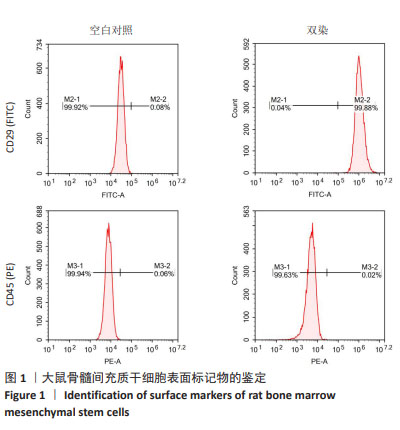
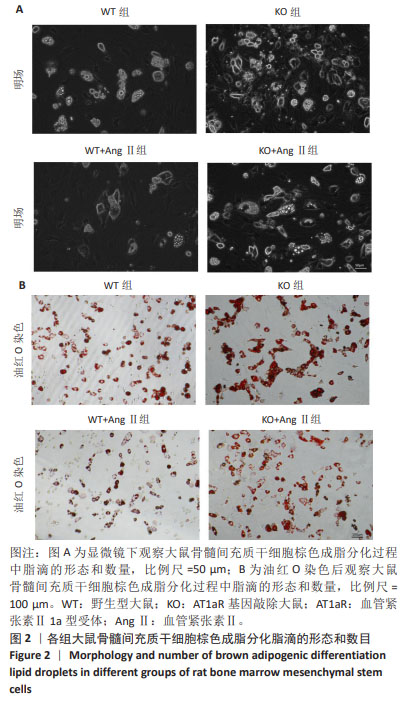
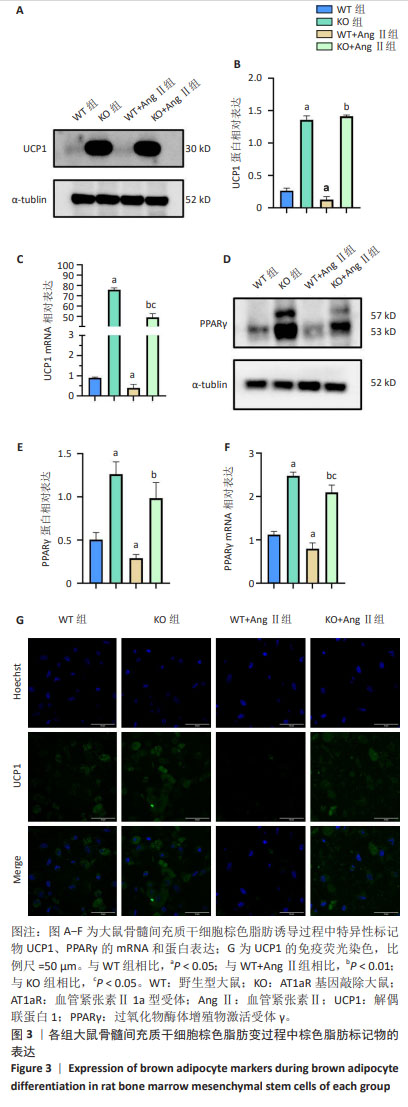
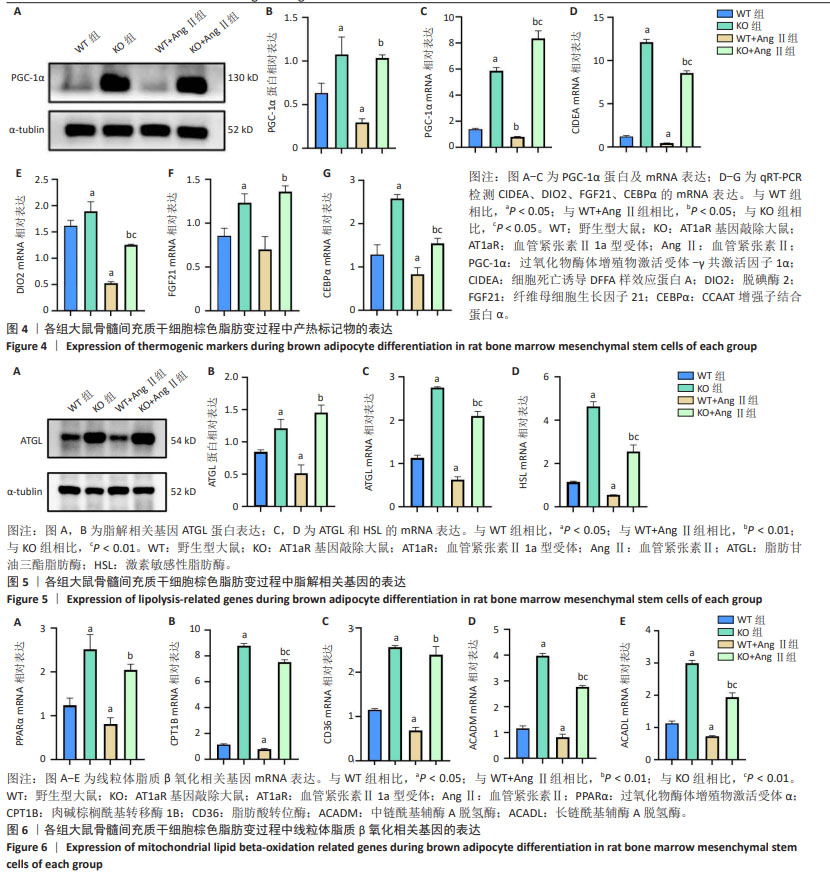
[1] NOVELLI G, CASSADONTE C, SBRACCIA P, et al. Genetics: A Starting Point for the Prevention and the Treatment of Obesity. Nutrients. 2023;15(12):2782.
[2] MATSUSHITA K, WU Y, PRATT RE, et al. Deletion of angiotensin II type 2 receptor accelerates adipogenesis in murine mesenchymal stem cells via Wnt10b/beta-catenin signaling. Lab Invest. 2016;96(8):909-917.
[3] PAHLAVANI M, KALUPAHANA NS, RAMALINGAM L, et al. Regulation and Functions of the Renin-Angiotensin System in White and Brown Adipose Tissue. Compr Physiol. 2017;7(4):1137-1150.
[4] CAI Z, FANG L, JIANG Y, et al. Angiotensin II Promotes White Adipose Tissue Browning and Lipolysis in Mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:6022601.
[5] LI A, SHI W, WANG J, et al. The gene knockout of angiotensin II type 1a receptor improves high-fat diet-induced obesity in rat via promoting adipose lipolysis. PLoS One. 2022;17(7):e0267331.
[6] LIU C, FAN Y, ZHOU L, et al. Pretreatment of mesenchymal stem cells with angiotensin II enhances paracrine effects, angiogenesis, gap junction formation and therapeutic efficacy for myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 2015;188:22-32.
[7] JIANG X, WU F, XU Y, et al. A novel role of angiotensin II in epidermal cell lineage determination: Angiotensin II promotes the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into keratinocytes through the p38 MAPK, JNK and JAK2 signalling pathways. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28(1):59-65.
[8] DI MAIO G, ALESSIO N, PELUSO G, et al. Molecular and Physiological Effects of Browning Agents on White Adipocytes from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(20):12151.
[9] RODRÍGUEZ-CANO MM, GONZÁLEZ-GÓMEZ MJ, SÁNCHEZ-SOLANA B,
et al. NOTCH Receptors and DLK Proteins Enhance Brown Adipogenesis in Mesenchymal C3H10T1/2 Cells. Cells. 2020;9(9):2032.
[10] VAN NGUYEN TT, VU VV, PHAM PV. Transcriptional Factors of Thermogenic Adipocyte Development and Generation of Brown and Beige Adipocytes From Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020;16(5):876-892.
[11] KAJIMURA S, SAITO M. A new era in brown adipose tissue biology: molecular control of brown fat development and energy homeostasis. Annu Rev Physiol. 2014;76:225-249.
[12] HUANG PI, CHEN YC, CHEN LH, et al. PGC-1α mediates differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells to brown adipose cells. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2011;18(11):966-980.
[13] LUO Y, YE S, CHEN X, et al. Rush to the fire: FGF21 extinguishes metabolic stress, metaflammation and tissue damage. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017;38:59-65.
[14] YAU WW, SINGH BK, LESMANA R, et al. Thyroid hormone (T3) stimulates brown adipose tissue activation via mitochondrial biogenesis and MTOR-mediated mitophagy. Autophagy. 2019;15(1):131-150.
[15] LIN SC, LI P. CIDE-A, a novel link between brown adipose tissue and obesity. Trends Mol Med. 2004;10(9):434-439.
[16] WANG J, LI D, ZHANG Y, et al. Angiotensin II type 1a receptor knockout ameliorates high-fat diet-induced cardiac dysfunction by regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2023; 55(9):1380-1392.
[17] CHENG L, ZHANG S, SHANG F, et al. Emodin Improves Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Disorders in Obese Mice via Activating Brown Adipose Tissue and Inducing Browning of White Adipose Tissue. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:618037.
[18] ABE I, OGURI Y, VERKERKE ARP, et al. Lipolysis-derived linoleic acid drives beige fat progenitor cell proliferation. Dev Cell. 2022;57(23):2623-2637.e8.
[19] LU T, ZHANG Z, BI Z, et al. TFAM deficiency in dendritic cells leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and enhanced antitumor immunity through cGAS-STING pathway. J Immunother Cancer. 2023;11(3):e005430.
[20] CHEN QM. Nrf2 for protection against oxidant generation and mitochondrial damage in cardiac injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;179:133-143.
[21] WIKSTROM JD, MAHDAVIANI K, LIESA M, et al. Hormone-induced mitochondrial fission is utilized by brown adipocytes as an amplification pathway for energy expenditure. EMBO J. 2014;33(5):418-436.
[22] KLEELE T, REY T, WINTER J, et al. Distinct fission signatures predict mitochondrial degradation or biogenesis. Nature. 2021;593(7859):435-439.
[23] MARQUEZ-CURTIS LA, JANOWSKA-WIECZOREK A, MCGANN LE, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells derived from various tissues: Biological, clinical and cryopreservation aspects. Cryobiology. 2015;71(2):181-197.
[24] MOON H, CHOI JW, SONG BW, et al. Isoliquiritigenin Enhances the Beige Adipocyte Potential of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells by JNK Inhibition. Molecules. 2020;25(23):5660.
[25] CARPENTIER AC, BLONDIN DP, HAMAN F, et al. Brown Adipose Tissue-A Translational Perspective. Endocr Rev. 2023;44(2):143-192.
[26] IKEDA K, MARETICH P, KAJIMURA S. The Common and Distinct Features of Brown and Beige Adipocytes. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2018;29(3):191-200.
[27] ALVAREZ-GALLEGO F, GONZÁLEZ-BLÁZQUEZ R, GIL-ORTEGA M, et al. Angiotensin II type 2 receptor as a novel activator of brown adipose tissue in obesity. Biofactors. 2023;49(6):1106-1120.
[28] LOH RKC, FORMOSA MF, LA GERCHE A, et al. Acute metabolic and cardiovascular effects of mirabegron in healthy individuals. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019;21(2):276-284.
[29] SLAMKOVA M, ZORAD S, KRSKOVA K. Alternative renin-angiotensin system pathways in adipose tissue and their role in the pathogenesis of obesity. Endocr Regul. 2016;50(4):229-240.
[30] NING K, LIU S, YANG B, et al. Update on the effects of energy metabolism in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation. Mol Metab. 2022;58:101450.
[31] HALLBERG M, MORGANSTEIN DL, KISKINIS E, et al. A functional interaction between RIP140 and PGC-1alpha regulates the expression of the lipid droplet protein CIDEA. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28(22):6785-6795.
[32] FARMER SR. Transcriptional control of adipocyte formation. Cell Metab. 2006;4(4):263-273.
[33] XU Y, YU T, MA G, et al. Berberine modulates deacetylation of PPARγ to promote adipose tissue remodeling and thermogenesis via AMPK/SIRT1 pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(12):3173-3187.
[34] 常华杰,勾文峰,郭江红,等.胡黄连苷Ⅰ、Ⅱ通过调节C/EBP-PPARγ通路抑制3T3-L1脂肪前体细胞的分化和脂肪合成[J].药物评价研究, 2023,46(6):1193-1200.
[35] PARK M, BAEK H, HAN JY, et al. Stevioside Enhances the Anti-Adipogenic Effect and β-Oxidation by Activating AMPK in 3T3-L1 Cells and Epididymal Adipose Tissues of db/db Mice. Cells. 2022;11(7):1076.
[36] FINCK BN, KELLY DP. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 (PGC-1) regulatory cascade in cardiac physiology and disease. Circulation. 2007;115(19):2540-2548.
[37] DUTCHAK PA, KATAFUCHI T, BOOKOUT AL, et al. Fibroblast growth factor-21 regulates PPARγ activity and the antidiabetic actions of thiazolidinediones. Cell. 2012;148(3):556-567.
[38] JASH S, BANERJEE S, LEE MJ, et al. CIDEA Transcriptionally Regulates UCP1 for Britening and Thermogenesis in Human Fat Cells. iScience. 2019;20: 73-89.
[39] ROSENWALD M, PERDIKARI A, RÜLICKE T, et al. Bi-directional interconversion of brite and white adipocytes. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15(6):659-667.
[40] YOON D, IMRAN KM, KIM YS. Distinctive effects of licarin A on lipolysis mediated by PKA and on formation of brown adipocytes from C3H10T1/2 mesenchymal stem cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018;340:9-20.
[41] STEC DE, GORDON DM, HIPP JA, et al. Loss of hepatic PPARα promotes inflammation and serum hyperlipidemia in diet-induced obesity. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2019;317(5):R733-R745.
[42] PATEL BV, YAO F, HOWENSTINE A, et al. Emergent Coordination of the CHKB and CPT1B Genes in Eutherian Mammals: Implications for the Origin of Brown Adipose Tissue. J Mol Biol. 2020;432(23):6127-6145.
[43] WU L, LIU C, CHANG DY, et al. The Attenuation of Diabetic Nephropathy by Annexin A1 via Regulation of Lipid Metabolism Through the AMPK/PPARα/CPT1b Pathway. Diabetes. 2021;70(10):2192-2203.
[44] TAHRI-JOUTEY M, ANDREOLETTI P, SURAPUREDDI S, et al. Mechanisms Mediating the Regulation of Peroxisomal Fatty Acid Beta-Oxidation by PPARα. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(16):8969.
[45] ZHU Q, AN YA, SCHERER PE. Mitochondrial regulation and white adipose tissue homeostasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2022;32(4):351-364.
[46] ROH HC, KUMARI M, TALEB S, et al. Adipocytes fail to maintain cellular identity during obesity due to reduced PPARγ activity and elevated TGFβ-SMAD signaling. Mol Metab. 2020;42:101086.
[47] CEDIKOVA M, KRIPNEROVÁ M, DVORAKOVA J, et al. Mitochondria in White, Brown, and Beige Adipocytes. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:6067349.
[48] KLINGENBERG M, HUANG SG. Structure and function of the uncoupling protein from brown adipose tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1415(2): 271-296.
[49] REN Z, ZHANG X, DING T, et al. Mitochondrial Dynamics Imbalance: A Strategy for Promoting Viral Infection. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:1992.
[50] UM JH, YUN J. Emerging role of mitophagy in human diseases and physiology. BMB Rep. 2017;50(6):299-307.
[51] TWIG G, HYDE B, SHIRIHAI OS. Mitochondrial fusion, fission and autophagy as a quality control axis: the bioenergetic view. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1777(9):1092-1097.
[52] LIESA M, SHIRIHAI OS. Mitochondrial dynamics in the regulation of nutrient utilization and energy expenditure. Cell Metab. 2013;17(4):491-506. |