lower extremity kinematics during running. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2012;27(10):1052-1057.
[35] JORGE RT, SOUZA MC, CHIARI A, et al. Progressive resistance exercise in women with osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2015;29(3):234-243.
[36] BAKER KR, NELSON ME, FELSON DT, et al. The efficacy of home based progressive strength training in older adults with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. J Rheumatol. 2001;28(7):1655-1665.
[37] SLED EA, KHOJA L, DELUZIO KJ, et al. Effect of a home program of hip abductor exercises on knee joint loading, strength, function, and pain in people with knee osteoarthritis: a clinical trial. Phys Ther. 2010;90(6):895-904.
[38] JEONG J, CHOI DH, SHIN CS. Core Strength Training Can Alter Neuromuscular and Biomechanical Risk Factors for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(1):183-192.
[39] HOTT A, BROX JI, PRIPP AH, et al. Effectiveness of Isolated Hip Exercise, Knee Exercise, or Free Physical Activity for Patellofemoral Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(6):1312-1322.
[40] HOTT A, BROX JI, PRIPP AH, et al. Patellofemoral pain: One year results of a randomized trial comparing hip exercise, knee exercise, or free activity. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020;30(4):741-753.
[41] YUENYONGVIWAT V, DUANGMANEE S, IAMTHANAPORN K, et al. Effect of hip abductor strengthening exercises in knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):284.
[42] SIGWARD SM, OTA S, POWERS CM. Predictors of frontal plane knee excursion during a drop land in young female soccer players. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2008;38(11):661-667. |