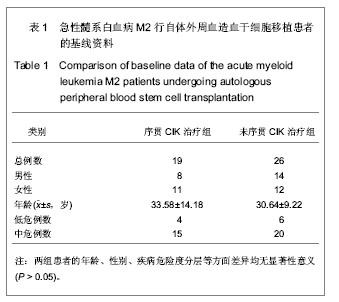
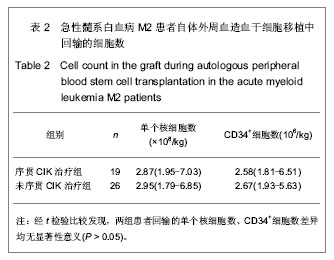
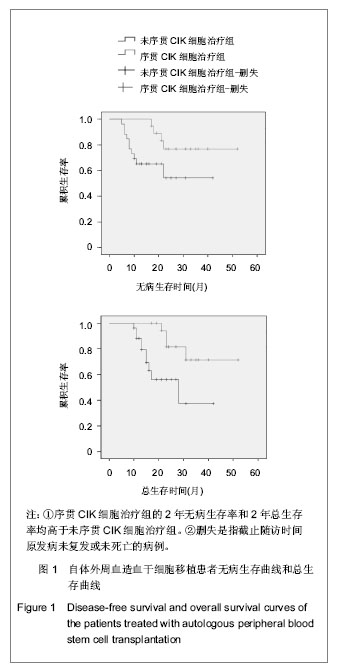
| [1] 黄晓军.血液病学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2009:91-96.[2] 王建祥.规范我国成人急性髓系白血病诱导治疗完全缓解患者的分层治疗[J].中华血液学杂志,2009,30(1):1-2. [3] 张德杰,黄世林,杨佩满.自体造血干细胞的体外净化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(3):542-545.[4] 程永贵,杨广民,肖中平.CIK 细胞对急性髓细胞白血病微小残留病作用的研究[J].吉林医学,2012,33(8):1571-1574.[5] 张之南,沈悌.血液病诊断及疗效标准[M].3版.北京:科学出版社, 2008:103-121,131-139,147-148,157-163,220-228.[6] Ruggeri L, Mancusi A, Burchielli E,et al.NK cell alloreactivity and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2008;40(1):84-90.[7] Koreth J, Schlenk R, Kopecky KJ,et al.Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission: systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective clinical trials.JAMA. 2009;301(22):2349-2361.[8] Fernandez HF, Sun Z, Litzow MR,et al.Autologous transplantation gives encouraging results for young adults with favorable-risk acute myeloid leukemia, but is not improved with gemtuzumab ozogamicin.Blood. 2011;117(20): 5306-5313.[9] Kim ST, Jung CW, Lee J,et al.Postremission therapy for acute myeloid leukemia in the first remission.Leuk Lymphoma. 2007; 48(5):937-943.[10] Jing Y, Li H, Zhao Y,et al.Efficacy of allogeneic and autologous hematopoietic SCT in patients with AML after first complete remission.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48(3): 383-389.[11] 王荷花,冯四洲,王玫,等.急性白血病患者第一次完全缓解期自体和异基因造血干细胞移植疗效的比较[J].中华血液学杂志,2004, 25(7):389-392. [12] Hamadani M, Awan FT, Copelan EA.Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adults with acute myeloid leukemia.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008;14(5):556-567.[13] Loh YS, Koh LP, Tai BC,et al.Long-term follow-up of Asian patients younger than 46 years with acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission: comparison of allogeneic vs. autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Leuk Lymphoma. 2007;48(1):72-79.[14] 靖彧,于力,刘海川,等.自体造血干细胞移植治疗急性髓系白血病77例[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(47): 9297- 9301.[15] Michallet AS, Chelghoum Y, Thiebaut A,et al.Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for adults with acute myeloid leukemia in complete remission: the Edouard Herriot Hospital experience.Hematology. 2006;11(3):157-164.[16] 刘辉,常乃柏,顾惜春,等.自体造血干细胞移植治疗急性白血病的临床观察[J].临床血液学杂志,2009,22(1):24-26.[17] 冯四洲,魏嘉璘,邹德惠,等.自体造血干细胞移植治疗急性白血病患者143例疗效分析[J].内科急危重症杂志,2005,11(3):112-115.[18] Schmidt-Wolf IG, Negrin RS, Kiem HP,et al.Use of a SCID mouse/human lymphoma model to evaluate cytokine-induced killer cells with potent antitumor cell activity.J Exp Med. 1991; 174(1):139-149.[19] Linn YC, Wang SM, Hui KM.Comparative gene expression profiling of cytokine-induced killer cells in response to acute myloid leukemic and acute lymphoblastic leukemic stimulators using oligonucleotide arrays.Exp Hematol. 2005; 33(6):671-681.[20] Verneris MR, Kornacker M, Mailänder V,et al.Resistance of ex vivo expanded CD3+CD56+ T cells to Fas-mediated apoptosis.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2000;49(6):335-345.[21] 薛重重,杨丽萍,徐新,等.血液肿瘤患者AHSCT后DC/CIK免疫治疗的疗效观察[J].中华全科医学,2012,10(3):341-342.[22] 王玲,史春雷,李颖,等.恶性血液病自体造血干细胞移植后DC-CIK细胞预防复发探讨[J].青岛大学医学院学报,2010,46(2): 142-144.[23] 苏毅,易海,范方毅,等.荷载自体白血病抗原的DC-CIK细胞预防急性髓细胞性白血病自体造血干细胞移植后复发的临床研究[J].中国输血杂志,2010,23(12):1024-1028.[24] Introna M, Borleri G, Conti E,et al.Repeated infusions of donor-derived cytokine-induced killer cells in patients relapsing after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a phase I study.Haematologica. 2007;92(7):952-959.[25] Nishimura R, Baker J, Beilhack A,et al.In vivo trafficking and survival of cytokine-induced killer cells resulting in minimal GVHD with retention of antitumor activity.Blood. 2008;112(6): 2563-2574. [26] 罗云,张萍,张颖,等.异基因造血干细胞移植后序贯输注供者CIK细胞治疗9例复发/难治性血液肿瘤疗效的初步探讨[J].肿瘤, 2012, 32(7):546-550.[27] 涂三芳,宋朝阳,李玉华,等.自体造血干细胞移植联合异体细胞因子诱导的杀伤细胞及白细胞介素2治疗高危急性髓系白血病2例[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(10):1897-1900. [28] Introna M, Franceschetti M, Ciocca A,et al.Rapid and massive expansion of cord blood-derived cytokine-induced killer cells: an innovative proposal for the treatment of leukemia relapse after cord blood transplantation.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2006;38(9):621-627.[29] 童春容,耿彦彪,陆道培.自体细胞因子诱导的杀伤细胞治疗急性白血病的临床研究[J].北京医科大学学报,2000,32(5):473-477.[30] 陈智超,李菁媛,姚军霞,等.DC-CIK细胞治疗自体外周血造血干细胞移植后急性髓性白血病的临床研究[J].临床内科杂志,2007, 24(9):596-598.[31] 赵红丽,洪珞珈.免疫细胞在白血病治疗应用的进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2008,8(11):2169-2172. |
.jpg)