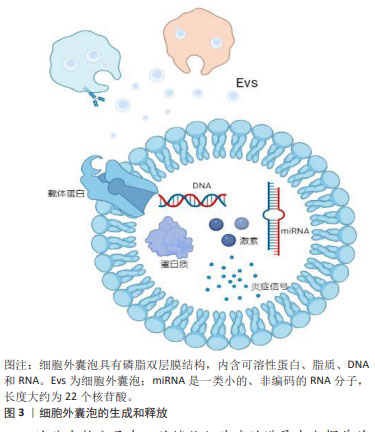
[1] 钟来平.口腔鳞状细胞癌临床诊治的规范化和个体化:机遇与挑战[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2020,38(5):484-488.
[2] WANG L, WEI Y, YAN Y, et al. CircDOCK1 suppresses cell apoptosis via inhibition of miR‑196a‑5p by targeting BIRC3 in OSCC. Oncol Rep. 2018; 39(3):951-966.
[3] 董云梅,陶艳,周瑜.口腔黏膜癌变过程中血清生化标志物的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2020,47(1):43-50.
[4] YU D, LI Y, WANG M, et al. Exosomes as a new frontier of cancer liquid biopsy. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):56.
[5] LI S, MAN Q, GAO X, et al. Tissue‐derived extracellular vesicles in cancers and non‐cancer diseases: present and future. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(14):e12175.
[6] ZHANG Y, LIU J, LIU S, et al. Extracellular vesicles in oral squamous cell carcinoma: current progress and future prospect. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1149662.
[7] 赵鹏程,陈莹,刘婷姣,等.细胞外囊泡miRNA在口腔鳞癌中的研究进展[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2021,35(3):200-203.
[8] LU Y, ZHENG Z, YUAN Y, et al. The emerging role of exosomes in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;22:9:628103.
[9] ABAK A, ABHARI A, RAHIMZADEH S. Exosomes in cancer: small vesicular transporters for cancer progression and metastasis, biomarkers in cancer therapeutics. Peer J. 2018;6:e4763.
[10] ALMERIA C, WEISS R, ROY M, et al. Hypoxia conditioned mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles induce increased vascular tube formation in vitro. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;23:7:292.
[11] SEOANE-ROMERO JM, VAZQUEZ-MAHIA I, SEOANE J, et al. Factors related to late stage diagnosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2012:e35-e40.
[12] 蒋宇磊,夏斌,饶南荃,等.外泌体在口腔鳞状细胞癌恶性进展及诊疗应用的研究[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2021,48(6):711-717.
[13] 毛露珈,史恩宇,王瀚平,等.细菌外膜囊泡在抗肿瘤治疗方面的研究进展[J].中国生物工程杂志,2022,42(5):100-105.
[14] STADLER ZK,THOM P, ROBSON ME, et al. Genome-wide association studies of cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2010;28(27): 4255-4267.
[15] AHMADI M, ABBASI R, REZAIE J. Tumor immune escape: extracellular vesicles roles and therapeutics application. Cell Commun Signal. 2024;22(1):9.
[16] 肖博林,张伟,陈刚.细胞外囊泡与口腔肿瘤免疫[J].口腔医学, 2023,43(9):769-774.
[17] 吴若怡,王晓宁,翟培淞,等.上皮癌来源细胞外囊泡亚群蛋白质谱分析[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2023,21(4):326-331.
[18] GONDALIYA P. Extracellular vesicle RNA signaling in the liver tumor microenvironment. Cancer Lett. 2023;558:216089.
[19] LI R, ZHOU Y, ZHANG M, et al. Oral squamous cell carcinoma-derived EVs promote tumor progression by regulating inflammatory cytokines and the IL-17A-induced signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;118:110094.
[20] 廖立,田卫东.间充质干细胞来源胞外囊泡在牙及颌面部组织再生中的研究与展望[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2022,40(1):7-13.
[21] PANVONGSA W, PEGTEL DM,VOORTMAN J. More than a bubble: extracellular vesicle microRNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancers. 2022;14(5):1160.
[22] MOMEN-HERAVI F, BALA S. Extracellular vesicles in oral squamous carcinoma carry oncogenic miRNA profile and reprogram monocytes via NF-κB pathway. Oncotarget. 2018;9(78):34838-34854.
[23] KACZOR-URBANOWICZ KE, MARTIN CARRERAS-PRESAS C, ARO K, et al. Saliva diagnostics - Current views and directions. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017;242(5):459-472.
[24] RAHIMI S, ROUSHANDEH AM, AHMADZADEH E, et al. Implication and role of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in cancer: lipocalin-2 as a potential novel emerging comprehensive therapeutic target for a variety of cancer types. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47(3):2327-2346.
[25] ARGYRIS PP, SLAMA Z M, ROSS KF, et al. Calprotectin and the Initiation and Progression of Head and Neck Cancer. J Dent Res. 2018;97(6):674-682.
[26] RAIMONDI L, DE LUCA A, AMODIO N, et al. Involvement of multiple myeloma cell-derived exosomes in osteoclast differentiation. Oncotarget. 2015;6(15):13772-13789.
[27] 张秀丽,武曦,李昀生.干细胞源性细胞外囊泡在牙周再生治疗中的研究进展[J].重庆医学,2022,51(7):1216-1219.
[28] CAVALLARI C, CAMUSSI G, BRIZZI MF. Extracellular vesicles in the tumour microenvironment:eclectic supervisors. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(18):6768.
[29] CHEN CM, CHU TH, CHOU CC, et al. Exosome-derived microRNAs in oral squamous cell carcinomas impact disease prognosis. Oral Oncol. 2021;120:105402.
[30] LI W, HAN Y, ZHAO Z, et al. Oral mucosal mesenchymal stem cell‑derived exosomes: a potential therapeutic target in oral premalignant lesions. Int J Oncol. 2019;54(5):1567-1578.
[31] YAMAGUCHI K, YAMAMOTO T, CHIKUDA J, et al. Impact of non-coding RNAs on chemotherapeutic resistance in oral cancer. Biomolecules. 2022;12(2):284.
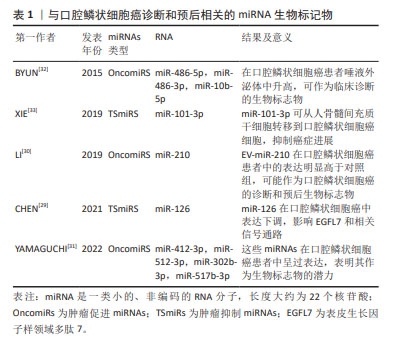
[32] BYUN JS, HONG SH, CHOI JK, et al. Diagnostic profiling of salivary exosomal microRNAs in oral lichen planus patients. Oral Dis. 2015; 21(8):987-993.
[33] XIE C, DU LY, GUO F, et al. Exosomes derived from microRNA-101-3p-overexpressing human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells suppress oral cancer cell proliferation, invasion,and migration. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019;458(1-2):11-26.
[34] CRISTALDI M, MAUCERI R, DI FEDE O, et al. Salivary biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis and follow-up: current status and perspectives. Front Physiol. 2019;10:1476.
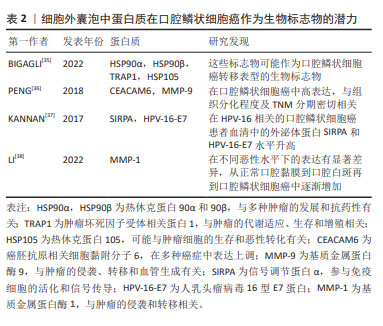
[35] BIGAGLI E, LOCATELLO LG, DI STADIO A, et al. Extracellular vesicles miR‐210 as a potential biomarker for diagnosis and survival prediction of oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. J Oral Pathol Med. 2022; 51(4):350-357.
[36] PENG Q, ZHANG J, ZHOU G. Differentially circulating exosomal microRNAs expression profiling in oral lichen planus. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10(9):2848-2858.
[37] KANNAN A, HERTWECK KL, PHILLEY JV, et al. Genetic mutation and exosome signature of human papilloma virus associated oropharyngeal cancer. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):46102.
[38] LI S, HAN Y, LU M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-exosome-mediated matrix metalloproteinase 1 participates in oral leukoplakia and carcinogenesis by inducing angiogenesis. J Oral Pathol Med. 2022; 51(7):638-648.
[39] FENG J, XIAO BL, ZHANG LZ, et al. Simultaneous detection of two extracellular vesicle subpopulations in saliva assisting tumor t staging of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Anal Chem. 2023;95(19):7753-7760.
[40] WANG J, MAN QW, FU QY, et al. Preliminary extracellular vesicle profiling in drainage fluid after neck dissection in OSCC. J Dent Res. 2023;102(2):178-186.
[41] WANG J, JING J, ZHOU C, et al. Emerging roles of exosomes in oral diseases progression. Int J Oral Sci. 2024;15;16(1):4.
[42] LI C, ZHOU Y, LIU J, et al. Potential markers from serum-purified exosomes for detecting oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2019;28(10):1668-1681.
[43] KANG SH, OH SY, LEE KY, et al. Differential effect of cancer-associated fibroblast-derived extracellular vesicles on cisplatin resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma via miR-876-3p. Theranostics. 2024;14(2): 460-479.
[44] 黄霞,魏津钿,苏琦,等.干细胞源性细胞外囊泡经RANKL/RANK/OPG通路促进牙槽骨成骨的研究进展[J].中国现代医学杂志,2023, 33(20):60-64.
[45] HUANG Z, ZHANG Q, WANG Y, et al. Inhibition of caspase-3-mediated GSDME-derived pyroptosis aids in noncancerous tissue protection of squamous cell carcinoma patients during cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Am J Cancer Res. 2020;10(12):4287-4307.
[46] SASABE E, TOMOMURA A, LIU H, et al. Epidermal growth factor/epidermal growth factor receptor signaling blockage inhibits tumor cell-derived exosome uptake by oral squamous cell carcinoma through macropinocytosis. Cancer Sci. 2022;113(2):609-621.
[47] LUO H, BIRJANDI AA, REN F, et al. Advances in oral mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in health and disease. Genes Dis. 2024;11(1):346-357.
[48] LIANG W, CHEN X, ZHANG S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells as a double-edged sword in tumor growth:focusing on MSC-derived cytokines. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2021;26(1):3.
[49] LIU T, CHEN G, SUN D, et al. Exosomes containing miR-21 transfer the characteristic of cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN and PDCD4 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2017;49(9): 808-816.
[50] KULKARNI B, GONDALIYA P, KIRAVE P, et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of miR-30a sensitize cisplatin-resistant variant of oral squamous carcinoma cells via modulating Beclin1 and Bcl2. Oncotarget. 2020; 11(20):1832-1845.
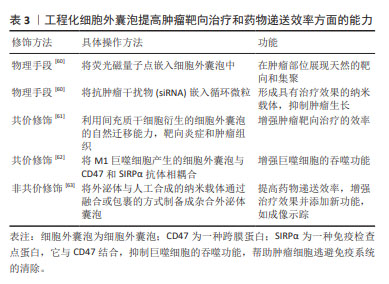
[51] XIE Q, HAO Y, LI N, et al. Cellular uptake of engineered extracellular vesicles:biomechanisms,engineered strategies, and disease treatment. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(2):e2302280.
[52] LI L, CAO B, LIANG X, et al. Microenvironmental oxygen pressure orchestrates an anti- and pro-tumoral γδ T cell equilibrium via tumor-derived exosomes. Oncogene. 2019;38(15):2830-2843.
[53] ZHANG F,GUO J,ZHANG Z, et al. Application of engineered extracellular vesicles for targeted tumor therapy. J Biomed Sci. 2022;29(1):14.
[54] DE ABREU RC, FERNANDES H, DA COSTA MARTINS PA, et al. Native and bioengineered extracellular vesicles for cardiovascular therapeutics. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17(11):685-697.
[55] LI S, XU J, QIAN J, et al. Engineering extracellular vesicles for cancer therapy:recent advances and challenges in clinical translation. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(24):6978-6991.
[56] KUČUK N, PRIMOŽIČ M, KNEZ Ž, et al. Exosomes engineering and their roles as therapy delivery tools, therapeutic targets, and biomarkers. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9543.
[57] SUN J, WANG X, DING Y, et al. Proteomic and phosphoproteomic landscape of salivary extracellular vesicles to assess OSCC therapeutical outcomes. Proteomics. 2023;23(5):e2200319.
[58] YASUI T, YANAGIDA T, ITO S, et al. Unveiling massive numbers of cancer-related urinary-microRNA candidates via nanowires. Sci Adv. 2017;3(12):e1701133.
[59] 雷可昕,白贺天,杨淞月,等.环状RNA与口腔鳞状细胞癌研究进展[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2020,38(4):425-430.
[60] YU ZL, ZHANG W, ZHAO JY, et al. Development of a dual-modally traceable nanoplatform for cancer theranostics using natural circulating cell-derived microparticles in oral cancer patients. Adv Funct Mater. 2017;27(40):1703482.
[61] LAW ZJ, KHOO XH, LIM PT, et al. Extracellular vesicle-mediated chemoresistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Front Mol Biosci. 2021; 8:629888.
[62] NIE W,WU G, ZHANG J, et al. Responsive exosome nano‐bioconjugates for synergistic cancer therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020;59(5): 2018-2022.
[63] 芦晓红,赵源,何军.杂合外泌体囊泡作为药物递送载体的研究进展[J].中国医药工业杂志,2023,54(7):1020-1025. |