中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (在线): 1-9.
• •
类风湿关节炎与冠状动脉粥样硬化的因果关系:GWAS数据库血清代谢物和炎症因子数据
张艺博1,卢健棋2,毛美玲1,庞 延1,董 礼1,杨尚冰1,肖 湘1
- 1广西中医药大学,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530000;2广西中医药大学第一附属医院心内科,国家中医心血管病临床医学研究中心 分中心,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530000
Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors
Zhang Yibo1, Lu Jianqi2, Mao Meiling1, Pang Yan1, Dong Li1, Yang Shangbing1, Xiao Xiang1
- 1Guangxi University of traditional Chinese Medicine Graduate School Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region; 2Department of Cardiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of traditional Chinese medicine, the sub center of the National Clinical Medical Research Center for cardiovascular diseases of traditional Chinese medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region
摘要:

文题释义:
孟德尔随机化:是一种利用遗传变异作为工具变量来探索暴露与结果的因果关系的分析,具有低成本、少时间、可行性高的优点,并且不易受到社会和心理因素等混杂因素的影响,可以最大程度地避免观察性研究中的反向因果偏差。
类风湿关节炎:是一种持久的免疫系统疾病,特征是关节炎症和不适。炎症与类风湿关节炎和冠状动脉粥样硬化均相关,表明这些疾病之间可能存在共同的病理生理途径。
背景:类风湿性关节炎与冠状动脉粥样硬化之间的关系受到广泛关注,炎症与类风湿性关节炎和冠状动脉粥样硬化均相关,表明这两种疾病之间可能存在共同的病理生理途径,但观察性研究尚未阐明因果关系。
目的:通过孟德尔随机化分析探讨类风湿关节炎与冠状动脉粥样硬化之间是否存在因果关系,以及与1 400种血清代谢物和91种炎症因子之间的潜在因果关联。
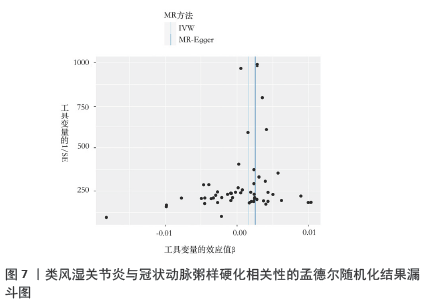
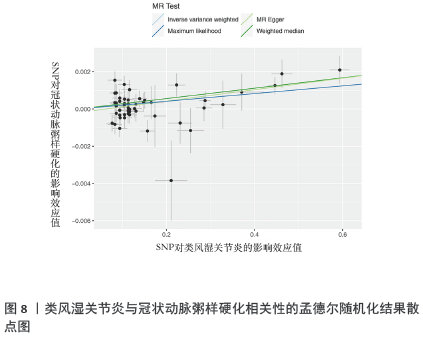
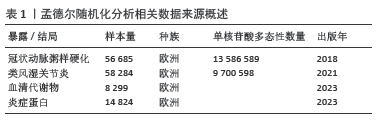
方法:冠状动脉粥样硬化数据来自Finngen数据库,类风湿关节炎数据来自IEU OpenGWAS数据库,血清代谢物数据来自加拿大老龄化纵向研究、奥格斯堡地区合作健康研究和英国双胞胎项目研究,91种炎症蛋白数据来源于2023年发表在《Nature Immunology》的研究。IEU OpenGWAS数据库是由布里斯托大学MRC综合流行病学单位开发的,提供了一个全面的全基因组关联研究数据集,该项目包含超过40 000个GWAS摘要数据集,涉及广泛的人类疾病和特征。FinnGen是一项全球性的GWAS荟萃分析,于2017年秋季在芬兰启动,由芬兰大学、医院和医院区、THL、生物库及国际制药公司共同开发。使用全基因组关联研究的数据进行孟德尔随机化分析,采用逆方差加权法、MR-Egger回归法、加权中位数法、加权模型法和简单模型法来评估因果效应,其中逆方差加权法是主要分析方法。为了增强稳健性,使用Cochran’s Q检验MR-Egger截距进行敏感性分析。
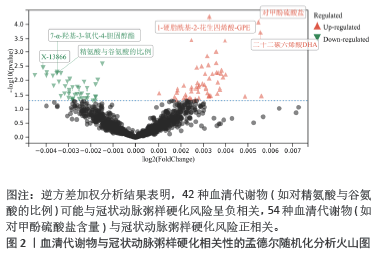
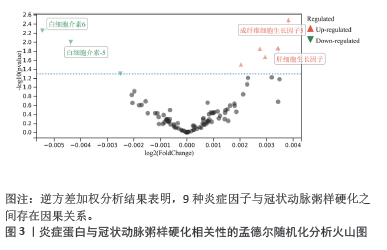
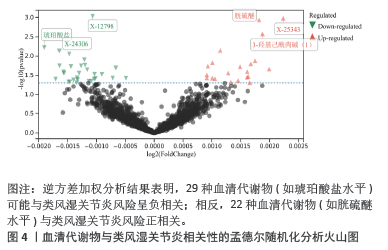
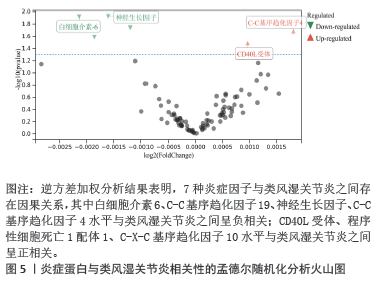
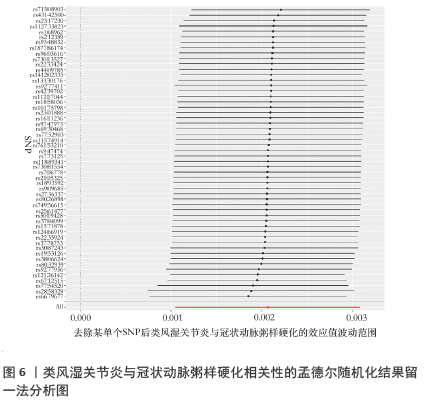
结果与结论:①逆方差加权分析结果显示,类风湿关节炎与冠状动脉粥样硬化相对风险增加呈正相关(OR=1.002,95%CI=1.001-1.003,P=0.003);冠状动脉粥样硬化与类风湿关节炎不存在反向因果关系;96种血清代谢物和9种炎症因子与冠状动脉粥样硬化之间存在因果关系;51种血清代谢物和7种炎症因子与类风湿关节炎之间存在因果关系。②研究提供了类风湿关节炎与冠状动脉粥样硬化之间的流行病学证据,强调了血清代谢物和炎症因子在这些疾病的发病机制中的潜在作用,可能有助于开发新的治疗策略。由于对亚洲人群数据收录有限,当下研究多采用国际数据库、欧洲群体分析,通过收集和分析欧洲人群的健康数据,可以更好地理解中国医学在欧洲的应用效果和潜在影响,进一步推进现代中西医结合的实践;同时通过与欧洲数据库的比较研究,可以揭示不同人群间的遗传差异和疾病易感性,从而为欧洲人群提供更全面的中国医学信息,为全球健康研究提供更多维度和视角。
关键词:类风湿关节炎;冠状动脉粥样硬化;血清代谢物;炎症因子;因果关系;孟德尔随机化分析;工程化组织构建
热点词:类风湿关节炎(10.3%),冠状动脉粥样硬化(11.7%)
中图分类号: