| [1] Hirschfield GM, Gershwin ME. The immunobiology and pathophysiology of primary biliary cirrhosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2013;8:303-330.[2] Crawford JM. Histologic findings in alcoholic liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2012;16(4):699-716.[3] Duddempudi AT. Immunology in alcoholic liver disease[J]. Clin Liver Dis. 2012;16(4):687-698.[4] Liao JC, Chen WJ, Chen LH, et al. Complications associated with instrumented lumbar surgery in patients with liver cirrhosis: a matched cohort analysis. Spine J. 2013, Mar 27. [Epub ahead of print][5] Pandey CK, Karna ST, Pandey VK, et al. Perioperative risk factors in patients with liver disease undergoing non-hepatic surgery. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2012;4(12): 267-274.[6] Sugimura Y, Toyama M, Katoh M, et al. Analysis of open heart surgery in patients with liver cirrhosis. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann.2012;20(3):263-268.[7] Nicoll A. Surgical risk in patients with cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27(10):1569-1575.[8] Mosko JD, Nguyen GC. Increased perioperative mortality following bariatric surgery among patients with cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;9(10): 897-901.[9] Khokhar N. Perioperative management of cirrhosis. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2011;21(10): 581-583.[10] Yuan B, Taunton MJ, Trousdale RT. Total hip arthroplasty for alcoholic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Orthopedics. 2009;32(6): 400.[11] Kuga Y. Factors associated with osteonecrosis in the femoral head in chronic alcoholism. Kurume Med J. 2000;47(2): 147-149.[12] 罗玉琛,肖刚,陈劲,等.酒精性晚期股骨头缺血性坏死[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2006,149(9): 669-671. [13] 胡新永,吕原,杨华清,等.非骨水泥型全髋关节置换术治疗酒精性股骨头坏死[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007, 15(18): 1385-1387. [14] Donaghy A.Issues of malnutrition and bone disease in patients with cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.2002; 17(4): 462-466.[15] Idilman R, de Maria N, Uzunalimoglu O, et al. Hepatic osteodystrophy: a review. Hepatogastroenterology. 1997; 44(14): 574-581.[16] Kelly DA, Tuddenham EG. Haemostatic problems in liver disease. Gut. 1986;27(3): 339-349.[17] Blake JC, Sprengers D, Grech P, et al. Bleeding time in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. BMJ. 1990;301(6742): 12-15.[18] Gomez F, Ruiz P, Schreiber AD. Impaired function of macrophage Fc gamma receptors and bacterial infection in alcoholic cirrhosis. N Engl J Med.1994; 331(17): 1122-1128.[19] Mansour A, Watson W, Shayani V, et al. Abdominal operations in patients with cirrhosis: still a major surgical challenge. Surgery. 1997;122(4): 730-735, 735-736.[20] Doberneck RC, Sterling WA Jr, Allison DC. Morbidity and mortality after operation in nonbleeding cirrhotic patients. Am J Surg.1983;146(3): 306-309.[21] Aranha GV, Greenlee HB. Intra-abdominal surgery in patients with advanced cirrhosis. Arch Surg. 1986;121(3): 275-277.[22] Schwartz SI. Biliary tract surgery and cirrhosis: a critical combination. Surgery. 1981;90(4): 577-583.[23] Rice HE, O'Keefe GE, Helton WS, et al. Morbid prognostic features in patients with chronic liver failure undergoing nonhepatic surgery. Arch Surg. 1997;132(8): 880-884, 884-885.[24] Ziser A, Plevak DJ, Wiesner RH, et al. Morbidity and mortality in cirrhotic patients undergoing anesthesia and surgery. Anesthesiology. 1999;90(1): 42-53.[25] Fede G, D'Amico G, Arvaniti V, et al. Renal failure and cirrhosis: a systematic review of mortality and prognosis. J Hepatol. 2012;56(4): 810-818.[26] Muscari F, Foppa B, Carrere N, et al. Resection of a transplantable single-nodule hepatocellular carcinoma in Child-Pugh class A cirrhosis: factors affecting survival and recurrence. World J Surg. 2011;35(5): 1055-1062.[27] Manizate F, Hiotis SP, Labow D, et al. Liver functional reserve estimation: state of the art and relevance to local treatments. Oncology. 2010;78 Suppl 1: 131-134.[28] 张秀明.现代临床生化检验学[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2001: 1165.[29] Tinkoff G, Rhodes M, Diamond D, et al. Cirrhosis in the trauma victim. Effect on mortality rates. Ann Surg. 1990; 211(2): 172-177.[30] Kearon C. Natural history of venous thromboembolism. Circulation. 2003;107(23 Suppl 1): 122-130.[31] 马海梅,张会英,朱广玉,等. 人工髋关节置换术围手术期凝血、抗凝活性变化[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2009, 23(7):646-647. [32] 邱贵兴. 中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版, 2009, 3(3): 380-383. [33] 黄瑾,王玲,曾建强,等.维生素K_1在肝硬化失代偿患者中应用的药学监护[J].中国新药杂志,2009, 18(2): 181-182. [34] 胡锦芳,蒋丽华,汤莉萍.维生素K_1在肝硬化失代偿期患者中的应用[J]. 实用临床医学. 2010,11(12): 19-20. [35] Sidhu P, O'Kane HO. Self-managed anticoagulation: results from a two-year prospective randomized trial with heart valve patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;72(5): 1523-1527.[36] Bruce W, Campbell D, Daly D,et al. Practical recommendations for patient blood management and the reduction of perioperative transfusion in joint replacement surgery. ANZ J Surg. 2013;83(4): 222-229.[37] Yang T, Zhang J, Lu JH, et al. Risk factors influencing postoperative outcomes of major hepatic resection of hepatocellular carcinoma for patients with underlying liver diseases. World J Surg. 2011;35(9): 2073-2082.[38] 易有峰,王晓娟,陈有元.肝硬化患者凝血指标检测的临床意义[J]. 中国肝脏病杂志:电子版,2010,2(3): 28-29. [39] 王静,马晓兰.肝硬化患者凝血功能检测的临床价值[J].中国热带医学,2010, 23(5): 593 [40] Hsieh PH, Chen LH, Lee MS, et al. Hip arthroplasty in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003; 85(6): 818-821.[41] 汤勃,陈玉琪,王慧芬.肝衰竭和失代偿期肝硬化患者肠外营养新理念[J].传染病信息,2010, 2: 111-115. [42] 杨先芬,荚卫东.肝硬化患者营养状况与营养支持[J].实用肝脏病杂志,2012,15(2): 174-176. [43] 卢瑞利,曹金光,罗建平,等.肠内营养在肝硬化治疗中的临床研究进展[J].临床荟萃,2011, 26(14): 1273-1275. [44] 梁长林.肝硬化患者营养不良的临床营养支持研究进展[J].中外医疗,2012, 34: 177-178. [45] 迟强,邰升.肝硬化患者的营养支持[J].临床外科杂志,2006,14(4): 194-195. [46] Kruimel JW, Naber TH, van der Vliet JA,et al.Parenteral structured triglyceride emulsion improves nitrogen balance and is cleared faster from the blood in moderately catabolic patients. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2001; 25(5): 237-244.[47] 杨先芬,荚卫东.肝硬化患者营养状况与营养支持[J].实用肝脏病杂志,2012,15(20: 174-176. [48] Kuwahata M, Kubota H, Kanouchi H, et al. Supplementation with branched-chain amino acids attenuates hepatic apoptosis in rats with chronic liver disease. Nutr Res. 2012; 32(7): 522-529.[49] Jurado Garcia J,Costan Rodero G,Calanas-Continente A.Importance of nutritional support in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Nutr Hosp. 2012;27(2): 372-381.[50] Kawaguchi T,Izumi N,Charlton MR,et al.Branched-chain amino acids as pharmacological nutrients in chronic liver disease. Hepatology. 2011;54(3): 1063-1070.[51] Michitaka K, Hiraoka A, Kume M, et al. Amino acid imbalance in patients with chronic liver diseases. Hepatol Res. 2010;40(4): 393-398.[52] 刘海燕,陈军贤,徐平珍,等.富含支链氨基酸的复方氨基酸液在肝硬化患者肠外营养中的作用[J].实用医学杂志,2010. 26(3): 454-456. |
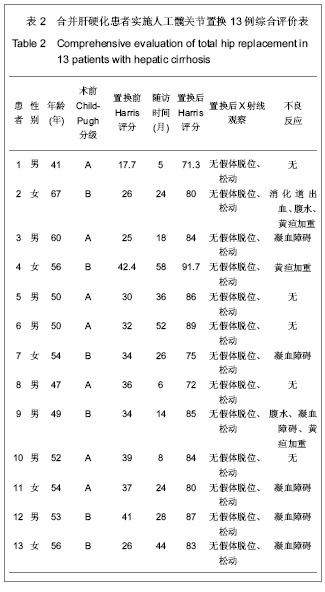
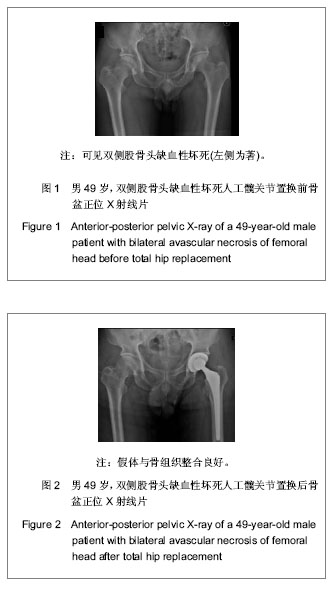
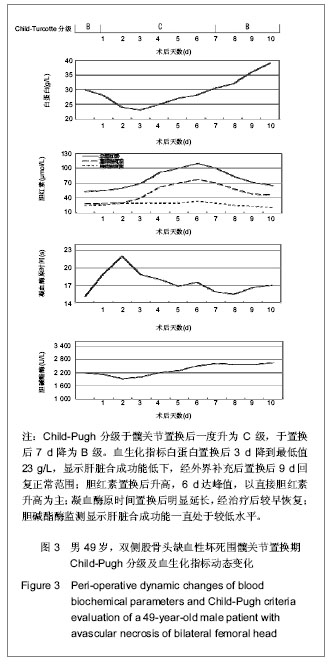
.jpg)