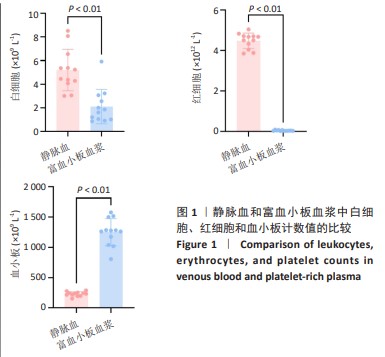
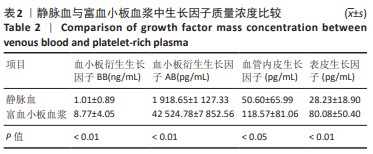
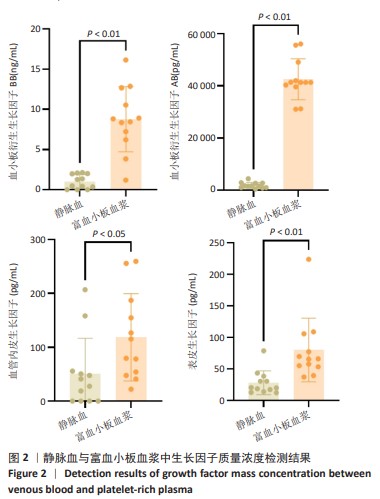
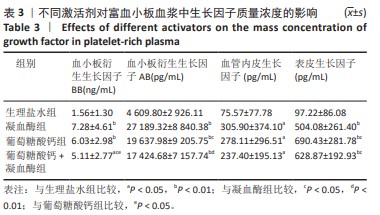
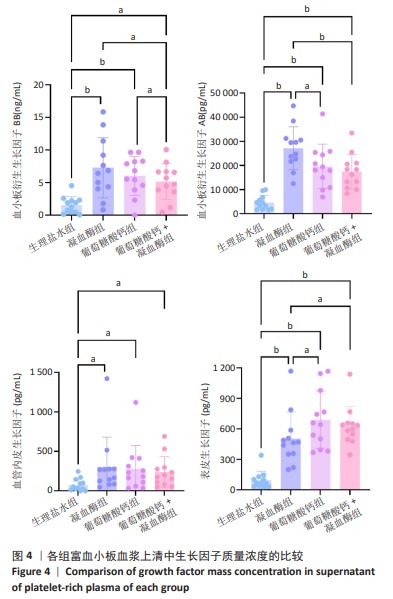
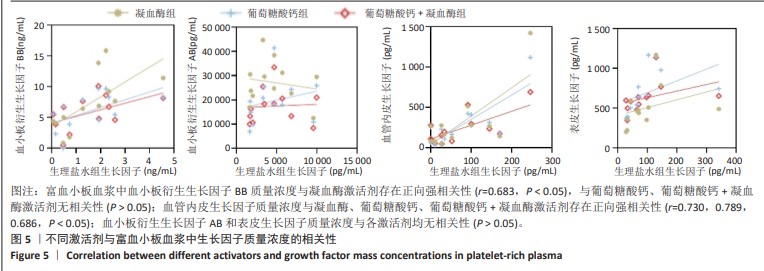
[1] KATAOKA T, MIFUNE Y, INUI A, et al. Combined therapy of platelet-rich plasma and basic fibroblast growth factor using gelatin-hydrogel sheet for rotator cuff healing in rat models. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):605.
[2] BILAL Ö, TOPAK D, KıNAŞ M, et al. Epidermal growth factor or platelet-rich plasma combined with induced membrane technique in the treatment of segmental femur defects: an experimental study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):601.
[3] RODRIGUES BL, MONTALVÃO SAL, CANCELA RBB, et al. Treatment of male pattern alopecia with platelet-rich plasma: A double-blind controlled study with analysis of platelet number and growth factor levels. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;80(3):694-700.
[4] BORSANI E, BUFFOLI B, BONOMINI F, et al. The Growth Factor Release from a Platelet-Rich Plasma Preparation Is Influenced by the Onset of Guttate Psoriasis: A Case Report. Appl Sci (Basel). 2022;12(14):7250.
[5] BEITIA M, DELGADO D, MERCADER J, et al. Action of Platelet-Rich Plasma on In Vitro Cellular Bioactivity: More than Platelets. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5367.
[6] LIM W, PARK SH, KIM B, et al. Relationship of cytokine levels and clinical effect on platelet-rich plasma-treated lateral epicondylitis. J Orthop Res. 2017;36(3):913-920.
[7] CELIKTEN M, SAHIN H, SENTURK GE, et al. The effect of platelet-rich fibrin, platelet-rich plasma, and concentrated growth factor in the repair of full thickness rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023:S1058-2746(23)00772-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2023.09.028.
[8] XU H, XU F, ZHAO J, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma Induces Autophagy and Promotes Regeneration in Human Dental Pulp Cells. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:659742.
[9] MYUNG H, JANG H, MYUNG JK, et al. Platelet-rich plasma improves the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells by enhancing their secretion of angiogenic factors in a combined radiation and wound injury model. Exp Dermatol. 2020;29(2):158-167.
[10] ABU-GHNAME A, PERDANASARI AT, DAVIS MJ, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma: Principles and Applications in Plastic Surgery. Semin Plast Surg. 2019;33(3):155-161.
[11] BOSWELL SG, SCHNABEL LV, MOHAMMED HO, et al. Increasing platelet concentrations in leukocyte-reduced platelet-rich plasma decrease collagen gene synthesis in tendons. Am J Sport Med. 2013;42(1):42-49.
[12] PINEDA-CORTEL MR, SUAREZ C, CABRERA JT, et al. Biotherapeutic Applications of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Regenerative Medicine. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023;20(6):811-828.
[13] 刘建香,吕孟兴,陈昊,等.自体富血小板血浆治愈儿童难治性骨髓炎合并骨折1例[J].中国输血杂志,2023,36(8):673-675.
[14] ORBAN YA, SOLIMAN MA, HEGAB YH, et al. Autologous platelet-rich plasma vs conventional dressing in the management of chronic diabetic foot ulcers. WOunds. 2022;33(2):36-42.
[15] CHIU CH, CHEN P, YEH WL, et al. The gelling effect of platelet-rich fibrin matrix when exposed to human tenocytes from the rotator cuff in small-diameter culture wells and the design of a co-culture device to overcome this phenomenon. Bone Joint Res. 2019;8(5):216-223.
[16] 中国输血协会临床输血管理学专业委员会.自体富血小板血浆制备技术专家共识[J].中国输血杂志,2021,34(7):677-683.
[17] KUSHIDA S, KAKUDO N, MORIMOTO N, et al. Platelet and growth factor concentrations in activated platelet-rich plasma: a comparison of seven commercial separation systems. J Artif Organs. 2014;17(2):186-192.
[18] 王淑君,赵广超,罗开云,等.不同处理方式对富血小板血浆相关生长因子的影响[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2022,30(6):1834-1838.
[19] WANG SL, LIU XL, KANG ZC, et al. Platelet-rich plasma promotes peripheral nerve regeneration after sciatic nerve injury. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(2):375-381.
[20] CROISÉ B, PARÉ A, JOLY A, et al. Optimized centrifugation preparation of the platelet rich plasma: Literature review. J Stomatol Oral Maxi. 2019; 121(2):150-154.
[21] STRAUM OK. The optimal platelet concentration in platelet-rich plasma for proliferation of human cells in vitro-diversity, biases, and possible basic experimental principles for further research in the field: A review. PeerJ. 2020;8:e10303.
[22] 高华,周世秋,刘作凤,等.富血小板血浆在不同激活剂下生长因子浓度的研究[J].中国输血杂志,2021,34(10):1086-1089.
[23] BARIA M, VASILEFF WK, MILLER M, et al. Cellular Components and Growth Factor Content of Platelet-Rich Plasma With a Customizable Commercial System. Am J Sport Med. 2019;47(5):1216-1222.
[24] 向仁雪,吴建君,王嘉嘉,等.手工与全自动法制备富血小板血浆的质量及治疗膝关节疾病的疗效分析[J].中国输血杂志,2021,34(7): 695-698.
[25] ANITUA E, ZALDUENDO MM, ALKHRAISAT MH, et al. Release kinetics of platelet-derived and plasma-derived growth factors from autologous plasma rich in growth factors. Ann Anat. 2013;195(5):461-466.
[26] 林盘玉,许放,赵良军.富血小板纤维蛋白中生长因子含量及释放周期的实验研究[J].中国医药科学,2023,13(5):29-32.
[27] ZHUANG YW, ZENG YM, CHEN YF, et al. [The effects of different activators on the release curve of human platelet-rich plasma]. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2018;41(11):868-872.
[28] 杨域,张卫,程飚.不同激活剂对人富血小板血浆形成凝胶及释放活性物质影响的实验研究[J].中华烧伤杂志,2017,33(1):12-17.
[29] 黄谦,吴涛,金丹,等.不同比例激活富血小板血浆对其生长因子浓度及人骨髓基质干细胞增殖的影响[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008, 10(10):965-969. |