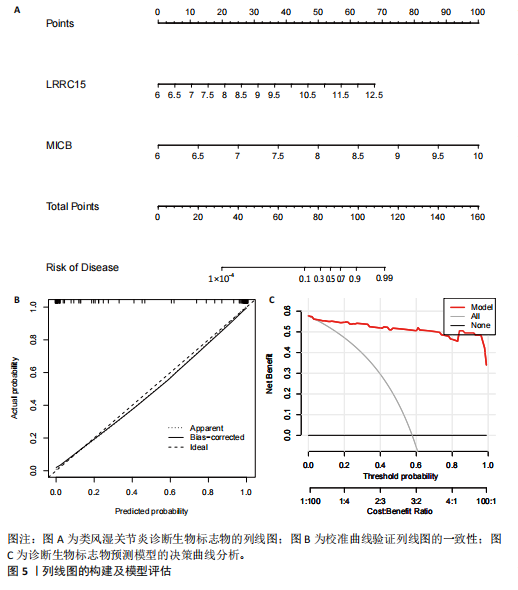
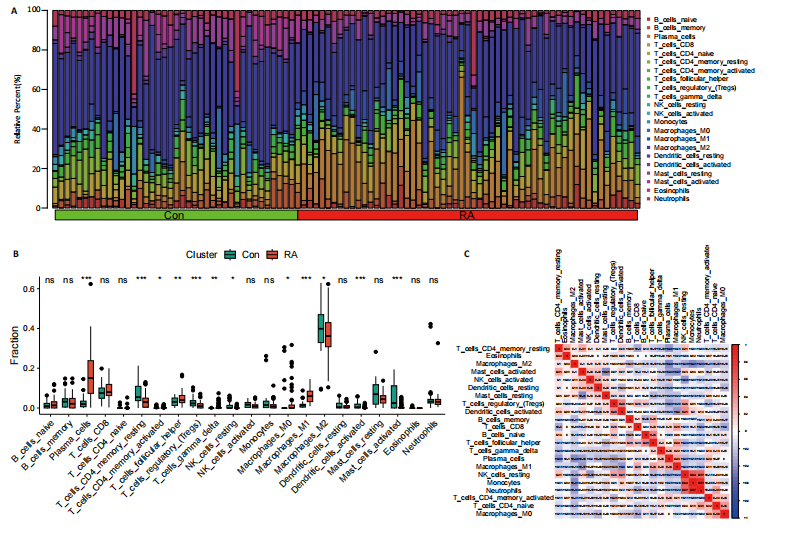
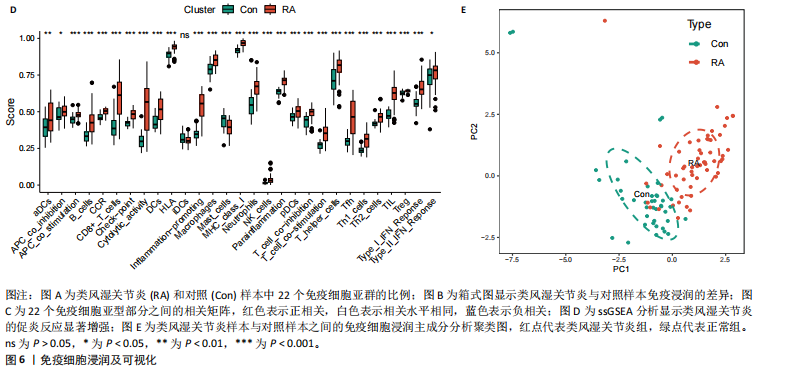
[1] MCINNES IB, SCHETT G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(23):2205-2219.
[2] DI MATTEO A, BATHON JM, EMERY P. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2023; 402(10416):2019-2033.
[3] LEE DM, WEINBLATT ME. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2001;358(9285):903-911.
[4] SILMAN AJ, PEARSON JE. Epidemiology and genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2002;4 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S265-S272.
[5] ALETAHA D, NEOGI T, SILMAN AJ, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(9):2569-2581.
[6] BARTOK B, FIRESTEIN GS. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2010; 233(1):233-255.
[7] WEYAND CM, GORONZY JJ. The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Immunol. 2021; 22(1):10-18.
[8] MÜLLER-LADNER U, OSPELT C, GAY S, et al. Cells of the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(6):223.
[9] WU F, GAO J, KANG J, et al. B Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Pathogenic Mechanisms and Treatment Prospects. Front Immunol. 2021;12:750753.
[10] FLOUDAS A, NETO N, ORR C, et al. Loss of balance between protective and pro-inflammatory synovial tissue T-cell polyfunctionality predates clinical onset of rheumatoid arthritis [published correction appears in Ann Rheum Dis. 2023; 82(2):e53]. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81(2): 193-205.
[11] JIANG Q, YANG G, LIU Q, et al. Function and Role of Regulatory T Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:626193.
[12] ZHONG Y, ZHANG W, HONG X, et al. Screening Biomarkers for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Based on Machine Learning and Exploring Their Expression Correlations With the Ratios of Various Immune Cells. Front Immunol. 2022;13:873787.
[13] YANG Y, CAO Y, HAN X, et al. Revealing EXPH5 as a potential diagnostic gene biomarker of the late stage of COPD based on machine learning analysis. Comput Biol Med. 2023;154:106621.
[14] UNGETHUEM U, HAEUPL T, WITT H, et al. Molecular signatures and new candidates to target the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Physiol Genomics. 2010;42A(4):267-282.
[15] WOETZEL D, HUBER R, KUPFER P, et al. Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R84.
[16] HUBER R, HUMMERT C, GAUSMANN U, et al. Identification of intra-group, inter-individual, and gene-specific variances in mRNA expression profiles in the rheumatoid arthritis synovial membrane. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(4):R98.
[17] BROEREN MG, DE VRIES M, BENNINK MB, et al. Disease-Regulated Gene Therapy with Anti-Inflammatory Interleukin-10 Under the Control of the CXCL10 Promoter for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Hum Gene Ther. 2016;27(3):244-254.
[18] GUO Y, WALSH AM, FEARON U, et al. CD40L-Dependent Pathway Is Active at Various Stages of Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Progression. J Immunol. 2017;198(11): 4490-4501.
[19] WANG H, YANG F, LUO Z. An experimental study of the intrinsic stability of random forest variable importance measures. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016;17:60.
[20] LIN X, LI C, ZHANG Y, et al. Selecting Feature Subsets Based on SVM-RFE and the Overlapping Ratio with Applications in Bioinformatics. Molecules. 2017;23(1):52.
[21] YANG C, DELCHER C, SHENKMAN E, et al. Machine learning approaches for predicting high cost high need patient expenditures in health care. Biomed Eng Online. 2018; 17(Suppl 1):131.
[22] SANZ H, VALIM C, VEGAS E, et al. SVM-RFE: selection and visualization of the most relevant features through non-linear kernels. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018; 19(1):432.
[23] ZENG D, YE Z, SHEN R, et al. IOBR: Multi-Omics Immuno-Oncology Biological Research to Decode Tumor Microenvironment and Signatures. Front Immunol. 2021;12:687975.
[24] RIVELLESE F, PITZALIS C. Cellular and molecular diversity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Semin Immunol. 2021;58:101519.
[25] JANG S, KWON EJ, LEE JJ. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Roles of Diverse Immune Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(2): 905.
[26] AN Q, RAHMAN S, ZHOU J, et al. A Comprehensive Review on Machine Learning in Healthcare Industry: Classification, Restrictions, Opportunities and Challenges. Sensors (Basel). 2023; 23(9):4178.
[27] TANG H, LIU W, XU Z, et al. Integrated microenvironment-associated genomic profiles identify LRRC15 mediating recurrent glioblastoma-associated macrophages infiltration. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(12):5534-5546.
[28] RAY U, PATHOULAS CL, THIRUSANGU P, et al. Exploiting LRRC15 as a Novel Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2022;82(9):1675-1681.
[29] PURCELL JW, TANLIMCO SG, HICKSON J, et al. LRRC15 Is a Novel Mesenchymal Protein and Stromal Target for Antibody-Drug Conjugates. Cancer Res. 2018;78(14):4059-4072.
[30] CHEN YJ, CHANG WA, HSU YL, et al. Deduction of Novel Genes Potentially Involved in Osteoblasts of Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Next-Generation Sequencing and Bioinformatic Approaches. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(11):2396.
[31] CHEN YJ, CHANG WA, WU LY, et al. Systematic Analysis of Transcriptomic Profile of Chondrocytes in Osteoarthritic Knee Using Next-Generation Sequencing and Bioinformatics. J Clin Med. 2018;7(12):535.
[32] WANG Y, LIU Y, ZHANG M, et al. LRRC15 promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by modulating p65 cytoplasmic/nuclear translocation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):65.
[33] SINGH P, WANG M, MUKHERJEE P, et al. Transcriptomic and epigenomic analyses uncovered Lrrc15 as a contributing factor to cartilage damage in osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):21107.
[34] FERRARI DE ANDRADE L, TAY RE, PAN D, et al. Antibody-mediated inhibition of MICA and MICB shedding promotes NK cell-driven tumor immunity. Science. 2018;359(6383):1537-1542.
[35] STEPHENS HA. MICA and MICB genes: can the enigma of their polymorphism be resolved? Trends Immunol. 2001;22(7): 378-385.
[36] FERRARI DE ANDRADE L, KUMAR S, LUOMA AM, et al. Inhibition of MICA and MICB Shedding Elicits NK-Cell-Mediated Immunity against Tumors Resistant to Cytotoxic T Cells. Cancer Immunol Res. 2020;8(6):769-780.
[37] COURAU T, BONNEREAU J, CHICOTEAU J, et al. Cocultures of human colorectal tumor spheroids with immune cells reveal the therapeutic potential of MICA/B and NKG2A targeting for cancer treatment. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7(1):74.
[38] ALVES DA SILVA PH, XING S, KOTINI AG, et al. MICA/B antibody induces macrophage-mediated immunity against acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2022;139(2):205-216.
[39] LÜ M, XIA B, LI J, et al. MICB microsatellite polymorphism is associated with ulcerative colitis in Chinese population. Clin Immunol. 2006;120(2):199-204.
[40] OTA M, KATSUYAMA Y, KIMURA A, et al. A second susceptibility gene for developing rheumatoid arthritis in the human MHC is localized within a 70-kb interval telomeric of the TNF genes in the HLA class III region. Genomics. 2001;71(3):263-270.
[41] LÓPEZ-ARBESU R, BALLINA-GARCÍA FJ, ALPERI-LÓPEZ M, et al. MHC class I chain-related gene B (MICB) is associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007;46(3):426-430. |