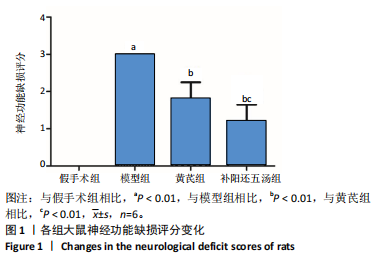
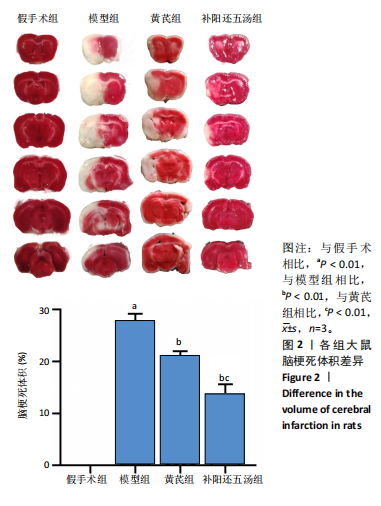
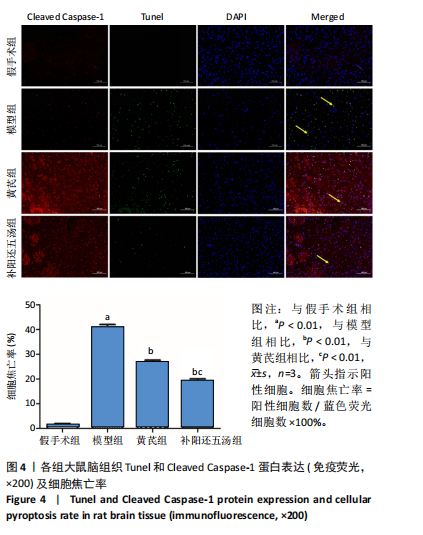
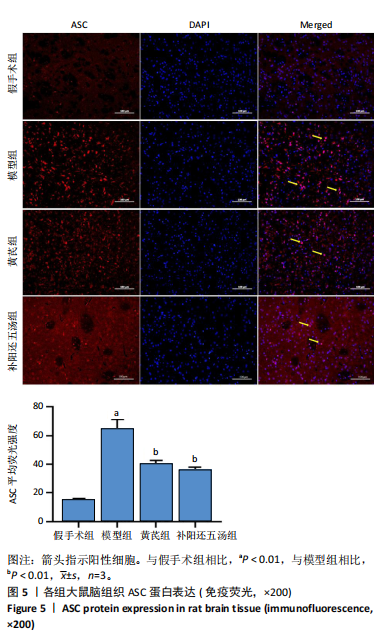
[1] ZHANG Y, LIU L, HOU X, et al. Role of Autophagy Mediated by AMPK/DDiT4/mTOR Axis in HT22 Cells Under Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation. ACS Omega. 2023;8(10):9221-9229.
[2] YU P, ZHANG X, LIU N, et al. Pyroptosis: mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):128.
[3] HU B, ZHANG J, HUANG J, et al. NLRP3/1-mediated pyroptosis: beneficial clues for the development of novel therapies for Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(11):2400-2410.
[4] YIN M, LIU Z, WANG J, et al. Buyang Huanwu decoction alleviates oxidative injury of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion through PKCε/Nrf2 signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;303:115953.
[5] PALOMINO-ANTOLIN A, NARROS-FERNÁNDEZ P, FARRÉ-ALINS V, et al. Time-dependent dual effect of NLRP3 inflammasome in brain ischaemia. Br J Pharmacol. 2022;179(7):1395-1410.
[6] LI MC, LI MZ, LIN ZY, et al. Buyang Huanwu Decoction promotes neurovascular remodeling by modulating astrocyte and microglia polarization in ischemic stroke rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;323:117620.
[7] 单玉栋,赵艳萌,靳晓飞,等.补阳还五汤通过PI3K/AKT通路调控自噬抗大鼠脑缺血/再灌注损伤的作用[J].中国药理学通报, 2023,39(2):386-391.
[8] 吴增,董贤慧,周晓红,等.补阳还五汤对脑缺血/再灌注大鼠神经干细胞移植后神经功能的保护作用[J].中国药理学通报,2019, 35(9):1289-1295.
[9] ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y, JIN XF, et al. The Role of Astragaloside IV against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury: Suppression of Apoptosis via Promotion of P62-LC3-Autophagy. Molecules. 2019;24(9):1838.
[10] XU J, KONG X, XIU H, et al. Combination of curcumin and vagus nerve stimulation attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced behavioral deficits. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;103:614-620.
[11] XIAO L, DAI Z, TANG W, et al. Astragaloside IV Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury through NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Pyroptosis Inhibition via Activating Nrf2. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021; 2021:9925561.
[12] TUO QZ, ZHANG ST, LEI P. Mechanisms of neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke and their therapeutic implications. Med Res Rev. 2022;42(1):259-305.
[13] FATTAKHOV N, NGO A, TORICES S, et al. Cenicriviroc prevents dysregulation of astrocyte/endothelial cross talk induced by ischemia and HIV-1 via inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024;326(2):C487-C504.
[14] AN D, XU W, GE Y, et al. Protection of Oxygen Glucose Deprivation-Induced Human Brain Vascular Pericyte Injury: Beneficial Effects of Bellidifolin in Cellular Pyroptosis. Neurochem Res. 2023;48(9):2794-2807.
[15] SHI J, GAO W, SHAO F. Pyroptosis: Gasdermin-Mediated Programmed Necrotic Cell Death. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017;42(4):245-254.
[16] LI J, XU P, HONG Y, et al. Lipocalin-2-mediated astrocyte pyroptosis promotes neuroinflammatory injury via NLRP3 inflammasome activation in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2023;20(1):148.
[17] 唐琼燕,陈勇军.细胞焦亡与脑卒中关系的研究进展[J].中南医学科学杂志,2021,49(4):493-496.
[18] XIAO L, MAGUPALLI VG, WU H. Cryo-EM structures of the active NLRP3 inflammasome disc. Nature. 2023;613(7944):595-600.
[19] TENG JF, MEI QB, ZHOU XG, et al. Polyphyllin VI Induces Caspase-1-Mediated Pyroptosis via the Induction of ROS/NF-κB/NLRP3/GSDMD Signal Axis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(1):193.
[20] FU J, WU H. Structural Mechanisms of NLRP3 Inflammasome Assembly and Activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2023;41:301-316.
[21] LIU Z, WANG C, RATHKEY JK, et al. Structures of the Gasdermin D C-Terminal Domains Reveal Mechanisms of Autoinhibition. Structure. 2018;26(5):778-784.e3.
[22] HUANG J, GUO W, CHEUNG F, et al. Integrating Network Pharmacology and Experimental Models to Investigate the Efficacy of Coptidis and Scutellaria Containing Huanglian Jiedu Decoction on Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Am J Chin Med. 2020;48(1):161-182.
[23] 马娴,高萍,刘真一,等.补阳还五汤减轻氧化应激保护脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠血脑屏障的作用研究[J].中国比较医学杂志,2024, 34(3):75-84+101.
[24] 周啸天,骆亚莉,李佳蔚,等.补阳还五汤防治缺血性脑卒中作用机制的研究现状[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2022,38(9):1011-1015.
[25] 唐强,张世强,朱路文,等.补阳还五汤治疗急性期缺血性中风系统评价[J].康复学报,2021,31(6):514-522.
[26] 徐鹏,张冬梅,吕志国,等.补阳还五汤治疗缺血性中风恢复期疗效的系统评价[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2018,20(11):1911-1923.
[27] WANG K, LEI L, CAO J, et al. Network pharmacology-based prediction of the active compounds and mechanism of Buyang Huanwu Decoction for ischemic stroke. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(4):1050.
[28] DINDA B, DINDA S, DASSHARMA S, et al. Therapeutic potentials of baicalin and its aglycone, baicalein against inflammatory disorders. Eur J Med Chem. 2017;131:68-80.
[29] YU L, ZHANG Y, CHEN Q, et al. Formononetin protects against inflammation associated with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by targeting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;149:112836.
[30] 陈雨菡,石小鹏,马善波,等.黄芪中毛蕊异黄酮的脑保护作用研究进展[J].中国急救医学,2021,41(11):1004-1008.
[31] MIAO R, JIANG C, CHANG WY, et al. Gasdermin D permeabilization of mitochondrial inner and outer membranes accelerates and enhances pyroptosis. Immunity. 2023;56(11):2523-2541.e8. |