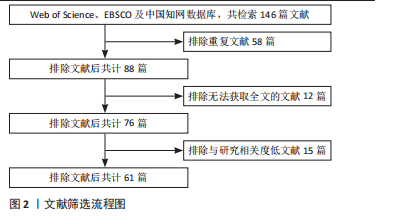
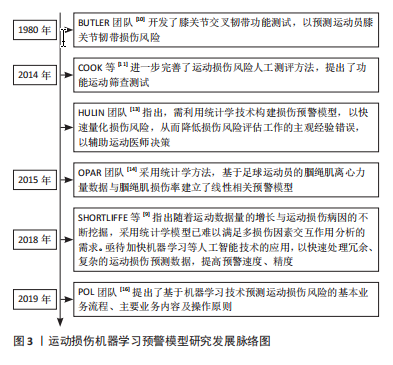
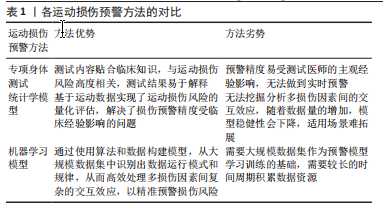
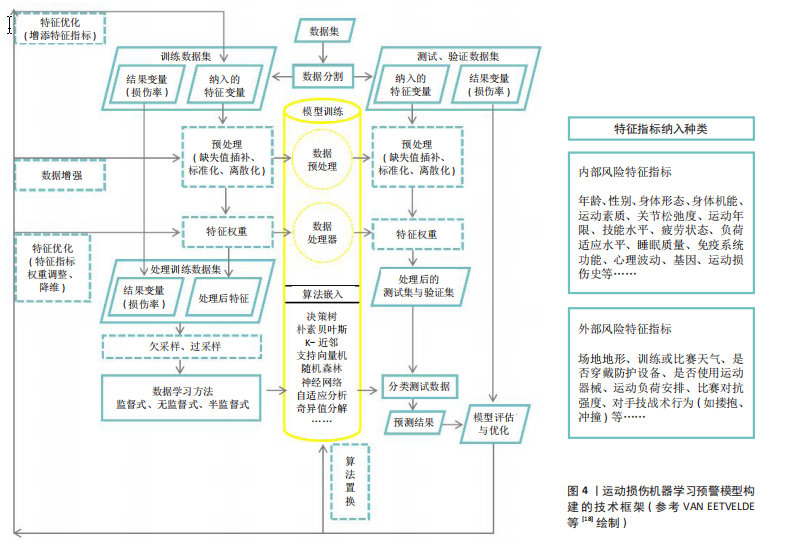
[1] REYNOLDS P. Agency for healthcare research and quality: extramural support for rehabilitation activities. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2005;84(12):1034-1035.
[2] YTTERSTAD B. The harstad injury prevention study: the epidemiology of sports injuries. An 8 year study. Br J Sports Med. 1996;30(1):64-68.
[3] WHITELEY R. ‘Moneyball’ and time to be honest about preseason screening: it is a sham making no inroads on the 1 billion dollar injury costs in baseball. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(14):835-836.
[4] THORBORG K, KROMMES KK, ESTEVE E, et al. Effect of specific exercise-based football injury prevention programmes on the overall injury rate in football: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the FIFA 11 and 11+ programmes. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(7):562-571.
[5] 钟亚平,刘鹏.基于RBF神经网络算法的田径运动损伤预警模型研究[J].计算机应用与软件,2014,31(6):48-51.
[6] ZADEH A, TAYLOR D, BERTSOS M, et al. Predicting sports injuries with wearable technology and data analysis. Inf Syst Front. 2021;23(2):1023-1037.
[7] RAJULA HSR, VERLATO G, MANCHIA M, et al. Comparison of conventional statistical methods with machine learning in medicine: diagnosis, drug development, and treatment. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020;56(9):455-465.
[8] MAJUMDAR A, BAKIROV R, HODGES D, et al. Machine learning for understanding and predicting injuries in football. Sports Med Open. 2022; 8(1):73-83.
[9] SHORTLIFFE EH, SEPÚLVEDA MJ. Clinical decision support in the era of artificial intelligence. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2018;320(21):2199-2200.
[10] BUTLER DL, NOYES FR, GROOD ES. Ligamentous restraints to anterior-posterior drawer in the human knee. A biomechanical study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980;62(2):259-270.
[11] COOK G, BURTON L, HOOGENBOOM BJ, et al. Functional movement screening: the use of fundamental movements as an assessment of function-part 1. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2014;9(3):396-409.
[12] ADAMHULME, FINCH C. From monocausality to systems thinking: a complementary and alternative conceptual approach for better understanding the development and prevention of sports injury. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;2(1):1-12.
[13] HULIN BT , GABBETT TJ , BLANCH P, et al. Spikes in acute workload are associated with increased injury risk in elite cricket fast bowlers. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48(8):708-712.
[14] OPAR DA, WILLIAMS MD, TIMMINS RG, et al. Eccentric hamstring strength and hamstring injury risk in Australian footballers. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015;47(4):857-865.
[15] CLAUDINO JG, CAPANEMA DO, SOUZA TV, et al. Current approaches to the use of artificial intelligence for injury risk assessment and performance prediction in team sports: a systematic review. Sports Med Open. 2019;5(1):1-12.
[16] POL R, HRISTOVSKI R, MEDINA D, et al. From microscopic to macroscopic sports injuries. Applying the complex dynamic systems approach to sports medicine: a narrative review. Br J Sports Med. 2019;53(19):1214-1220.
[17] SARKER IH. Machine learning: algorithms, real-world applications and research directions. SN Comput Sci. 2021;2(3):1-21.
[18] VAN EETVELDE H, MENDONCA LD, LEY C, et al. Machine learning methods in sport injury prediction and prevention: a systematic review. J Exp Orthop. 2021;8(1):27-42.
[19] KOKKOTIS C, MOUSTAKIDIS S, PAPAGEORGIOU E, et al. Machine learning in knee osteoarthritis: a review. Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2020;2(3):100069.
[20] BAHR R. Understanding injury mechanisms a key component of preventing injury in sport. Br J Sports Med. 2005;39(6):324-329.
[21] MEEUWISSE WH, TYREMAN H, HAGEL B, et al. A dynamic model of etiology in sport injury: the recursive nature of risk and causation. Clin J Sport Med. 2007;17(3):215-219.
[22] WINDT J, GABBETT TJ. How do training and competition workloads relate to injury? The workload—injury aetiology model. Br J Sports Med. 2016;51(5): 428-435.
[23] BITTENCOURT NFN, MEEUWISSE WH, MENDON ALD, et al. Complex systems approach for sports injuries: moving from risk factor identification to injury pattern recognition—narrative review and new concept. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(21):1309-1314.
[24] PUDJIHARTONO N, FADASON T, KEMPALIEHR AW, et al. A review of feature selection methods for machine learning-based disease risk prediction. Front Bioinform. 2022;27(2):1-17.
[25] SAROJ A, MONALI B, BISWAJIT P. Review on feature selection and classification using neuro-fuzzy approaches. Int J Appli Evolu Comput. 2016;7(4):28-44.
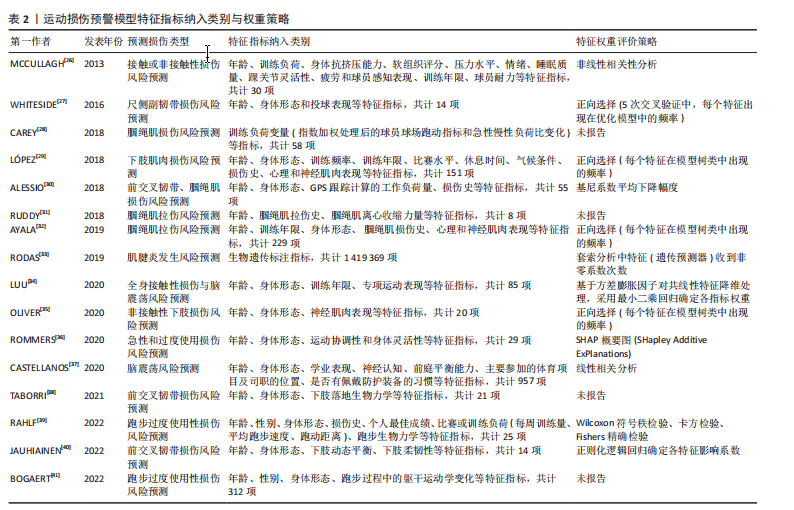
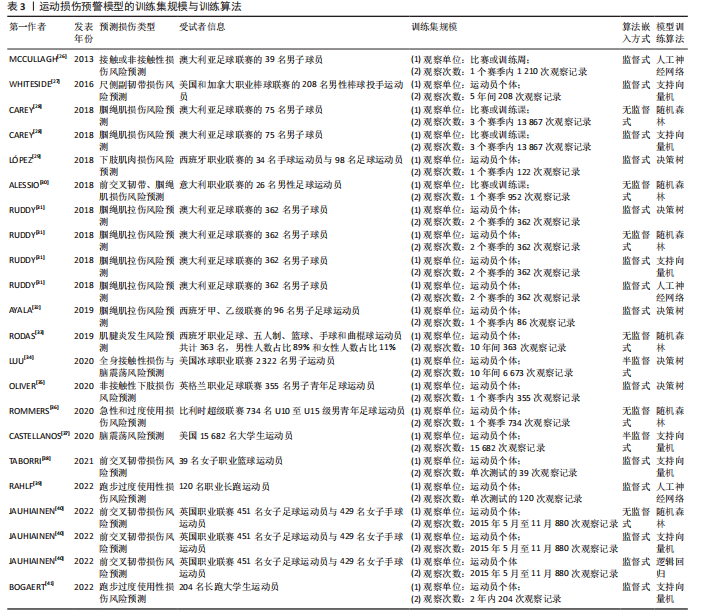
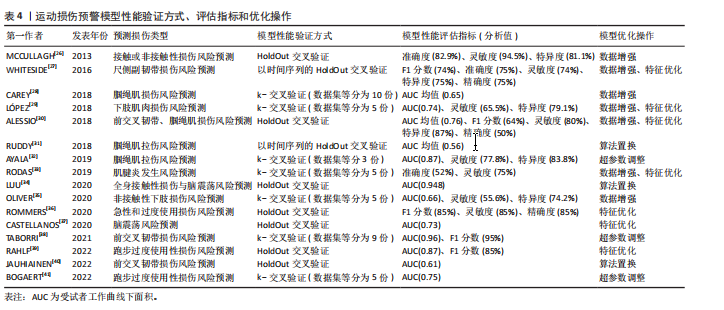
[26] MCCULLAGH J, WHITFORT T. An investigation into the application of artificial neural networks to the prediction of injuries in sportInt. J Sport Health Sci. 2013;7(7):1356-1360.
[27] WHITESIDE D, MARTINI DN, LEPLEY AS, et al. Predictors of ulnar collateral ligament reconstruction in major league baseball pitchers. Am J Sports Med. 2016;3(1):1-8.
[28] CAREY DL, CROSSLEY KM, WHITELEY R, et al. Modeling training loads and injuries: the dangers of discretization. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018;50(11):1-8.
[29] LÓPEZ V, ALEJANDRO, AYALA F, et al. Preventive model for muscle injuries: a novel approach based on learning algorithms. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018;50(5):915-927.
[30] ALESSIO R, LUCA P, PAOLO C, et al. Effective injury forecasting in soccer with GPS training data and machine learning. Plos One. 2018;13(7):1-15.
[31] RUDDY JD, SHIELD AJ, MANIAR N, et al. Predictive modeling of hamstring strain injuries in elite australian footballers. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018;50(5):906-914.
[32] AYALA, FRANCISCOLOPEZ V, ALEJANDROGAMEZ M, et al. A preventive model for hamstring injuries in professional soccer: learning algorithms. Int J Sports Med. 2019;40(5):1-27.
[33] RODAS G, OSABA L, ARTETA D, et al. Genomic prediction of tendinopathy risk in elite team sports. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2019;15(4):1-7.
[34] LUU BC, WRIGHT AL, HAEBERLE HS, et al. Machine learning outperforms logistic regression analysis to predict next-season nhl player injury: an analysis of 2322 players from 2007 to 2017. Orthop J Sports Med. 2020; 8(9):1-8.
[35] OLIVER B, FA C, MDSC D, et al. Using machine learning to improve our understanding of injury risk and prediction in elite male youth football players. J Sci Med Sport. 2020;23(11):1044-1048.
[36] ROMMERS N, RSSLER R, VERHAGEN E, et al. A machine learning approach to assess injury risk in elite youth football players. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2020;52(8):1745-1751.
[37] CASTELLANOS J, PHOO CP, ECKNER JT, et al. Predicting risk of sport-related concussion in collegiate athletes and military cadets: a machine learning approach using baseline data from the care consortium study. Sports Med. 2020;51(3):567-579.
[38] TABORRI J, MOLINARO L, SANTOSPAGNUOLO A, et al. A machine-learning approach to measure the anterior cruciate ligament injury risk in female basketball players. Sensors. 2021;21(9):3141-3158.
[39] RAHLF AL, HOENIG T, STÜRZNICKEL J, et al. A machine learning approach to identify risk factors for running-related injuries: study protocol for a prospective longitudinal cohort trial. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2022; 14(1):1-11.
[40] JAUHIAINEN S, KAUPPI JP, KROSSHAUG T, et al. Predicting acl injury using machine learning on data from an extensive screening test battery of 880 female elite athletes. Am J Sports Med. 2022;5(11):2917-2924.
[41] BOGAERT S, DAVIS J, VAN RS. Impact of gender and feature set on machine-learning-based prediction of lower-limb overuse injuries using a single trunk-mounted accelerometerhe. Sensor. 2022;22(11):2860-2877.
[42] Charilaou P, Battat R. Machine learning models and over-fitting considerations. World J Gastroenterol. 2022;28(5):605-607.
[43] RAJPUT D, WANG WJ, CHEN CC. Evaluation of a decided sample size in machine learning applications. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023;24(1):48-65.
[44] VONDRICK C , PATTERSON D , RAMANAN D. Efficiently scaling up crowdsourced video annotation: a set of best practices for high quality, economical video labeling. Int J Comput Vis. 2013;101(1):184-204.
[45] VABALAS A, GOWEN E, POLIAKOFF E. Machine learning algorithm validation with a limited sample size. PLoS One. 2019;14(11):1-20.
[46] DEIST TM, PATTI A, WANG Z, et al. Simulation-assisted machine learning. Bioinformatics. 2019;35(20):4072-4080.
[47] GABBETT TJ. The training-injury prevention paradox: should athletes be training smarter and harder? Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(5):273-280.
[48] CHAMBERS R, GABBETT TJ, COLE MH, et al. The use of wearable microsensors to quantify sport-specific movements. Sports Med. 2015; 45(7):1065-1081.
[49] WEHBE GM, GABBETT TJ, HARTWIG TB, et al. Reliability of a cycle ergometer peak power test in running-based team sport athletes: a technical report. J Strength Cond Res. 2015;29(7):2050-2055.
[50] GALLO T, CORMACK S, GABBETT T, et al. Characteristics impacting on session rating of perceived exertion training load in Australian footballers. J Sports Sci. 2015;33(5):467-475.
[51] KALKHOVEN JT, WATSFORD ML, IMPELLIZZERI FM. A conceptual model and detailed framework for stress-related, strain-related, and overuse athletic injury. J Sci Med Sport. 2020;23(8):726-734.
[52] TOOHEY LA, DREW MK, FORTINGTON LV, et al. An updated subsequent injury categorisation model (SIC-2.0): data-driven categorisation of subsequent injuries in sport. Sports Med. 2018;48(9):2199-2210.
[53] SHRIER I, STEELE RJ, ZHAO M, et al. A multistate framework for the analysis of subsequent injury in sport (M-FASIS). Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2016; 26(2):128-139.
[54] SHRIER I, STEELE RJ. Classification systems for reinjuries: a continuing challenge. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48(18):1338-1339.
[55] KIEFER AW, KUSHNER AM, GROENE J, et al. A Commentary on real-time biofeedback to augment neuromuscular training for ACL injury prevention in adolescent athletes. J Sports Sci Med. 2015;14(1):1-8.
[56] BIRÓ A, CUESTA-VARGAS AI, SZILÁGYI L. AI-assisted fatigue and stamina control for performance sports on IMU-generated multivariate times series datasets. Sensors (Basel). 2023;24(1):132-139.
[57] WILKERSON GB, GUPTA A, COLSTON MA. Mitigating sports injury risks using internet of things and analytics approaches. Risk Anal. 2018;38(7):1348-1360.
[58] HULIN BT, GABBETT TJ, JOHNSTON RD, et al. Wearable microtechnology can accurately identify collision events during professional rugby league match-play. J Sci Med Sport. 2017;20(7):638-642.
[59] CUI J, DU H, WU X. Data analysis of physical recovery and injury prevention in sports teaching based on wearable devices. Prev Med. 2023;173:107589.
[60] JOHNSON WR, MIAN A, LLOYD DG, et al. On-field player workload exposure and knee injury risk monitoring via deep learning. J Biomech. 2019;93:185-193.
[61] CHAWLA S, ESTEPHAN J, GUDMUNDSSON J, et al. Classification of passes in football matches using spatiotemporal data. ACM Trans Spat Algorithms Syst. 2017;3(2):1-30.
|