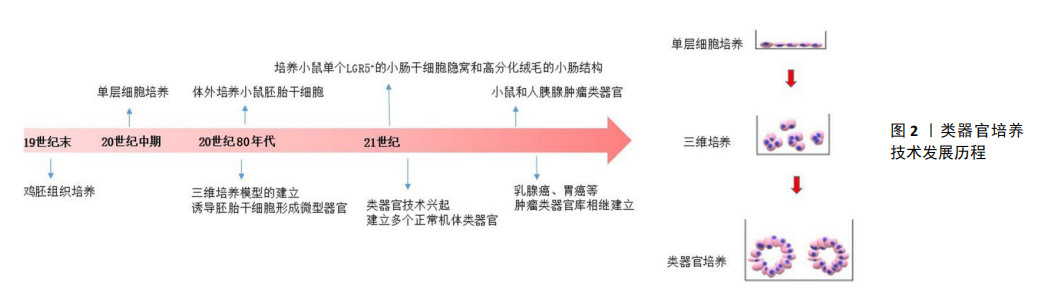
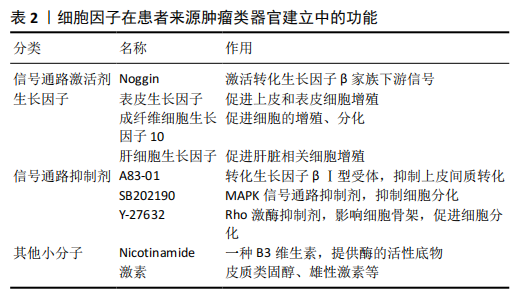
[1] LANCASTER MA, KNOBLICH JA. Organogenesis in a dish:Modeling development and disease using organoid technologies. Science. 2014; 345:1247125.
[2] CHAN AS, YAN HHN, LEUNG SY. Breakthrough Moments:Organoid models of cancer. Cell Stem Cell. 2019;24:839-840.
[3] DAGOGO-JACK I, SHAW AT. Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15:81-94.
[4] FONG EL, HARRINGTON DA, FARACH-CARSON MC, et al. Heralding a new paradigm in 3D tumor modeling. Biomaterials. 2016;108:197-213.
[5] FONTOURA JC, VIEZZER C, DOS SANTOS FG, et al. Comparison of 2D and 3D cell culture models for cell growth, gene expression and drug resistance. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;107:110264.
[6] FAN H, DEMIRCI U, CHEN P. Emerging organoid models: leaping forward in cancer research. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12:142.
[7] BLEIJS M, VAN DE WETERING M, CLEVERS H, et al. Xenograft and organoid model systems in cancer research. EMBO J. 2019;38:e101654.
[8] BRADLEY A, EVANS M, KAUFMAN MH, et al. Formation of germ-line chimaeras from embryo-derived teratocarcinoma cell lines. Nature. 1984;309(5965):255-256.
[9] SATO T, VRIES RG, SNIPPERT HJ, et al. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature. 2009;459:262-265.
[10] CHEN HI, SONG H, MING GL. Applications of human brain organoids to clinical problems. Dev Dyn. 2019;248:53-64.
[11] POMPAIAH M, BARTFELD S. Gastric Organoids:An emerging model system to study helicobacter pylori pathogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017;400:149-168.
[12] BOJ SF, HWANG CI, BAKER LA, et al. Organoid models of human and mouse ductal pancreatic cancer. Cell. 2015;160:324-338.
[13] SATO T, STANGE DE, FERRANTE M, et al. Long-term expansion of epithelial organoids from human colon, adenoma,adenocarcinoma,and barrett\”s epithelium. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(5):1762-1772.
[14] YAN HHN, SIU HC, LAW S, et al. A comprehensive human gastric cancer organoid biobank captures tumor subtype heterogeneity and enables therapeutic screening. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;23:882-897.e11
[15] GAO D, VELA I, SBONER A, et al. Organoid cultures derived from patients with advanced prostate cancer. Cell. 2014;159:176-187.
[16] LEE SH, HU W, MATULAY JT, et al. Tumor evolution and drug response in patient-derived organoid models of bladder cancer. Cell. 2018;173: 515-528.e17.
[17] LI X, FRANCIES HE, SECRIER M, et al. Organoid cultures recapitulate esophageal adenocarcinoma heterogeneity providing a model for clonality studies and precision therapeutics. Nat Commun. 2018;9:2983
[18] GIRDA E, HUANG EC, LEISEROWITZ GS, et al. The use of endometrial cancer patient-derived organoid culture for drug sensitivity testing is feasible. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2017;27:1701-1707.
[19] SACHS N, DE LIGT J, KOPPER O, et al. A living biobank of breast cancer organoids captures disease heterogeneity. Cell. 2018;172:373-386.e10.
[20] NUCIFORO S, FOFANA I, MATTER MS, et al. Organoid models of human liver cancers derived from tumor needle biopsies. Cell Rep. 2018;24: 1363-1376.
[21] SAITO Y, MURAMATSU T, KANAI Y, et al. Establishment of patient-derived organoids and drug screening for biliary tract carcinoma. Cell Rep. 2019;27:1265-1276.e4.
[22] DRIEHUIS E, KOLDERS S, SPELIER S, et al. Oral mucosal organoids as a potential platform for personalized cancer therapy. Cancer Discov. 2019;9:852-871.
[23] VAN DE WETERING M, FRANCIES HE, FRANCIS JM, et al. Prospective derivation of a living organoid biobank of colorectal cancer patients.Cell. 2015;161:933-945.
[24] MARU Y, TANAKA N, ITAMI M, et al. Efficient use of patient-derived organoids as a preclinical model for gynecologic tumors. Gynecol.Oncol. 2019;154:189-198.
[25] KELLER L, PANTEL K. Unravelling tumour heterogeneity by single-cell profiling of circulating tumour cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 2019;19:553-567.
[26] ZHANG Z, SHIRATSUCHI H, PALANISAMY N, et al. Expanded circulating tumor cells from a patient with ALK-positive lung cancer present with EML4-ALK rearrangement along with resistance mutation and enable drug sensitivity testing: a case study. Thorac Oncol. 2017;12(2):397-402.
[27] VISVADER JE, LINDEMAN GJ. Cancer stem cells in solid tumours: accumulating evidence and unresolved questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:755-768.
[28] FENDLER A, BAUER D, BUSCH J, et al. Inhibiting WNT and NOTCH in renal cancer stem cells and the implications for human patients. Nat Commun. 2020;11:929.
[29] HWANG JW, LOISEL-DUWATTEZ J, DESTERKE C, et al. A novel neuronal organoid model mimicking glioblastoma (GBM) features from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC).Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2020;1864:129540.
[30] CANTOR JR. The rise of physiologic media.Trends Cell Biol.2019;29: 854-861.
[31] PINTO D, GREGORIEFF A, BEGTHEL H, et al.Canonical Wnt signals are essential for homeostasis of the intestinal epithelium. Genes Dev. 2003;17(14):1709-1713.
[32] KIM KA, KAKITANI M, ZHAO J, et al. Mitogenic Influence of human R-Spondin1 on the intestinal epithelium. Science. 2005;309(5738): 1256-1259.
[33] DROST J, KARTHAUS WR, GAO D, et al. Organoid culture systems for prostate epithelial and cancer tissue. Nature Protocols. 2016;11(2): 347-358.
[34] BENTON G, ARNAOUTOVA I, GEORGE J, et al. Matrigel: From discovery and ECM mimicry to assays and models for cancer research. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2014;79-80:3-18.
[35] LEWIS MT, LANDUA JD, ADAMS HC 3RD, et al. A mystery wrapped in an enigma: Matrigel enhancement of mammary cell growth and morphogenesis. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2012;17:99-101.
[36] BARKA T, GRESIK ES, MIYAZAKI Y. Differentiation of a mouse submandibular gland-derived cell line (SCA) grown on matrigel. Exp Cell Res. 2005;308:394-406.
[37] BALACHANDER GM, BALAJI SA, RANGARAJAN A, et al. Enhanced metastatic potential in a 3D tissue scaffold toward a comprehensive in vitro model for breast cancer metastasis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:27810-27822.
[38] NAYAK B, BALACHANDER GM, MANJUNATH S, et al. Tissue mimetic 3D scaffold for breast tumor-derived organoid culture toward personalized chemotherapy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;180:334-343.
[39] SHIMOKAWA M, OHTA Y, NISHIKORI S, et al. Visualization and targeting of LGR5 human colon cancer stem cells. Nature. 2017;545:187-192.
[40] SZVICSEK Z, OSZVALD Á, SZABÓ L, et al. Extracellular vesicle release from intestinal organoids is modulated by Apc mutation and other colorectal cancer progression factors. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76: 2463-2476.
[41] APARICIO S, HIDALGO M, KUNG AL. Examining the utility of patient-derived xenograft mouse models. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15:311-316.
[42] PAULI C, HOPKINS BD, PRANDI D, et al. Personalized in vitro and in vivo cancer models to guide precision medicine. Cancer Discovery. 2017;7(5):462.
[43] BOEHNKE K, IVERSEN PW, SCHUMACHER D, et al. Assay establishment and validation of a high-throughput screening platform for three-dimensional patient-derived colon cancer organoid cultures. J Biomol Screen. 2016;21:931-941.
[44] VLACHOGIANNIS G, HEDAYAT S, VATSIOU A, et al. Patient-derived organoids model treatment response of metastatic gastrointestinal cancers. Science. 2018;359:920-926.
[45] TUVESON D, CLEVERS H. Cancer modeling meets human organoid technology. Science. 2019;364:952-955. |
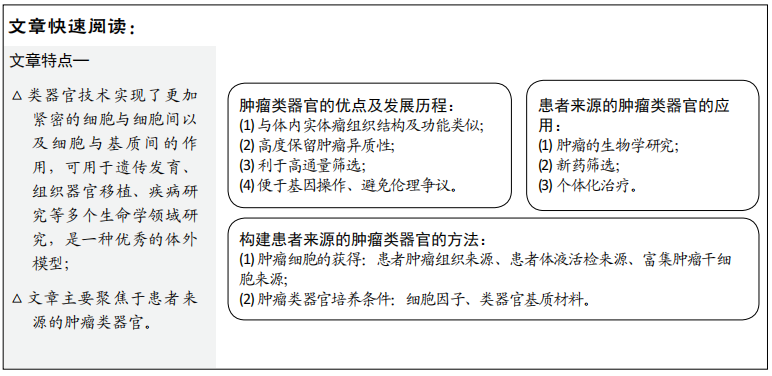
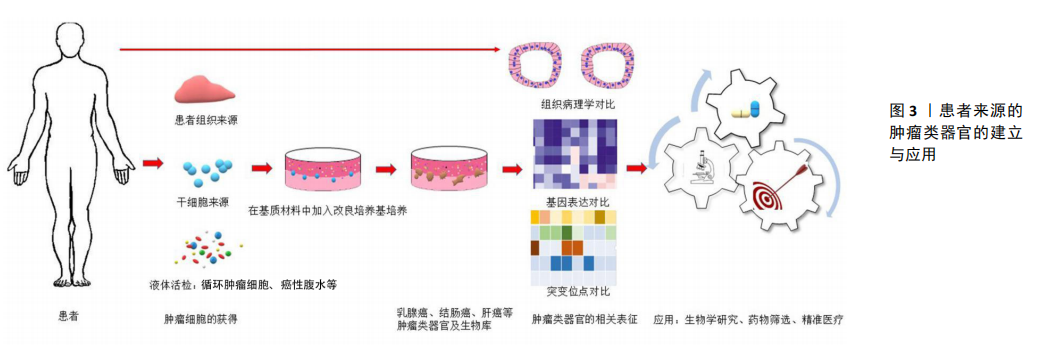
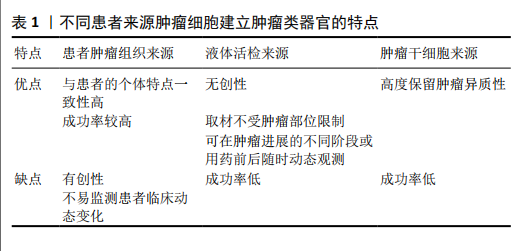 (1)患者肿瘤组织来源:肿瘤组织主要是通过手术、组织活检等途径获得,通过酶消化方法进行组织处理得到肿瘤细胞来进行类器官培养。SACHS等[19]利用乳腺癌患者手术取得的肿瘤组织在剪碎、胶原酶消化及裂解红细胞等处理后得到单个悬浮的肿瘤细胞,将其种植于基底膜提取物,再加入含细胞因子的改良培养基成功培养出乳腺癌类器官。其中典型的乳腺癌类器官形态与患者原发肿瘤的组织病理学、激素受体状态和HER2表达情况相匹配。DNA拷贝数和序列变化在来源肿瘤与类器官中也是一致的,即使在传代后也可基本保持稳定;除了从患者的手术标本直接取材外,组织活检等微创途径得到的肿瘤组织也可以用于肿瘤类器官的培养。NUCIFORO等[20]将从肝癌针刺活检中得到的肿瘤组织用Ⅳ型胶原酶消化后接种到Ⅱ型基底膜提取物上,通过含不同细胞因子的培养基传代培养后得到肝癌类器官,并且发现其同样保留了原始肿瘤的组织形态和遗传学特征。这种直接通过患者肿瘤组织来源获取肿瘤细胞的方法是目前比较成熟、运用最广泛的肿瘤类器官建立方法,通过这种方法已经成功建立了胆管癌[21]、头颈鳞癌和结直肠癌等多种肿瘤类器官[22-23]。患者肿瘤组织来源建立的肿瘤类器官,具有与患者的个体特点一致性高、可以反映肿瘤体内真实的生物学特点、培养技术较成熟的优点,但不易监测患者临床动态变化,且从患者肿瘤组织中取材属于有创操作。
(1)患者肿瘤组织来源:肿瘤组织主要是通过手术、组织活检等途径获得,通过酶消化方法进行组织处理得到肿瘤细胞来进行类器官培养。SACHS等[19]利用乳腺癌患者手术取得的肿瘤组织在剪碎、胶原酶消化及裂解红细胞等处理后得到单个悬浮的肿瘤细胞,将其种植于基底膜提取物,再加入含细胞因子的改良培养基成功培养出乳腺癌类器官。其中典型的乳腺癌类器官形态与患者原发肿瘤的组织病理学、激素受体状态和HER2表达情况相匹配。DNA拷贝数和序列变化在来源肿瘤与类器官中也是一致的,即使在传代后也可基本保持稳定;除了从患者的手术标本直接取材外,组织活检等微创途径得到的肿瘤组织也可以用于肿瘤类器官的培养。NUCIFORO等[20]将从肝癌针刺活检中得到的肿瘤组织用Ⅳ型胶原酶消化后接种到Ⅱ型基底膜提取物上,通过含不同细胞因子的培养基传代培养后得到肝癌类器官,并且发现其同样保留了原始肿瘤的组织形态和遗传学特征。这种直接通过患者肿瘤组织来源获取肿瘤细胞的方法是目前比较成熟、运用最广泛的肿瘤类器官建立方法,通过这种方法已经成功建立了胆管癌[21]、头颈鳞癌和结直肠癌等多种肿瘤类器官[22-23]。患者肿瘤组织来源建立的肿瘤类器官,具有与患者的个体特点一致性高、可以反映肿瘤体内真实的生物学特点、培养技术较成熟的优点,但不易监测患者临床动态变化,且从患者肿瘤组织中取材属于有创操作。