设计:随机分组,细胞学实验对比观察。
时间及地点:2010年9月至2012年6月在解放军第四军医大学口腔医学院中心实验室完成实验。
材料:
牵张应力介导细胞成骨分化及相关基因的表达实验试剂及仪器:
实验方法:
细胞培养:用含有体积分数10%胎牛血清、100 U/mL青霉素、100 U/mL链霉素和1%谷氨酰胺的DMEM培养液,在37 ℃、体积分数5%CO2孵箱中常规培养MC3T3-E1细胞,每3 d更换培养液1次,传代时先用 2.5 g/L胰蛋白酶消化,再以1∶3的比例进行传代。生长良好的MC3T3-E1细胞,胰酶消化后吹散,细胞计数后调整浓度至2×108 L-1,加入6孔弹性基底膜培养(Flexcell,USA),标准环境下以含体积分数10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养液孵育24 h后,然后按实验分组,利用自行研制的多通道细胞牵张应力加载系统,对培养在6孔弹性基底膜培养板上的MC3T3-E1细胞进行加载,细胞的加载作用时间为24 h。所有加力组细胞的力学刺激频率为6周/min,即5 s拉伸,5 s松弛。
实验分组:将同步化生长的细胞随机分为4组,每组6孔细胞。4组为:①非加载正常对照组。②应力加载组:12%牵张应力24 h。③应力加载+ PD098059干预组:先以终浓度为10 μmol/L的ERK1/2通路特异性抑制剂 PD098059预孵育30 min,再加载12%牵张应力24 h。④应力加载+PDTC干预组:先以终浓度为100 μmol/L的核因子κB通路抑制剂二硫代氨基甲酸吡咯烷(PDTC)预孵育30 min,再加载12%牵张应力24 h。
细胞牵张应力加载:采用解放军第四军医大学口腔医学院自行研制的多通道细胞牵张应力加载系统[4],以美国Flexcell公司生产的BioFlex®弹性膜6孔培养板作为细胞培养单元,通过单片机控制可以3个通道同时进行不同形变大小的应力加载。细胞所受力值大小由培养皿底部弹性膜拉伸应变率(%)表示,加载范围0%-20%细胞表面拉伸率。
Western Blotting检测牵张应力对ERK1/2及核因子κB信号通路的影响:MC3T3-E1细胞力学刺激分别30,60及120 min后,冷PBS冲洗贴壁生长的细胞2 mL/次×3次;将裂解液直接加在弹性膜上,冰上原位裂解细胞 30 mim;用细胞刮将细胞刮离弹性膜,收集此混悬液入EP管;4 ℃低温离心14 000 r/min×15 min,收集上清液。取40 μg 细胞总蛋白点样于8%SDS-PAGE 胶电泳分离,电转至硝酸纤维素膜,再分别用P-ERK、ERK、p-IKK、IKK、IκB-α、核因子κB(p65)抗体杂交,检测P-ERK、ERK、p-IKK、IKK、IκB-α、核因子κB(p65)蛋白质表达,ECL法显示免疫复合物。采用Image-Pro Plus软件分析各组染色条带的灰度值,染色条带的灰度值减去背景灰度值后得到的相对灰度值,以排除背景及非特异性条带的干扰。各蛋白条带灰度值与β-actin灰度的比值作为相对蛋白含量水平。
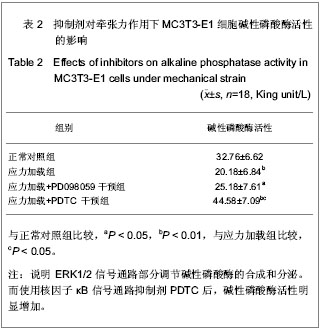
碱性磷酸酶活性的检测:细胞应力加载后,取出孔内培养液,用0.01 mol/L PBS洗涤2次,每孔加入0.2% TritonX-100 1 mL,4 ℃过夜。按碱性磷酸酶检测试剂盒要求:每孔取5 μL细胞裂解液放入96孔细胞培养板,加入基质液及缓冲液各50 μL,充分混匀37 ℃孵育 15 min,加入150 μL显色剂,混匀后在490 nm波长下测定各孔的吸光度值(A值),同时设标准及空白对照,每孔细胞测3次,取平均值。按公式计算碱性磷酸酶活性。
碱性磷酸酶活性(金氏单位/100 mL)=样品管吸光度×标准管酚的
含量(0.005 mg)×100 mL/标准管吸光度×0.05 mL
|
Real-time PCR方法检测Ⅰ型胶原、骨钙蛋白及白细胞介素6 mRNA的表达:实验细胞用2.5 g/L胰蛋白酶消化后, 800 r/min离心6 min,PBS清洗再次离心后,收集细胞,根据TRIzol Reagent产品说明提取总RNA。收集的细胞加入1 mL TRIzol试剂,室温作用5 min后加入氯仿 0.2 mL,充分混匀后室温孵育2.0-3.0 min,4 ℃下 12 000 r/min离心15 min,收集水相,将水相转移到新离心管中。水相与异丙醇混合以沉淀其中的RNA,每 1 mL的TRIZOL试剂匀浆的样品中加0.5 mL的异丙醇。混匀后室温孵育10 min,然后4 ℃下12 000 r/min离心 10 min,再用体积分数75%乙醇洗涤后4 ℃下以 7 500 r/min离心5 min,空气中自然干燥RNA后加入无菌水,-70 ℃保存备用。
根据Revert Aid™ First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit 操作说明将2 µg总RNA反转录为cDNA。使用引物设计软件Primer Premier 5.0进行引物序列设计,实时定量PCR使用引物序列见表1。
将DNA模板以及所有cDNA样品分别配置Realtime PCR反应体系。将配置的PCR反应溶液置于Realtime PCR仪上进行PCR反应,40个PCR循环(94 ℃,20 s;退火温度,20 s;72 ℃,30 s)。基因表达的相对定量基于比较CT值法,每个样本的RNA含量均根据各自的β-actin含量进行标准化。mRNA表达量结果以相对荧光值表示。
主要观察指标:①牵张应力对ERK1/2及核因子κB信号通路的影响。②ERK1/2及核因子κB通路抑制剂对牵张力作用下MC3T3-E1细胞碱性磷酸酶活性的影响。③ERK1/2及核因子κB通路抑制剂对牵张力作用下MC3T3-E1细胞Ⅰ型胶原、骨钙蛋白、白细胞介素6基因表达的影响。
统计学分析:采用SPSS 12.0统计软件对数据进行分析处理,所有数据均来自3次实验结果,取其平均数值,表示为x±s,组间均数比较采用单因素方差分析。



.jpg)
.jpg)