1.1 设计 “WGCNA”分析、“GO”与“KEGG”功能富集分析、“Random Forest”机器学习算法、“LASSO”机器学习算法、“GMM”机器学习算法、类风湿关节炎预测模型构建及验证、外部样本验证、“CIBERSORT”免疫浸润、“ssGSEA”免疫调控分析、“ssGSEA” 生物学功能分析。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2024年5-7月在广西中医药大学附属瑞康医院完成。
1.3 资料 从“GEO DataSets”公共数据库(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)筛选类风湿关节炎相关微阵列数据集,搜索关键字为“rheumatoid arthritis”,具体检索语句如下:(“arthritis, rheumatoid”[MeSH Terms] OR rheumatoid arthritis[All Fields]) AND “Homo sapiens”[porgn] AND (“gse”[Filter] AND “Expression profiling by array”[Filter]),共获得198个相关数据集,按样本量从高到底排序,过滤掉与类风湿关节炎诊断二分类变量不相关的数据集,筛选获得训练集GSE15573芯片,获得验证集GSE97779芯片与GSE55235芯片(表1)。

1.4 方法
1.4.1 类风湿关节炎差异表达基因筛选 使用R软件中“limma”包与“affy”包,对GSE15573、GSE97779和GSE55235基因数据集进行数据清洗与矩阵整理,对基因表达矩阵数据去除重复值、去除缺失值、表达分布归一化和log2标准化处理,制作分组矩阵、比较矩阵并进一步利用“贝叶斯”函数处理校正。对于独立训练集GSE15573进行差异基因筛选。采用平均绝对折叠变化法,计算所有差异基因 log FC绝对值的平均值与二倍绝对值的标准差之和,从而确定符合数据分布情况的log FC Cut Off阈值,当log FC绝对值大于此阈值且当-log10 (P.Value) < 0.05时,所筛选的基因作为类风湿关节炎差异表达基因,继而使用“ggplot2”函数包和“pheatmap”函数包绘制类风湿关节炎差异表达基因的火山图和差异化热图。
1.4.2 “WGCNA”分析 加权基因共表达网络分析(Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis,WGCNA)是一种用于分析基因相关性的系统生物学模式办法,主要应用于不同样品间的基因表达数据。该方法能够识别在表达水平上表现出高度一致变化的基因组,并通过分析这些基因组之间的关系及其与特定表型的关联,来识别潜在的生物标志物或治疗靶标。为了分析数据清洗后的基因表达矩阵,使用R中的“WGCNA”和“limma”包,首先去除非典型样本,然后对各样本进行聚类,继而构建拓扑重叠矩阵和无标度网络,随之进行动态基因模块的融合,并识别与临床表型最一致的模块,最后将所挑出模块中的基因进行组织汇总,获得“WGCNA”特征基因。
1.4.3 类风湿关节炎-线粒体自噬相关基因筛选及“GO”和“KEGG”分析 从“MitoCarta3.0”数据库(https://www.broadinstitute.org/mitocarta/)中下载人类线粒体相关表达基因[16]。使用类风湿关节炎差异表达基因、 “WGCNA”特征基因和“MitoCarta3.0”数据库基因取交集得到类风湿关节炎-线粒体自噬相关基因,继而将交集过程利用“VennDiagram”函数包绘制成Venn图。然后使用R函数包“enrichplot”和“clusterProfiler”,将整理好的类风湿关节炎-线粒体自噬相关基因进行“GO”和“KEGG”功能富集分析并可视化。
1.4.4 “Random Forest”机器学习算法筛选核心基因 运用R软件的“randomForest”和“ggplot2”包,对类风湿关节炎-线粒体自噬相关基因表达数据进行进一步“RF”算法分析,以筛选出具有显著分类能力的“RF Genes” 特征基因。
1.4.5 “LASSO”机器学习算法筛选核心基因 利用R软件的“broom”和“glmnet”包,对类风湿关节炎-线粒体自噬相关基因表达数据进行“LASSO”机器学习算法筛选,获得显著特征基因“LASSO Genes”。
1.4.6 “GMM”机器学习算法同级验证核心基因 使用“GMM”算法相关R包“mclust”和“SimDesign”对“RF Genes”特征基因和“LASSO Genes”特征基因同时分别进行独立聚类验证,使筛选出的特征基因得到进一步确认,确保其在分类任务中具有稳定的表现和高准确性。进一步将验证后的“RF Genes”与“LASSO Genes”作交集,以获得类风湿关节炎-线粒体自噬(RA-Mitophagy)核心互作基因,并进行Venn图可视化。
1.4.7 预测模型构建及验证 基于类风湿关节炎-线粒体自噬核心互作基因,通过引用R包“rms” “nomogramFormula” “Hmisc” “rmda”构建二项逻辑回归模型,继而预测个体是否存在患类风湿关节炎的风险。通过绘制Nomogram图将预测模型可视化,并生成预测分数“nomoscore”。同时基于Bootstrap方法对模型进行校准,绘制校准曲线后观察所构建预测模型的拟合效果,从而进行内部验证。最后进行临床决策曲线分析(Decision Curve Analysis,DCA),以评估预测模型的临床效用。
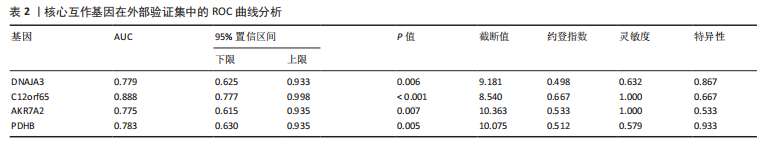
1.4.8 外部患者样本的工作特征曲线验证 综合“sva” “tinyarray” “FactoMineR” “factoextra” R包对GSE97779与GSE55235数据集进行去批次合并,并在合并前后进行主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis,PCA)以验证去批次效果,从而制作外部验证所使用的独立验证集。在独立外部验证集中,对预测模型对应的类风湿关节炎-线粒体自噬核心互作基因进行诊断效能外部验证。通过“pROC” R函数包进行ROC受试者工作特征曲线(Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve,ROC)绘制,观察各核心互作基因所对应AUC曲线下面积(Area Under the Curve,AUC),当AUC>0.6时,代表其诊断效能良好,以确保筛选出的特征基因在实际应用中的稳定性和准确性,以进一步支持核心互作基因在分类任务中的有效性,从而为后续研究提供可靠的依据。
1.4.9 “CIBERSORT”免疫浸润分析 结合“MsigDB”数据库(https://www.gsea-msigdb.org/gsea/msigdb/)22种免疫细胞“gmt”文件数据[17],并基于“CIBERSORT” “ggpubr” “reshape2” “tidyverse” “preprocessCore” “doParallel” R包函数,深入分析类风湿关节炎样本中的免疫细胞浸润情况,识别出与类风湿关节炎关联性较高的关键免疫细胞类型并分析免疫细胞亚群之间的相关性,继而通过两种可视化手段展示分析结果。
1.4.10 “ssGSEA”单样本—免疫细胞亚群间关联性分析 采用“ssGSEA”(Single-sample Gene Set Enrichment Analysis)方法对类风湿关节炎样本进行免疫浸润分析。“ssGSEA”是一种扩展的基因集合富集分析方法,用于评估每个样本中预定义基因集的富集程度,与传统“GSEA”不同,“ssGSEA”可以在单个样本上进行分析,而不是对样本组进行比较。通过“ssGSEA”分析,深入了解每个样本中免疫相关基因集的活性,为类风湿关节炎的免疫机制研究提供重要的参考依据。此研究主要通过R软件“GSVA”及“GSEABase”函数包对样本及相关免疫细胞数据集进行处理分析,获取各样本与免疫细胞亚群间相关性数据,进行样本-免疫细胞相关性热图可视化及分组箱式表达差异可视化。
1.4.11 类风湿关节炎-线粒体自噬核心互作基因—免疫细胞亚群间关联性分析 采用“ggcorrplot”函数包进行分析,获取核心互作基因与免疫细胞亚群间关联性数据集,然后绘制各个核心互作基因与免疫细胞亚群间相关性“棒棒糖”图,最后利用“linkET”函数包,构建核心互作基因-免疫细胞亚群间关联性网络矩阵图。
1.4.12 基于“ssGSEA”的核心互作基因相关生物学功能分析 采用“ssGSEA”方法,结合“MsigDB”数据库中“GO”与“KEGG”通路相关“gmt”文件数据,分析核心互作基因与相关生物学功能之间的关联程度,并筛选出其中与线粒体自噬过程密切相关的基因-功能映射,以从线粒体自噬角度阐发核心互作基因的相关生物学功能,为探索类风湿关节炎的发病机制提供新的视角和理论依据。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①类风湿关节炎-线粒体自噬相关基因的筛选及关键细胞通路可视化结果;②多机器学习算法下类风湿关节炎-线粒体自噬核心互作基因的筛选及验证;③预测模型的构建与外部验证;④核心互作基因与免疫细胞亚群间的关联性及免疫调控过程;⑤核心互作基因与线粒体相关的生物学功能分析结果。
1.6 统计学分析 采用R (版本:4.4.1)软件进行数据分析。采用GraphPad Prism (版本:10.3.0)和R (版本:4.4.1)软件进行绘图。本研究实验均已重复3次,以非配对t检验进行组间差异比较,以Spearman相关性分析研究基因、免疫细胞、生物学功能或通路间关联程度,当P < 0.05时具有统计学意义。此研究统计学方法由广西中医药大学生物医学专家指导与审核。