[1] ABDULLAH AF, DITTO EW 3RD, BYRD EB, et al. Extreme-lateral lumbar disc herniations. Clinical syndrome and special problems of diagnosis. J Neurosurg. 1974;41(2):229-234.
[2] BERRA LV, DI RITA A, LONGHITANO F, et al. Far lateral lumbar disc herniation part 1: Imaging, neurophysiology and clinical features. World J Orthop. 2021;12(12):961-969.
[3] AHN Y, YOO BR, JUNG JM. The irony of the transforaminal approach: A comparative cohort study of transforaminal endoscopic lumbar discectomy for foraminal versus paramedian lumbar disc herniation. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(40):e27412.
[4] GOKYAR A, TONGA F. Clinical experience on intertransverse extraforaminal approach for far lateral disc herniations: 132 cases. Niger J Clin Pract. 2022;25(5):630-635.
[5] ÜNSAL ÜÜ SR, SENTURK S. Minimally Invasive Far-Lateral Microdiscectomy: A New Retractor for Far-Lateral Lumbar Disc Surgery. Cureus. 2021;13(1):e12625.
[6] REN W, CHEN Y, XIANG L. Minimally invasive surgical techniques for the therapy of far lateral disc herniation in middle-aged and elderly patients. Comput Assist Surg (Abingdon). 2019;24(sup1):13-19
[7] LIN L, KE ZY, CHU L, et al. Full-endoscopic lumbar discectomy via lateral superior articular process approach for treating far lateral lumbar disc herniation: a retrospective study and technical note. Int Orthop. 2023;47(11):2843-2850.
[8] HEO DH, SHARMA S, PARK CK. Endoscopic Treatment of Extraforaminal Entrapment of L5 Nerve Root (Far Out Syndrome) by Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic Approach: Technical Report and Preliminary Clinical Results. Neurospine. 2019;16(1):130-137.
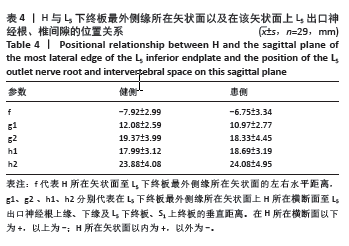
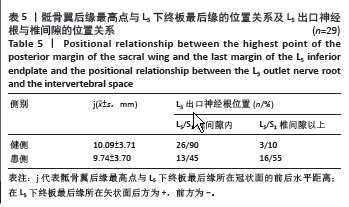
[9] 毕经纬,任佳彬,刘鑫,等.3D-CT指导单侧双通道内镜下定位L5、S1神经根及椎间隙[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(33):5283-5289.
[10] AHN Y, LEE U, KIM WK, et al. Five-year outcomes and predictive factors of transforaminal full-endoscopic lumbar discectomy. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(48):e13454.
[11] CONNOLLY J, BORJA AJ, KVINT S, et al. Postoperative Outcomes and Resource Utilization Following Open vs Endoscopic Far Lateral Lumbar Discectomy. Int J Spine Surg. 2023;17(3):350-355.
[12] LI P, YANG F, CHEN Y, et al. Percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy for different types of lumbar disc herniation: A retrospective study. J Int Med Res. 2021;49(10): 3000605211055045.
[13] CHU PL, WANG T, ZHENG JL, et al. Global and Current Research Trends of Unilateral Biportal Endoscopy/Biportal Endoscopic Spinal Surgery in the Treatment of Lumbar Degenerative Diseases: A Bibliometric and Visualization Study. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(4):635-643.
[14] 刘昌震,黄卫国,李骥征,等.单孔分体内镜辅助后外侧入路腰椎椎体间融合术治疗L4、5退变性腰椎滑脱症的临床疗效分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(8):989-995.
[15] ZHANG Y, FENG B, HU P, et al. One-hole split endoscopy technique versus unilateral biportal endoscopy technique for L5-S1 lumbar disk herniation: analysis of clinical and radiologic outcomes. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):668.
[16] LUAN J, WANG Q, LYU D, et al. Comparable effectiveness of transforaminal endoscopic spine system technique combined with selective nerve root block between far lateral lumbar disc herniation and central or paracentral herniation. Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2022;33(3): 513-520.
[17] DE BONIS P, MUSIO A, MONGARDI L, et al. Transpars approach for L5-S1 foraminal and extra-foraminal lumbar disc herniations: technical note. J Neurosurg Sci. 2023;67(2):213-218.
[18] EVRAN S, KATAR S. Evaluation of the effectiveness of transforaminal epidural steroid injection in far lateral lumbar disc herniations. A transforaminalis epiduralis szteroidbefecskendezés hatékonyságának értékelése távoli lateralis ágyéki sérv esetén. Ideggyogy Sz. 2021;74(1-2):27
[19] GURBUZ H, SECER M, GOKBEL A. Efficacy of epidural steroid injections and evaluation of surgical and anesthetic approaches in far-lateral disc herniations. Pain Manag. 2023;13(2):95-104.
[20] DOGU H, OZDEMIR NG, YILMAZ H, et al. Long-term follow-up results of surgically treated patients with foraminal and far lateral disc herniations. Br J Neurosurg. 2023;37(1):49-52.
[21] ALBAYRAK S, ATCI İB. A Retrospective Study of Far Lateral Midline Microlumbar Discectomy in 20 Patients at a Single Center in Turkey. Med Sci Monit. 2023;29:e941257.
[22] TELFEIAN AE, OYELESE A, FRIDLEY J, et al. Prognosis for Recovery of Foot Drop after Transforaminal Endoscopic Decompression of Far Lateral Lumbar 5-Sacral 1 Herniated Disc: Case Series. Pain Physician. 2019;22(2):E97-E103.
[23] 崔冠宇,舒雄,刘亚军,等.经皮椎间孔镜下椎间盘切除治疗伴有高髂嵴的L5/S1椎间盘突出症[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(27): 4333-4338.
[24] ANTONY J, NGOC LE DH, YANG L. Case Series of Tubular Retractor Assisted Minimally Invasive Extraforaminal L5/S1 Microdiskectomy. World Neurosurg. 2022;165:e563-e570.
[25] AHN Y, LEE U, LEE YJ, et al. Laser-Assisted Microdiscectomy for Far Lateral Lumbar Disc Herniation at the L5-S1 Level. Photomed Laser Surg. 2018;36(10):555-561.
[26] PHAN K, DUNN AE, RAO PJ, et al. Far lateral microdiscectomy: a minimally-invasive surgical technique for the treatment of far lateral lumbar disc herniation. J Spine Surg. 2016;2(1):59-63.
[27] SIU TLT, LIN K. Direct Tubular Lumbar Microdiscectomy for Far Lateral Disc Herniation: A Modified Approach. Orthop Surg. 2016;8(3): 301-308.
[28] BERRA LV, FOTI D, AMPOLLINI A, et al. Contralateral approach for far lateral lumbar disc herniations: a modified technique and outcome analysis of nine patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(6):709-713.
[29] DI RITA A, LEVI V, GRIBAUDI GL, et al. The interlaminar contralateral approach to far-lateral lumbar disc herniations: a single-center comparison with traditional techniques. J Neurosurg Sci. 2023;67(2): 191-199.
[30] KONG L, HUANG Y, YAO T, et al. Retrospective Analysis of Paraspinal Muscle-Splitting Microscopic-Assisted Discectomy Versus Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy for the Treatment of Far-Lateral Lumbar Disc Herniation. Turk Neurosurg. 2023;33(4):541-547.
[31] PARK JH, JUNG JT, LEE SJ. How I do It: L5/S1 foraminal stenosis and far-lateral lumbar disc herniation with unilateral bi-portal endoscopy. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2018;160(10):1899-1903.
[32] RAN B, CHEN R, SONG C, et al. Percutaneous Endoscopic Discectomy Via a Transforaminal Approach for L5/S1 Far-Lateral Disc Herniation Assisted by Intraoperative Computed Tomography. World Neurosurg. 2022;166:e823-e831.
[33] ZHANG Y, FENG B, NING H, et al. One-hole split endoscope technique for migrated lumbar disc herniation: a single-centre, retrospective study of a novel technique. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):483.
[34] 刘昌震,王红艳,刘鑫,等.单孔分体内镜颈椎钩状突部分切除三维影像解剖测量[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(13):1214-1219.
[35] LI T, WU G, DONG Y, et al. Kambin’s triangle-related data based on magnetic resonance neurography and its role in percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic lumbar interbody fusion. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):543.
[36] NAGAMATSU M, MASTE P, TANAKA M, et al. Usefulness of 3D CT/MRI Fusion Imaging for the Evaluation of Lumbar Disc Herniation and Kambin’s Triangle. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022;12(4):956.
[37] SOLIMAN H, FRIDLEY J, TELFEIAN A, et al. Minimally Invasive, Far Lateral Lumbar Microdiscectomy with Intraoperative Computed Tomography Navigational Assistance and Electrophysiological Monitoring. World Neurosurg. 2019;122:e1228-e1239.
[38] WANG S, AIKEREMU D, KAHAER A, et al. Anatomical and imaging measurements of the angle between the axis of the lumbar pedicle and lateral isthmus margin and its clinical significance. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):509.
[39] KAYA M, KESKIN E, CEYLAN D, et al. Surgical Treatment of Far Lateral Lumbar Disc Herniation: Outcomes of the Safe and Simple Midline Approach. Cureus. 2022;14(8):e27907.
[40] AL-KHAWAJA DO, MAHASNEH T, LI JC. Surgical treatment of far lateral lumbar disc herniation: a safe and simple approach. J Spine Surg. 2016;2(1):21-24.
[41] GREIL ME, OGUNLADE JI, BERGQUIST J, et al. Full-endoscopic trans-pars interarticularis approach for far lateral lumbar discectomy. Eur Spine J. 2023;32(8):2709-2716.
|