[1] LIANG Y, SONG Y, WANG L, et al. Research progress on antibacterial activity of medical titanium alloy implant materials. Odontology. 2023;111(4):813-829.
[2] WANG W, JIANG B, SUN H, et al. Prevalence, Incidence, and Mortality of Stroke in China: Results from a Nationwide Population-Based Survey of 480 687 Adults. Circulation. 2017;135(8):759-771.
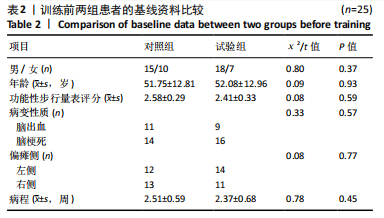
[3] COHEN JW, IVANOVA TD, BROUWER B, et al. Do Performance Measures of Strength, Balance, and Mobility Predict Quality of Life and Community Reintegration After Stroke? Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2018;99(4):713-719.
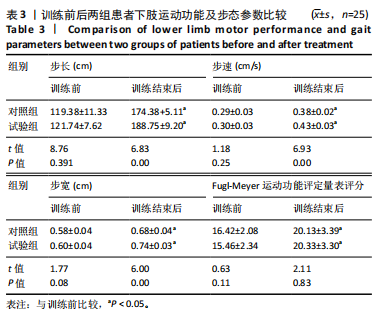
[4] PARK J, KIM TH. The effects of balance and gait function on quality of life of stroke patients. Neuro Rehabilitation. 2019;44:37-41.
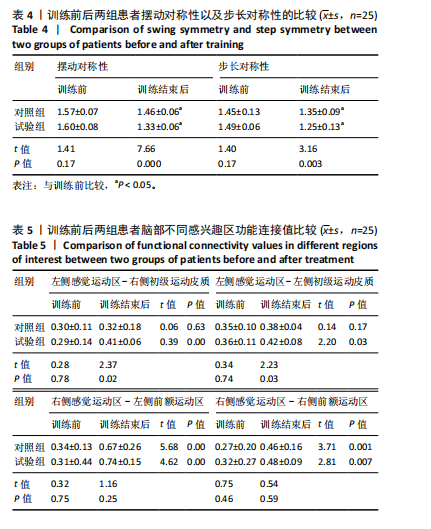
[5] ZHANG B, WONG KP, KANG R, et al. Efficacy of Robot-Assisted and Virtual Reality Interventions on Balance, Gait, and Daily Function in Patients With Stroke: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;104(10):1711-1719.
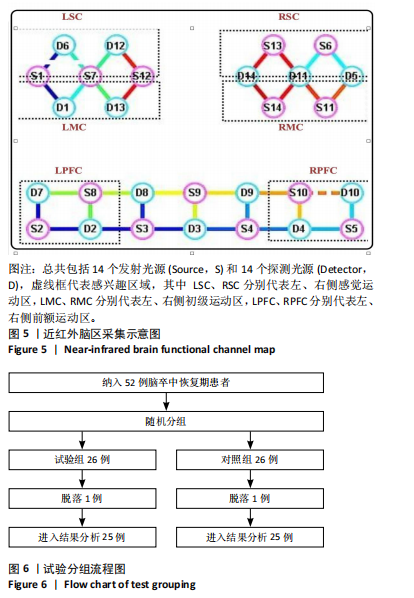
[6] SYLVESTER CM, KAPLAN S, MYERS MJ, et al. Network-specific selectivity of functional connections in the neonatal brain. Cereb Cortex. 2023; 33(5):2200-2214.
[7] BAI Z, FONG KNK, ZHANG J, et al. Cortical mapping of mirror visual feedback training for unilateral upper extremity: A functional near-infrared spectroscopy study. Brain Behav. 2020;10(1):e01489.
[8] LIU Y, LUO J, FANG J, et al. Screening diagnosis of executive dysfunction after ischemic stroke and the effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation: A prospective functional near-infrared spectroscopy study. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023;29(6):1561-1570.
[9] PARK KR, KIM H, SEONG S, et al. A study on the functional near-infrared spectroscopy on impaired prefrontal activation and impulsivity during cognitive task in patients with major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord. 2023;339:548-555.
[10] SONG Z, ZHOU Y, ZHENG Y, et al. Factors influencing functional near-infrared spectroscopy in postpartum depression: A cross-sectional study. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2023;161(3):1046-1052.
[11] MIHARA M, MIYAI I, HATTORI N, et al. Neurofeedback using real-time near-infrared spectroscopy enhances motor imagery related cortical activation. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e32234.
[12] DOBKIN BH. Strategies for stroke rehabilitation. Lancet Neurol. 2004; 3:528-536.
[13] RAHMAN MS, PENG W, ADAMS J, et al. The use of self-management strategies for stroke rehabilitation: a scoping review. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2023;30(6):552-567.
[14] CALAFIORE D, NEGRINI F, TOTTOLI N, et al. Efficacy of robotic exoskeleton for gait rehabilitation in patients with subacute stroke : a systematic review. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2022;58(1):1-8.
[15] CALABRÒ RS, NARO A, RUSSO M, et al. Shaping neuroplasticity by using powered exoskeletons in patients with stroke: a randomized clinical trial. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2018;15(1):35.
[16] YOO M, CHUN MH, HONG GR, et al. Effects of Training with a Powered Exoskeleton on Cortical Activity Modulation in Hemiparetic Chronic Stroke Patients: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;104(10):1620-1629.
[17] MOLTENI F, GASPERINI G, GAFFURI M, et al. Wearable robotic exoskeleton for over-ground gait training in sub-acute and chronic hemiparetic stroke patients: preliminary results. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2017;53:676-684.
[18] TANG X, WANG X, JI X, et al. A Wearable Lower Limb Exoskeleton: Reducing the Energy Cost of Human Movement. Micromachines (Basel). 2022;13(6):900.
[19] 陈瑞旦,黄山城,李天裕.姿势镜对脑卒中后偏瘫患者运动功能障碍恢复的影响[J].深圳中西医结合杂志,2021,31(6):152-154.
[20] 中华医学会神经病学分会,中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管 病学组.中国各类主要脑血管病诊断要点2019 [J].中华神经科杂志, 2019,52(9):710-715.
[21] 支亮,王玉龙,张清芳,等.脑卒中患者偏瘫步态中的推进力缺陷[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(35):5709-5715.
[22] CERFOGLIO S, FERRARIS C, VISMARA L, et al. Kinect-Based Assessment of Lower Limbs during Gait in Post-Stroke Hemiplegic Patients: A Narrative Review. Sensors (Basel). 2022;22(13):4910.
[23] YAO J, SADO T, WANG W, et al. The Kickstart Walk Assist System for improving balance and walking function in stroke survivors: a feasibility study. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2021;18(1):42.
[24] PARK YH, LEE DH, LEE JH. A Comprehensive Review: Robot-Assisted Treatments for Gait Rehabilitation in Stroke Patients. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60(4):620.
[25] LIN YN, HUANG SW, KUAN YC, et al. Hybrid robot-assisted gait training for motor function in subacute stroke: a single-blind randomized controlled trial. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2022;19(1):99.
[26] 程雪,白定群,彭晓华,等.下肢外骨骼康复机器人在脑卒中康复中的应用和研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2021,36(10): 1327-1332.
[27] 孙丰云,高亮,苏振峰.网格姿势镜对卒中后患者共济运动障碍训练的作用[J].中国实用医药,2012,7(15):26-27.
[28] SHIN J, CHUNG Y. The effects of treadmill training with visual feedback and rhythmic auditory cue on gait and balance in chronic stroke patients: A randomized controlled trial. NeuroRehabilitation. 2022;51(3):443-453.
[29] YANG SH, CHUNG EJ, LEE J, et al. The Effect of Trunk Stability Training Based on Visual Feedback on Trunk Stability, Balance, and Upper Limb Function in Stroke Patients: A Randomized Control Trial. Healthcare (Basel). 2021;9(5):532.
[30] MUDIE MH, WINZELER-MECRAY U, RADWNA S, et al. Training symmetry of weight distribution after stroke: a randomized controlled pilor study comparing task-related reach,bobath and feedback training approaches. Clin Rehabil. 2002;16(6):582-592.
[31] 伍娟,曾奕,蔡素芳对处于软瘫期的脑卒中患者用镜像疗法结合运动想象疗法进行康复治疗的效果[J].当代医药论丛,2019,17(1):19-21.
[32] WU Y, DONG Y, TANG Y, et al. Relationship between motor performance and cortical activity of older neurological disorder patients with dyskinesia using fNIRS: A systematic review. Front Physiol. 2023;14: 1153469.
[33] LI Y, WEI Q, GOU W, et al. Effects of mirror therapy on walking ability, balance and lower limb motor recovery after a stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Rehabil. 2018;32(8):1007-1021.
[34] LIM SB, YANG CL, PETERS S, et al. Phase-dependent Brain Activation of the Frontal and Parietal Regions During Walking After Stroke - An fNIRS Study. Front Neurol. 2022;13:904722.
[35] ONO Y, NOAH JA, ZHANG X, et al. Motor learning and modulation of prefrontal cortex: an fNIRS assessment. J Neural Eng. 2015;12:066004.
[36] BERGER A, HORST F, STEINBERG F, et al. Increased gait variability during robot-assisted walking is accompanied by increased sensorimotor brain activity in healthy people. J Neuro Rehabilitation. 2019;16(1):161.
[37] SCHRADER M, STERR A, KETTLITZ R, et al. The effect of mirror therapy can be improved by simultaneous robotic assistance. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2022;40(3):185-194.
[38] MOLTENI F, GASPERINI G, GAFFURI M, et al. Wearable robotic exoskeleton for overground gait training in sub-acute and chronic hemiparetic stroke patients: preliminary results. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2017;53:676-684.
[39] JIAE K, CHUN MH, LEE J, et al. Intensity control of robot-assisted gait training based on biometric data: Preliminary study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(38):e30818.
[40] HEROLD F, WIEGEL P, SCHOLKMANN F, et al. Functional near-infrared spectroscopy in movement science: a systematic review on cortical activity in postural and walking tasks. 2017;4:41403.
[41] LIM SB, YANG CL, PETERS S, et al. Phase-dependent Brain Activation of the Frontal and Parietal Regions During Walking After Stroke-An fNIRS Study. Front Neurol. 2022;13:904722.
[42] XU Y, HOU QH, RUSSELL SD, et al. Neuroplasticity in post-stroke gait recovery and noninvasive brain stimulation. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(12):2072-2080. |