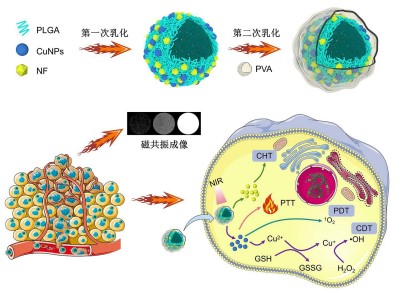
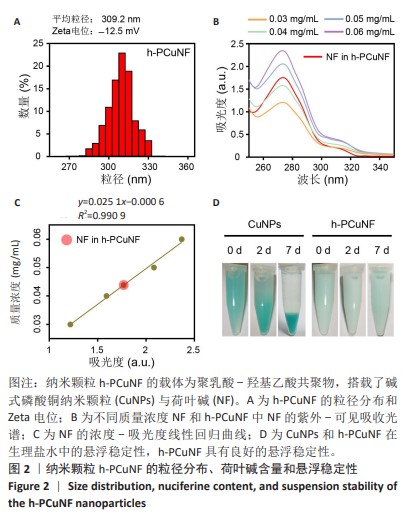
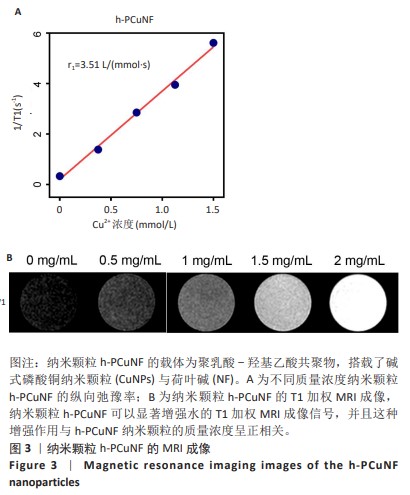
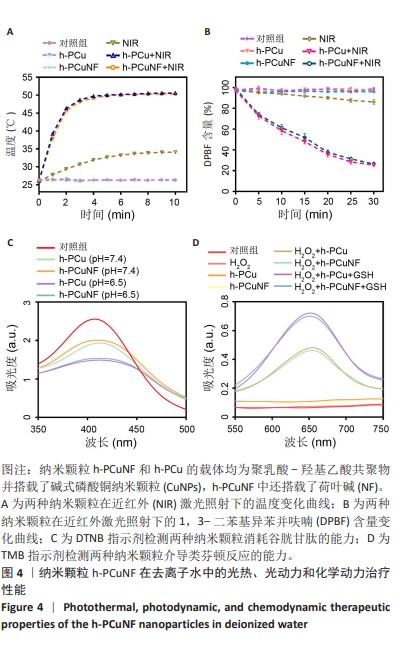
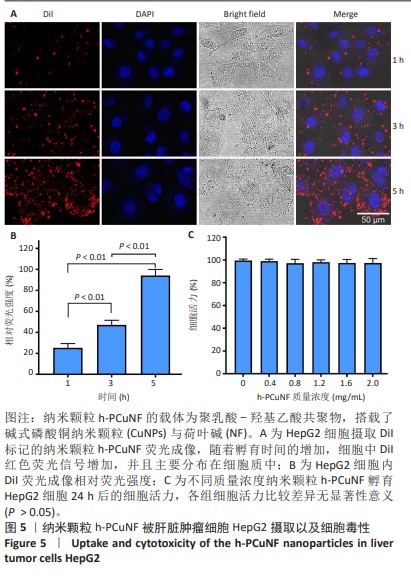
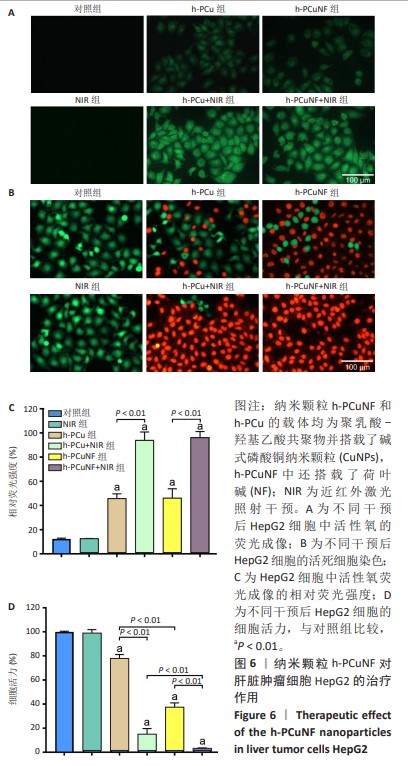
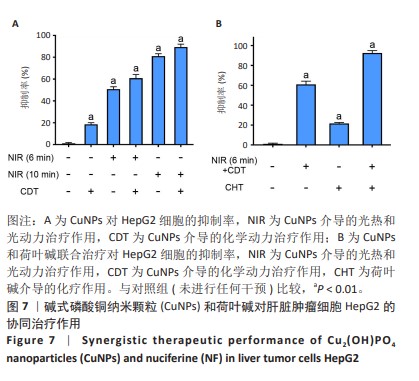
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249.
[2] XIA C, DONG X, LI H, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022; 135(5):584-590.
[3] GILLES H, GARBUTT T, LANDRUM J. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 2022;34(3):289-301.
[4] LAI Z, HE M, BU X, et al. Lenvatinib, toripalimab plus hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in patients with high-risk advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A biomolecular exploratory, phase II trial. Eur J Cancer. 2022;174:68-77.
[5] ZHANG L, OUDENG G, WEN F, et al. Recent advances in near-infrared-II hollow nanoplatforms for photothermal-based cancer treatment. Biomater Res. 2022;26(1):61.
[6] GUSTALIK J, AEBISHER D, BARTUSIK-AEBISHER D. Photodynamic therapy in breast cancer treatment. J Appl Biomed. 2022;20(3):98-105.
[7] JIA C, GUO Y, WU FG. Chemodynamic Therapy via Fenton and Fenton-Like Nanomaterials: Strategies and Recent Advances. Small. 2022;18(6): e2103868.
[8] GUO W, QIU Z, GUO C, et al. Multifunctional Theranostic Agent of Cu2(OH)PO4 Quantum Dots for Photoacoustic Image-Guided Photothermal/Photodynamic Combination Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(11):9348-9358.
[9] CHEN Y, LIU P, SUN P, et al. Oncogenic MSH6-CXCR4-TGFB1 Feedback Loop: A Novel Therapeutic Target of Photothermal Therapy in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Theranostics. 2019;9(5):1453-1473.
[10] KIM SD, KWAG EB, YANG MX, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Ginger on the Side Effects of Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(19):11267.
[11] KIM SM, PARK EJ, LEE HJ. Nuciferine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inflammatory responses by inhibiting p38 MAPK/ATF2 signaling pathways. Inflammopharmacology. 2022;30(6):2373-2383.
[12] SHARMA BR, GAUTAM LN, ADHIKARI D, et al. A Comprehensive Review on Chemical Profiling of Nelumbo Nucifera: Potential for Drug Development. Phytother Res. 2017;31(1):3-26.
[13] LIU Y, WU X, MI Y, et al. PLGA nanoparticles for the oral delivery of nuciferine: preparation, physicochemical characterization and in vitro/in vivo studies. Drug Deliv. 2017;24(1):443-451.
[14] LIU RM, XU P, CHEN Q, et al. A multiple-targets alkaloid nuciferine overcomes paclitaxel-induced drug resistance in vitro and in vivo. Phytomedicine. 2020;79:153342.
[15] LI L, LI Z, GUO Y, et al. Preparation of uniform-sized GeXIVA[1,2]-loaded PLGA microspheres as long-effective release system with high encapsulation efficiency. Drug Deliv. 2022;29(1):2283-2295.
[16] LI Y, DING Y, ZHANG Y, et al. An engineered cascade-sensitized red-emitting upconversion nanoplatform with a tandem hydrophobic hydration-shell and metal-phenolic network decoration for single 808 nm triggered simultaneous tumor PDT and PTT enhanced CDT. Nanoscale. 2023;15(23):10067-10078.
[17] BRUNO F, ARRIGONI F, MARIANI S, et al. Advanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of soft tissue tumors: techniques and applications. Radiol Med. 2019;124(4):243-252.
[18] Di Matteo A, Smerilli G, Cipolletta E, et al. Imaging of Joint and Soft Tissue Involvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021;23(9):73.
[19] AVASTHI A, CARO C, POZO-TORRES E, et al. Magnetic Nanoparticles as MRI Contrast Agents. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2020;378(3):40.
[20] YOKOYAMA M, SHIRAISHI K. Stability evaluation of Gd chelates for macromolecular MRI contrast agents. MAGMA. 2020;33(4):527-536.
[21] FORTE E, FIORENZA D, TORINO E, et al. Radiolabeled PET/MRI Nanoparticles for Tumor Imaging. J Clin Med. 2019;9(1):89.
[22] MALIKIDOGO KP, MARTIN H, BONNET CS. From Zn(II) to Cu(II) Detection by MRI Using Metal-Based Probes: Current Progress and Challenges. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020;13(12):436.
[23] MBUGUA SN. Targeting Tumor Microenvironment by Metal Peroxide Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy. Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2022;2022:5041399.
[24] Zhou W, Jia Y, Liu Y, et al. Tumor Microenvironment-Based Stimuli-Responsive Nanoparticles for Controlled Release of Drugs in Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(11):2346.
[25] Zhang L, Li CX, Wan SS, et al. Nanocatalyst-Mediated Chemodynamic Tumor Therapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(2):e2101971.
[26] TANG Z, LIU Y, HE M, et al. Chemodynamic Therapy: Tumour Microenvironment-Mediated Fenton and Fenton-like Reactions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019;58(4):946-956.
[27] WANG XW, ZHONG XY, LIU Z, et al. Recent progress of chemodynamic therapy-induced combination cancer therapy. Nano Today. 2020;35: 100946.
[28] ZHAO DH, LI CQ, HOU XL, et al. Tumor Microenvironment-Activated Theranostics Nanozymes for Fluorescence Imaging and Enhanced Chemo-Chemodynamic Therapy of Tumors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(47):55780-55789.
[29] XIAO Z, ZUO W, CHEN L, et al. H2O2 Self-Supplying and GSH-Depleting Nanoplatform for Chemodynamic Therapy Synergetic Photothermal/Chemotherapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(37):43925-43936.
[30] POMEROY AE, SCHMIDT EV, SORGER PK, et al. Drug independence and the curability of cancer by combination chemotherapy. Trends Cancer. 2022;8(11):915-929.
[31] JIN H, WANG L, BERNARDS R. Rational combinations of targeted cancer therapies: background, advances and challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023;22(3):213-234.
[32] YONG T, WEI Z, GAN L, et al. Extracellular-Vesicle-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Enhanced Antitumor Therapies through Modulating the Cancer-Immunity Cycle. Adv Mater. 2022;34(52):e2201054.
[33] ZHANG D, LIU L, WANG J, et al. Drug-loaded PEG-PLGA nanoparticles for cancer treatment. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:990505.
[34] NARMANI A, JAHEDI R, BAKHSHIAN-DEHKORDI E, et al. Biomedical applications of PLGA nanoparticles in nanomedicine: advances in drug delivery systems and cancer therapy. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2023; 20(7):937-954.
[35] Rocha CV, Gonçalves V, da Silva MC, et al. PLGA-Based Composites for Various Biomedical Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(4):2034.
[36] AHMADI TEHRANI A, OMRANPOOR MM, VATANARA A, et al. Formation of nanosuspensions in bottom-up approach: theories and optimization. Daru. 2019;27(1):451-473.
[37] WANG J, HUANG J, ZHOU W, et al. Hypoxia modulation by dual-drug nanoparticles for enhanced synergistic sonodynamic and starvation therapy. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):87.
|