|
[1] SONOYAMA W, LIU Y, FANG D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated functional tooth regeneration in swine. PLoS One. 2006;1:e79.
[2] CHUEH LH, HUANG GT. Immature teeth with periradicular periodontitis or abscess undergoing apexogenesis: a paradigm shift. J Endod. 2006;32(12):1205-1213.
[3] 张羽,吴家媛.生长因子对根尖牙乳头干细胞增殖及分化的影响[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2016,9(3):187-190.
[4] 张莹,张郁,金岩.转化生长因子-β受体在人牙髓中的表达和意义[J].实用口腔医学杂志,1999,15(5):361-363.
[5] 张莹,张郁,金岩.转化生长因子β受体在牙胚发育过程中的表达和意义[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,1999,9(1):11.
[6] 丁芳,吴家媛,贾谦,等. TGF-β1对人根尖牙乳头干细胞增殖和分化的影响[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2011,21(7):375-379.
[7] BELLAMY C, SHRESTHA S, TORNECK C, et al. Effects of a Bioactive Scaffold Containing a Sustained Transforming Growth Factor-β1-releasing Nanoparticle System on the Migration and Differentiation of Stem Cells from the Apical Papilla. J Endod. 2016;42(9):1385-1392.
[8] 顾雪凝,权家苗,郭雨晴,等.环磷酸腺苷反应元件结合蛋白调控转化生长因子β1对人根尖牙乳头干细胞分化的作用[J].口腔疾病防治, 2018,26(7): 428-433.
[9] 陈尽欢,孙建勋,陈新梅.转化生长因子-β超家族成员在牙本质发生发育中的作用[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2016,43(4):477-481.
[10] 程敏,程琳,冯志远,等.骨形态发生蛋白-2在牙发育各阶段中的表达[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2009,36(6):639-642.
[11] WANG W, DANG M, ZHANG Z, et al. Dentin regeneration by stem cells of apical papilla on injectable nanofibrous microspheres and stimulated by controlled BMP-2 release. Acta Biomater. 2016;36: 63-72.
[12] LI J, GUO W, XIONG M, et al. Effect of SDF-1/CXCR4 axis on the migration of transplanted bone mesenchymal stem cells mobilized by erythropoietin toward lesion sites following spinal cord injury. Int J Mol Med. 2015;36(5):1205-1214.
[13] XIAO M, QIU J, KUANG R, et al. Synergistic effects of stromal cell-derived factor-1α and bone morphogenetic protein-2 treatment on odontogenic differentiation of human stem cells from apical papilla cultured in the VitroGel 3D system. Cell Tissue Res. 2019;378(2):207-220.
[14] XIAO M, YAO B, ZHANG BD, et al. Stromal-derived Factor-1α signaling is involved in bone morphogenetic protein-2-induced odontogenic differentiation of stem cells from apical papilla via the Smad and Erk signaling pathways. Exp Cell Res. 2019;381(1): 39-49.
[15] 李俊俊. NF-κB信号通路在人根尖牙乳头干细胞增殖及定向分化中的作用机制研究[D].南京:南京医科大学, 2014.
[16] ZHANG W, ZHANG X, LING J, et al. Proliferation and odontogenic differentiation of BMP2 gene‑transfected stem cells from human tooth apical papilla: an in vitro study. Int J Mol Med. 2014;34(4):1004-1012.
[17] ZHANG W, ZHANG X, LING J, et al. Osteo-/odontogenic differentiation of BMP2 and VEGF gene-co-transfected human stem cells from apical papilla. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(5): 3747-3754.
[18] ZHANG W, ZHANG X, LI J, et al. Foxc2 and BMP2 Induce Osteogenic/Odontogenic Differentiation and Mineralization of Human Stem Cells from Apical Papilla. Stem Cells Int. 2018; 2018:2363917.
[19] 赵丹,罗进勇. BMP9促进间充质干细胞C3H10T1/2成骨分化的研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2011,10(16):1225-1226.
[20] 王金华. BMP9调控小鼠根尖牙乳头干细胞成牙本质分化及其机制的初步研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2013.
[21] 孔令姣,王金华. BMP9通过ERK5信号通路调控根尖牙乳头干细胞成骨/成牙本质分化[J].中国医科大学学报,2017,46(6):527-531.
[22] 陈冰,孔令姣,雷金霞,等.BMP9经Smad信号通路调控iSCAP成骨/成牙本质分化[J].中国生物工程杂志,2016,36(8):16-22.
[23] KIM TH, BAE CH, YANG S, et al. Nfic regulates tooth root patterning and growth. Anat Cell Biol. 2015;48(3):188-194.
[24] GAO S, ZHAO YM, GE LH. Nuclear factor I-C expression pattern in developing teeth and its important role in odontogenic differentiation of human molar stem cells from the apical papilla. Eur J Oral Sci. 2014;122(6):382-390.
[25] 张菁.转录因子NFIC在人根尖牙乳头干细胞分化中的作用及其机制研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2013.
[26] 梁妍,张菁,李颂.转录因子NFIC在cAMP信号通路调控根尖牙乳头干细胞分化中的作用[J].安徽医科大学学报, 2017,52(2):190-193.
[27] 肖佩芳,柴忆欢,何军,等.环磷酸腺苷反应元件结合蛋白在儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病中表达的意义[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2008,23(3): 200-202.
[28] SIDDAPPA R, MARTENS A, DOORN J, et al. cAMP/PKA pathway activation in human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro results in robust bone formation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105(20):7281-7286.
[29] 苏圣哲.转录因子CREB在根尖牙乳头干细胞定向分化中的作用[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2016.
[30] 李由由. Wnt5a对根尖牙乳头干细胞体内成牙/成骨分化的影响[D].遵义:遵义医学院,2016.
[31] 姚睿,范志朋.组蛋白去甲基化酶KDM4B促进根尖牙乳头干细胞中成骨和成牙本质分化[J].北京口腔医学,2013,21(4):181-184.
[32] 岑洪,林茂芳,黄河,等.雌激素受体α和β在间充质干细胞体外成骨、成脂肪分化中的表达变化[J].广西医科大学学报,2005,22(6):883-885.
[33] 卢亚蝶,闫明,于金华.雌激素受体α高表达慢病毒载体对根尖牙乳头干细胞成牙/成骨分化的影响[J].口腔医学,2016,36(6):485-488.
[34] BUTLER WT, RITCHIE H. The nature and functional significance of dentin extracellular matrix proteins. Int J Dev Biol. 1995;39(1): 169-179.
[35] 马兆峰,李石,翁希里,等.牙本质非胶原蛋白对人根尖牙乳头干细胞增殖及分化能力的影响[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2016,26(5): 283-287.
[36] WU J, JIA Q, HE W, et al. Conditioned medium from periapical follicle cells induces the odontogenic differentiation of stem cells from the apical papilla in vitro. J Endod. 2013;39(8):1015-1022.
[37] 付越,刘尧,陈旭.富血小板纤维蛋白应用于口腔组织再生研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2016,9(1):59-62.
[38] ABUARQOUB D, AWIDI A, ABUHARFEIL N. Comparison of osteo/odontogenic differentiation of human adult dental pulp stem cells and stem cells from apical papilla in the presence of platelet lysate. Arch Oral Biol. 2015;60(10):1545-1553.
[39] 黄奕智.根尖牙乳头干细胞和富含血小板血浆在SD大鼠模型中进行牙髓牙本质再生的研究[D].南昌:南昌大学,2017.
[40] SONG JS, TAKIMOTO K, JEON M, et al. Decellularized Human Dental Pulp as a Scaffold for Regenerative Endodontics. J Dent Res. 2017;96(6):640-646.
[41] 卢陈佩,王旭东,沈国芳.生物陶瓷在骨组织工程中的应用进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(22):3576-3582.
[42] BI J, LIU Y, LIU XM, et al. iRoot FM exerts an antibacterial effect on Porphyromonas endodontalis and improves the properties of stem cells from the apical papilla. Int Endod J. 2018;51(10): 1139-1148.
[43] WONGWATANASANTI N, JANTARAT J, SRITANAUDOMCHAI H, et al. Effect of Bioceramic Materials on Proliferation and Odontoblast Differentiation of Human Stem Cells from the Apical Papilla. J Endod. 2018;44(8):1270-1275.
[44] MILLER AA, TAKIMOTO K, WEALLEANS J, et al. Effect of 3 Bioceramic Materials on Stem Cells of the Apical Papilla Proliferation and Differentiation Using a Dentin Disk Model. J Endod. 2018;44(4): 599-603.
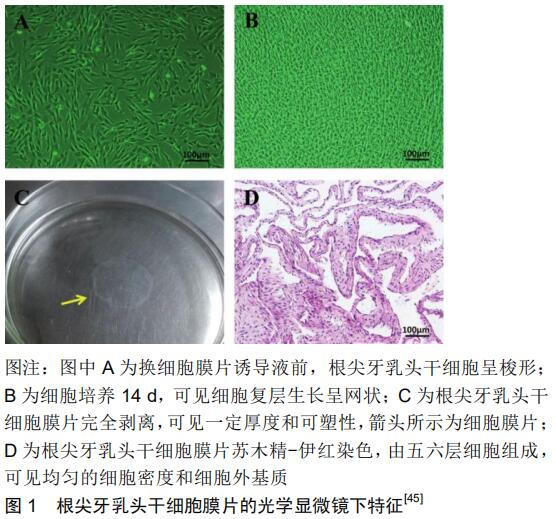
[45] 马学娟,刘雪梅,毕静,等.根尖牙乳头干细胞细胞膜片构建及其成骨/成牙本质分化性能研究[J].上海口腔医学,2018,27(2):123-128.
[46] NA S, ZHANG H, HUANG F, et al. Regeneration of dental pulp/dentine complex with a three-dimensional and scaffold-free stem-cell sheet-derived pellet. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016; 10(3):261-270.
[47] SHRESTHA S, DIOGENES A, KISHEN A. Temporal-controlled Dexamethasone Releasing Chitosan Nanoparticle System Enhances Odontogenic Differentiation of Stem Cells from Apical Papilla. J Endod. 2015;41(8):1253-1258.
[48] CHREPA V, AUSTAH O, DIOGENES A. Evaluation of a Commercially Available Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel (Restylane) as Injectable Scaffold for Dental Pulp Regeneration: An In Vitro Evaluation. J Endod. 2017;43(2):257-262.
[49] HA M, ATHIRASALA A, TAHAYERI A, et al. Micropatterned hydrogels and cell alignment enhance the odontogenic potential of stem cells from apical papilla in-vitro. Dent Mater. 2020;36(1): 88-96.
[50] UM S, CHOI JR, LEE JH, et al. Effect of leptin on differentiation of human dental stem cells. Oral Dis. 2011;17(7):662-669.
[51] 尹小萍,熊华翠,陈柯,等.瘦素对人根尖乳头干细胞成骨/成牙本质相关基因表达的影响[J].口腔疾病防治,2019,27(1):23-29.
[52] FU SP, WANG W, LIU BR, et al. β-Hydroxybutyric sodium salt inhibition of growth hormone and prolactin secretion via the cAMP/PKA/CREB and AMPK signaling pathways in dairy cow anterior pituitary cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(2):4265-4280.
[53] 苏圣哲,朱永娜,张菁,等. cAMP信号通路在根尖牙乳头干细胞定向分化中的作用[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2016,32(5):650-654.
[54] TANAKA Y, SONODA S, YAMAZA H, et al. Acetylsalicylic Acid Treatment and Suppressive Regulation of AKT Accelerate Odontogenic Differentiation of Stem Cells from the Apical Papilla. J Endod. 2019;45(5):591-598.
[55] 杜希希,李波,袁小平.机械牵张应力对人根尖牙乳头干细胞增殖分化的影响[J].医学研究生学报, 2017,30(10):1041-1047.
[56] 肖敏.机械压应力刺激对人牙髓干细胞和根尖牙乳头干细胞增殖、分化影响的体外研究[D].西安:第四军医大学, 2015.
|