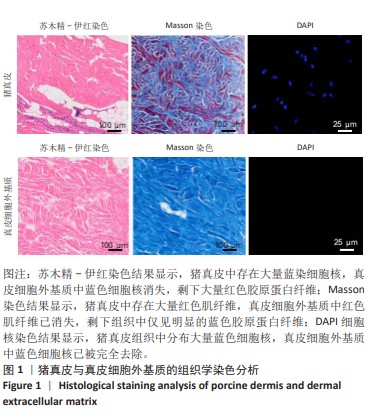
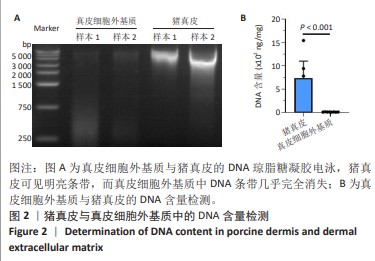
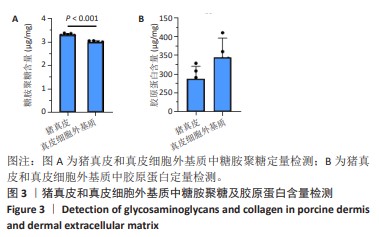
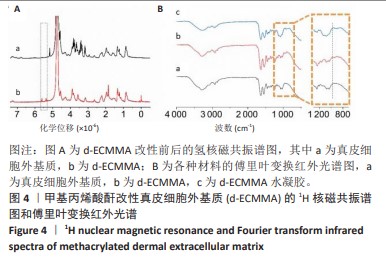
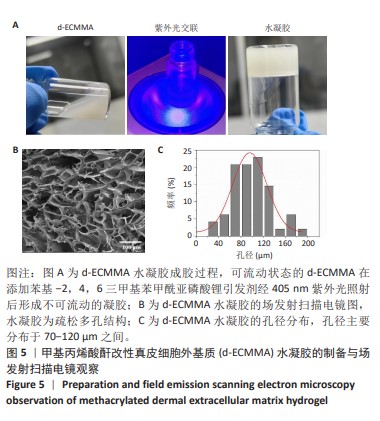
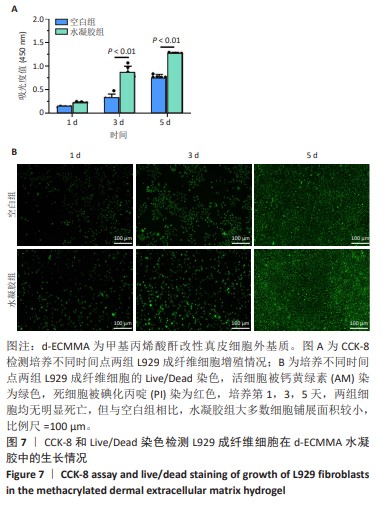
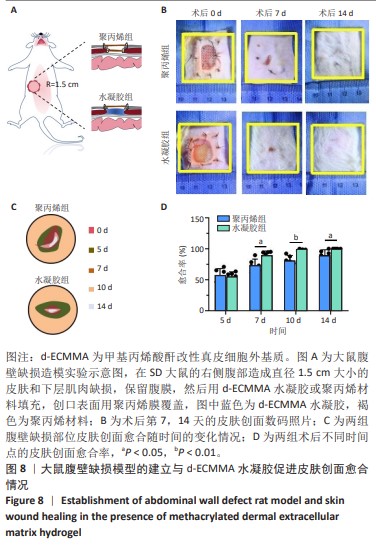
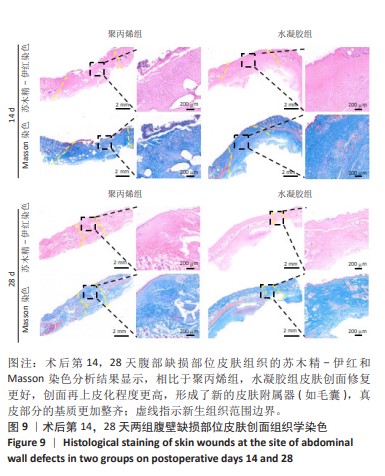
[1] GONG W, CHENG T, LIU Q, et al. Surgical repair of abdominal wall defect with biomimetic nano/microfibrous hybrid scaffold. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;93:828-837.
[2] YANG Z, SONG Z, NIE X, et al. A smart scaffold composed of three-dimensional printing and electrospinning techniques and its application in rat abdominal wall defects. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):533.
[3] CHERLA D, HOPE W, LIANG MK. Recurrence and Mesh-Related Complications After Incisional Hernia Repair. JAMA. 2017;317(5): 536-537.
[4] LIN CY, LIU TY, CHEN MH, et al. An injectable extracellular matrix for the reconstruction of epidural fat and the prevention of epidural fibrosis. Biomed Mater. 2016;11(3): 035010.
[5] 董鸿斐,黄启林,孙红玉,等.真皮细胞外基质水凝胶促进大鼠急性皮肤创面修复[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(10):1555-1560.
[6] 蒋永生,李锐,韩春婵,等.脱细胞基质水凝胶促组织再生的研究进展[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2021,40(5):628-635.
[7] PARTHIBAN SP, ATHIRASALA A, TAHAYERI A, et al. BoneMA-synthesis and characterization of a methacrylated bone-derived hydrogel for bioprinting ofin-vitrovascularized tissue constructs. Biofabrication. 2021;13(3).doi:10.1088/1758-5090/abb11f
[8] 袁勋,丁振罡,付力伟,等.甲基丙烯酰化透明质酸/脱细胞华通胶水凝胶支架的制备与表征[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(22): 3517-3523.
[9] WOLF MT, DALY KA, BRENNAN-PIERCE EP, et al. A hydrogel derived from decellularized dermal extracellular matrix. Biomaterials. 2012;33(29): 7028-7038.
[10] JIA L, HUA Y, ZENG J, et al. Bioprinting and regeneration of auricular cartilage using a bioactive bioink based on microporous photocrosslinkable acellular cartilage matrix . Bioact Mater. 2022;16: 66-81.
[11] 郑翠,乔静,张伟,等.甲壳素疝补片修复大鼠腹壁部分缺损模型的研究[J].中国海洋药物,2018,37(3):18-24.
[12] LIU Y, CHAN-PARK MB. A biomimetic hydrogel based on methacrylated dextran-graft-lysine and gelatin for 3D smooth muscle cell culture. Biomaterials. 2010;31(6): 1158-1170.
[13] 徐娜,王学川,任龙芳,等.甲基丙烯酸酐改性胶原蛋白的研究[J].中国皮革,2018,47(3):9-15+29.
[14] VRIEND L, SINKUNAS V, CAMARGO CP, et al. Extracellular Matrix-Derived Hydrogels to Augment Dermal Wound Healing: A Systematic Review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022;28(5):1093-1108.
[15] 吴益栋,洪丹,郝文娟,等.超快动态交联的可注射壳聚糖-透明质酸水凝胶及促创伤愈合研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2021, 40(5):590-596.
[16] 孙慧,王立军,崔艾鑫,等.负载成纤维细胞3D打印甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶支架的体外促血管化[J].中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(22):3484-3489.
[17] 李航宇,顾岩,王明刚,等.腹腔内补片修补术中国专家共识 (2022版) [J].中国实用外科杂志,2022,42(7):721-729.
[18] 陶齐,王合丽,陈雷,等.人脱细胞真皮基质在乳房切除术后即刻乳房重建术中应用的研究进展[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版), 2021,16(2):147-152.
[19] HU J, TAO M, SUN F, et al. Multifunctional hydrogel based on dopamine-modified hyaluronic acid, gelatin and silver nanoparticles for promoting abdominal wall defect repair. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;222(Pt A):55-64.
[20] 陈召阳,舒军,陶然,等.脂肪组织细胞外基质水凝胶的制备、检测和应用[J].中华整形外科杂志,2022,38(1):104-108.
[21] VALENTIN JE, TURNER NJ, GILBERT TW, et al. Functional skeletal muscle formation with a biologic scaffold. Biomaterials. 2010;31(29): 7475-7484
[22] JANG J, KIM TG, KIM BS, et al. Tailoring mechanical properties of decellularized extracellular matrix bioink by vitamin B2-induced photo-crosslinking. Acta Biomater. 2016;33:88-95.
[23] 丁能,付新新,吴海媚,等.甲基丙烯酸酐化明胶水凝胶在创面修复领域中的应用研究进展[J].中华烧伤与创面修复杂志,2022, 38(11):1096-1100.
[24] 陈一宁,但卫华,但年华,等.脱细胞真皮基质的改性及应用概述[J].材料导报,2018,32(13):2311-2319.
[25] REHAK L, GIURATO L, MELONI M, et al. The Immune-Centric Revolution in the Diabetic Foot: Monocytes and Lymphocytes Role in Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration—A Narrative Review. J Clin Med. 2022;11(3):889.
[26] ERIKSSON E, LIU PY, SCHULTZ GS, et al. Chronic wounds: Treatment consensus. Wound Repair Regen. 2022;30(2):156-171.
[27] RODRIGUES M, KOSARIC N, BONHAM CA, et al. Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective. Physiol Rev. 2019;99(1):665-706.
[28] MONY MP, HARMON KA, HESS R, et al. An Updated Review of Hypertrophic Scarring. Cells. 2023;12(5):678.
[29] BONDIOLI E, PURPURA V, ORLANDI C, et al. The use of an acellular matrix derived from human dermis for the treatment of full-thickness skin wounds. Cell Tissue Bank. 2019;20(2):183-192.
[30] 陈双,江志鹏.腹壁的机械特性:各向异性及其临床意义[J].外科理论与实践,2021,26(5):383-385.
[31] GURTNER GC, WERNER S, BARRANDON Y, et al. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature. 2008;453(7193):314-321.
[32] WANG ZC, ZHAO WY, CAO Y, et al. The Roles of Inflammation in Keloid and Hypertrophic Scars. Front Immunol. 2020;11:603187.
[33] SONG Y, YOU Y, XU X, et al. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Biopotentiated Extracellular Matrix Hydrogels Accelerate Diabetic Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(30):e2304023.
[34] LIANG K, DING C, LI J, et al. A Review of Advanced Abdominal Wall Hernia Patch Materials. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(10):e2303506.
[35] HUANG Z, CHENG J, SU W. A Double Cross-Linked Injectable Hydrogel Derived from Muscular Decellularized Matrix Promotes Myoblast Proliferation and Myogenic Differentiation. Materials (Basel). 2023; 16(15):5335. |