| [1] Zhang Y, Wu XX. Research progress on procyanidins. Zhongyao Yaoli yu Linchuang ZaZhi. 2011;27(6): 112-116. [2] Lelono RA, Tachibana S. Bioassay-guided isolation and identification of antioxidative compounds from the bark of Eugenia polyantha. Pak J Biol Sci. 2013;16(16): 812-818. [3] Monagas M, Quintanilla-López JE, Gómez-Cordovés C, et al. MALDI-TOF MS analysis of plant proanthocyanidins. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2010;51(2):358-372. [4] Sun CF. Research progress on procyanidins. Shipin yu Jixie. 2010;26(4):146-152. [5] Vitseva O, Varghese S, Chakrabarti S, et al. Grape seed and skin extracts inhibit platelet function and release of reactive oxygen intermediates. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2005;46(4):445-451. [6] Bayatli F, Akku? D, Kilic E, et al. The protective effects of grape seed extract on MDA, AOPP, apoptosis and eNOS expression in testicular torsion: an experimental study. World J Urol. 2013;31(3):615-622. [7] Serra AT, Rocha J, Sepodes B, et al. Evaluation of cardiovascular protective effect of different apple varieties - Correlation of response with composition. Food Chem. 2012;135(4):2378-2386. [8] Tyagi A, Raina K, Gangar S, et al. Differential effect of grape seed extract against human non-small-cell lung cancer cells: the role of reactive oxygen species and apoptosis induction. Nutr Cancer. 2013;65 Suppl 1: 44-53. [9] Charradi K, Elkahoui S, Karkouch I, et al. Grape seed and skin extract alleviates high-fat diet-induced renal lipotoxicity and prevents copper depletion in rat. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2013;38(3):259-267. [10] Nishizuka T, Fujita Y, Sato Y, et al. Procyanidins are potent inhibitors of LOX-1: a new player in the French Paradox. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2011; 87(3):104-113. [11] Wang JS, Zhao J, Lv WJ, et al. Study on fillet quality of pseudosciaena crocea dip by oligomeric proanthocyanidins during cold storage. Zhongguo Shipin Xuebao. 2013;13(2):130-136. [12] Harrison DG, Gongora MC. Oxidative stress and hypertension. Med Clin North Am. 2009;93(3): 621-635. [13] Zhang H, Yerigui, Yang Y, et al. Structures and antioxidant and intestinal disaccharidase inhibitory activities of A-type proanthocyanidins from peanut skin. J Agric Food Chem. 2013;61(37):8814-8820. [14] Sivaprakasapillai B, Edirisinghe I, Randolph J, et al. Effect of grape seed extract on blood pressure in subjects with the metabolic syndrome. Metabolism. 2009;58(12):1743-1746. [15] Belcaro G, Ledda A, Hu S, et al. Grape seed procyanidins in pre- and mild hypertension: a registry study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013; 2013:313142. [16] Auger C, Chaabi M, Anselm E, et al. The red wine extract-induced activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase is mediated by a great variety of polyphenolic compounds. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2010; 54 Suppl 2: S171-183. [17] Holt RR, Heiss C, Kelm M, et al. The potential of flavanol and procyanidin intake to influence age-related vascular disease. J Nutr Gerontol Geriatr. 2012;31(3):290-323. [18] Zhao G, Gao H, Qiu J, et al. The molecular mechanism of protective effects of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on reperfusion arrhythmias in rats in vivo. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33(5):759-767. [19] Ding P, Xu YM, Qin FP. Research on antioxidant activities and optimization of process for micro- encapsulation of Lithospermum erythrorhizon using β-cyclodextrin.Shipin Gongye Keji. 2009;30(2): 184-188. [20] Lewandowska U, Szewczyk K, Owczarek K, et al. Procyanidins from evening primrose (Oenothera paradoxa) defatted seeds inhibit invasiveness of breast cancer cells and modulate the expression of selected genes involved in angiogenesis, metastasis, and apoptosis. Nutr Cancer. 2013;65(8):1219-1231. [21] Liu XH, Mai WL, Zheng Q, et al. Effects of proanthocyanidins on nerve conduction velocity of type 2 diabetes rats. Chuanbei Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2014;29(5):429-431. [22] Zhang TX, He D, Niu CQ, et al. Vasodilation of procyanidins from grape seeds on isolated rabbit aorta. Zhongcaoyao. 2006;37(1):87-89. [23] Nyhan D, Gaine S, Hales M, et al. Pulmonary vascular endothelial responses are differentially modulated after cardiopulmonary bypass. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1999;34(4):518-525. [24] Chen L, Lv Z. Study on effects of insulin on senescence and Akt expression of endothelial cell. Chuanbei Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2013;28(6):540-543. [25] Li HF, Wang LD, Tian ZF, et al. Effects of phytoestrogens resveratrol and phloretin on contractile response of aortic strips in rabbits. Zhongguo Yaolixue yu Dulixue Za Zhi. 2006;20(1):26-32. [26] Niu CQ, Mai WL, Zhang TX. Contraction effects of Total alkali sophora alopecuroids on rat’s sinus ventriculi circular muscle in vitro. Sichuan Zhongyi. 2012;30(11): 55-58. [27] Zhang T, Niu C, Lan H, et al. Vasorelaxant effects of procyanidins on rabbit pulmonic ring in vitro. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2009;34(21): 2813-2816. [28] Zhang H, Wang F. Study on the effects of ethanol extract of spatholobus suberectus on platelet aggregation and isolated vascular. Zhongguo Yaofang. 2013;35(24):3271-3273. [29] Xu DZ, Zhao DY. Procedures for estimating pharmaco-receptor parameters,pD2,pA2,and pD2’ including a common computer program. Shanghai Diyi Yixueyuan Xuebao. 1985;12(5):342-349. [30] Schramm DD, Wang JF, Holt RR, et al. Chocolate procyanidins decrease the leukotriene-prostacyclin ratio in humans and human aortic endothelial cells. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001;73(1):36-40. [31] Karim M, McCormick K, Kappagoda CT. Effects of cocoa extracts on endothelium-dependent relaxation. J Nutr. 2000;130(8S Suppl):2105S-2108S. [32] Kim SH, Kang KW, Kim KW, et al. Procyanidins in crataegus extract evoke endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation in rat aorta. Life Sci. 2000;67(2): 121-131. [33] Fitzpatrick DF, Bing B, Maggi DA, et al. Vasodilating procyanidins derived from grape seeds. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;957:78-89. [34] Aldini G, Carini M, Piccoli A, et al. Procyanidins from grape seeds protect endothelial cells from peroxynitrite damage and enhance endothelium- dependent relaxation in human artery: new evidences for cardio-protection. Life Sci. 2003; 73(22): 2883-2898. [35] Komori K, Suzuki H. Heterogeneous distribution of muscarinic receptors in the rabbit saphenous artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1987;92(3):657-664. [36] Yue P, Lü YJ, Yang BF. Advances in the study of cardiac M3 receptor as a novel target of antiarrhythmic drugs. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2006;41(8): 702-705. [37] Hammarström AK, Parkington HC, Coleman HA. Release of endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor (EDHF) by M3 receptor stimulation in guinea-pig coronary artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1995; 115(5):717-722. [38] Shi H, Wang H, Li D, et al. Differential alterations of receptor densities of three muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes and current densities of the corresponding K+ channels in canine atria with atrial fibrillation induced by experimental congestive heart failure. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2004;14(1-2):31-40. [39] Wang S, Han HM, Jiang YN, et al. Activation of cardiac M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors has cardioprotective effects against ischaemia-induced arrhythmias. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2012; 39(4):343-349. [40] Wang T, Hogan-Cann A, Kang Y, et al. Muscarinic receptor activation increases hERG channel expression through phosphorylation of ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-2. Mol Pharmacol. 2014;85(6):877-886. [41] Liu Y, Wang S, Wang C, et al. Upregulation of M? muscarinic receptor inhibits cardiac hypertrophy induced by angiotensin II. J Transl Med. 2013;11:209. [42] Shan LM, Wang H. Pharmacological characteristics of the endothelial target for acetylcholine induced vascular relaxation. Life Sci. 2002;70(11):1285-1298. [43] Qi YM, Yang DJ, Duan X, et al. Endomorphins inhibit contractile responses of rat thoracic aorta rings induced by phenylephrine and angiotensin II in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2002;23(1):40-44. [44] Furuuchi R, Sakai H, Hirokawa N, et al. Antihypertensive effect of boysenberry seed polyphenols on spontaneously hypertensive rats and identification of orally absorbable proanthocyanidins with vasorelaxant activity. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2012;76(9):1694-1701. [45] Zhang TX, Niu CQ, Hu JM, et al. Vasorelaxational effects of procyanidins on rabbit aorta in vitro and decreasing arterial blood pressure in vivo. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2008;33(14):1720-1723. [46] Wu X, Guo RN, Guo RZ, et al. Effects of grape seed procyanidin on blood pressure in renovascular hypertensive rats. Zhongguo Binglixue Zazhi .2011; 27(3):593-595. [47] Martin W, Villani GM, Jothianandan D, et al. Selective blockade of endothelium-dependent and glyceryl trinitrate-induced relaxation by hemoglobin and by methylene blue in the rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985;232(3):708-716. [48] Zhang JJ, Pu Y, Li Y. Influence of PI3K and MAPKs signaling pathways on expression of VEGF in human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells. Chuanbei Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2014;29(1):44-48. [49] Ruan GX, Kazlauskas A. Axl is essential for VEGF-A- dependent activation of PI3K/Akt. EMBO J. 2012; 31(7): 1692-1703. [50] Ruan GX, Kazlauskas A. VEGF-A engages at least three tyrosine kinases to activate PI3K/Akt. Cell Cycle. 2012;11(11):2047-2048. [51] Iwamoto Y, Ohishi M, Yuan M, et al. β-Adrenergic receptor gene polymorphism is a genetic risk factor for cardiovascular disease: a cohort study with hypertensive patients. Hypertens Res. 2011;34(5): 573-577. [52] Lei KI, Huang XN, Wu Q, et al. Bre inhibited[Ca2+]i elevaton induced by NA while enhanced tat induced by kalium chloride. Chuanbei Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2004;19(4):6-7. [53] Martel G, Hamet P, Tremblay J. Central role of guanylyl cyclase in natriuretic peptide signaling in hypertension and metabolic syndrome. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010;334(1-2):53-65. [54] Liu B, Liu J, Jian SH, et al. Expression and significance of Eag1, HIF-1α and VEGF in cervical cancer. Chuanbei Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2014;29(1): 57-62. [55] Morgado M, Cairrão E, Santos-Silva AJ, et al. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent relaxation pathways in vascular smooth muscle. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012;69(2): 247-266. [56] Jiang YG, Wang H. Potassium channels and the modulators in vascular smooth muscle cells. Zhongguo Yaolixue Tongbao. 2002;18(5):494-497. [57] Shen W, Wang H. Regulation of eNOS phosphorylation by natakalim via activating ATP-sensitive potassium channel subtype SUR2B/Kir6.1 in endothelial cells. Yaolixue Tongbao. 2014;30(2):229-232. [58] Zhang XY, Li WG, Gao MT. Protective effect on injured myocardial cells of proanthoc yanidins in vitro. Zhongyao Yaoli yu Linchuang. 2001;17:14-17. [59] Ling ZQ, Xie BJ, Jiang T. Protective effects of procyanidins' extract from the lotus' seedpod on experimental myocadial injury in rat. Zhongguo Yaolixue Tongbao. 2001;17(6):687-690. |
.jpg)
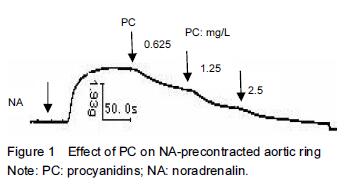
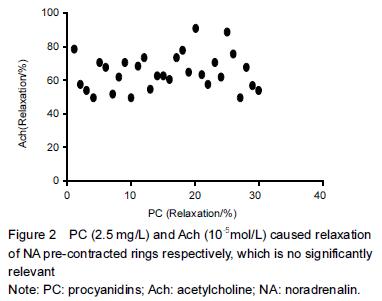

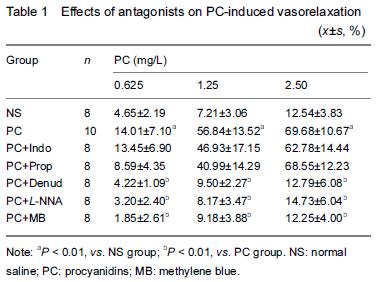
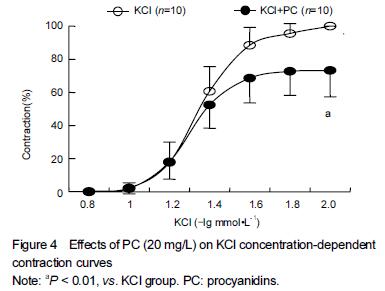
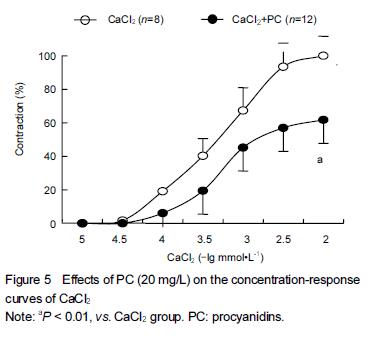

.jpg)