| [1] Sueblinvong V,Weiss DJ. Stem cells and cell therapy approachesin lung biology and diseases. Transl Res.2010; 156(3):188-205. [2] Sueblinvong V,Weiss DJ. Cell therapy approaches for lung diseases: current status. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009;9(3): 268-273.[3] 王娟,陆琰,何冬梅,等.人脐带间充质干细胞体外分离、纯化及鉴定[J]. 暨南大学学报:自然科学与医学版,2009,30(4):367-372.[4] Behr B,Ko SH,Wong VW,et al.Stem cells.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126(4):1163-1171.[5] Wang HS, Hung SC, Peng ST, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in the Wharton's jelly of the human umbilical cord. Stem Cells. 2004;22(7):1330-1337.[6] Chen MY,Lie PC,Li ZL,et al.Endothelial differentiation of Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells in comparison with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Experimental hematology. 2009;37(5):629-640.[7] Stenderup K ,Justesen J ,Clausen C, et al. Aging is associated with decreased maximal life span and accelerated senescence of bone marrow stromal cells. Bone.2003; 33(6): 919-926.[8] Baksh D,Yao R,Tuan RS.Comparison of proliferative and multilineage differentiation potential of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord and bone marrow. Stem Cells.2007;25(6):1384-1392.[9] Fan CG, Zhang QJ, Zhou JR.Therapeutic potentials of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord. Stem Cell Rev. 2011;7(1):195-207.[10] Garcia O, Carrarro G, Navarro S, et al. Cell-based therapies for lung disease. Br Med Bull.2012;101:147-161.[11] Lau AN, Goodwin M, Kim CF, et al. Stem cells and regenerative medicine in lung biology and diseases. Mol Ther. 2012;10(6):1116-1130.[12] Gupta N, Su X, Popov B, et al. Intrapulmonary delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves survival and attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. J Immunol. 2007;179(3):1855-1863.[13] 孙磊,王小明,斯琴,等.移植骨髓间充质干细胞减轻脂多糖诱导的小鼠急性肺损伤[J].基础医学与临床,2009,29(12):1233-1238.[14] Mei SH, Mccarter SD, Deng Y, et al.Prevention of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing angiopoietin 1. PLoS Med. 2007;4(9):e269.[15] Lee JW, Fang X, Gupta N, et al. Allogeneic human mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of E. coli endotoxin- induced acute lung injury in the ex vivo perfused human lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(38):16357-16362.[16] Krause DS,Theise ND,Collector MI,et al.Multi-organ, multi-lineage engraftment by a single bone marrow-derived stem cell.Cell. 2001;105(3):369-377.[17] Arajo IM, Abreu SC, Maron-gutierrez T, et al. Bone marrow-derived mononuclear cell therapy in experimental pulmonary and extrapulmonary acute lung injury. Critical care medicine. 2010;38(8):1733-1741.[18] Ortiz LA , Dutreil M, Fattman C, et al. Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist mediates the a ntiinflammatory and antifibrotic effect of mesenchymal stem cells during lung injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(26):11002-11007.[19] Ortiz LA, Gambelli F, Mcbride C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell engraftment in lung is enhanced in response to bleomycin exposure and ameliorates its fibrotic effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(14):8407-8411.[20] Kinnaird T, Stabile E, Burnett MS, et al. Marrow-derived stromal cells express genes encoding a broad spectrum of arteriogenic cytokines and promote in vitro and in vivo arteriogenesis through paracrine mechanisms. Circ Res. 2004;94(5):678-685.[21] Rojas M, Xu J, Woods CR, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in repair of the injured lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2005;33(2):145-152.[22] Corcidone A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions. Blood. 2006;107(1):367-372.[23] Anzalone R, Loiacono M, Corrao S, et al. New emerging potentials for human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells: immunological features and hepatocyte-like differentiative capacity. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(4):423-438.[24] Nmeth K, Leelahavanichkul A, Yuen PST, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate sepsis via prostaglandin E2–dependent reprogramming of host macrophages to increase their interleukin-10 production. Nature medicine. 2008;15(1):42-49. |
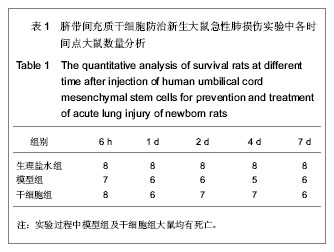


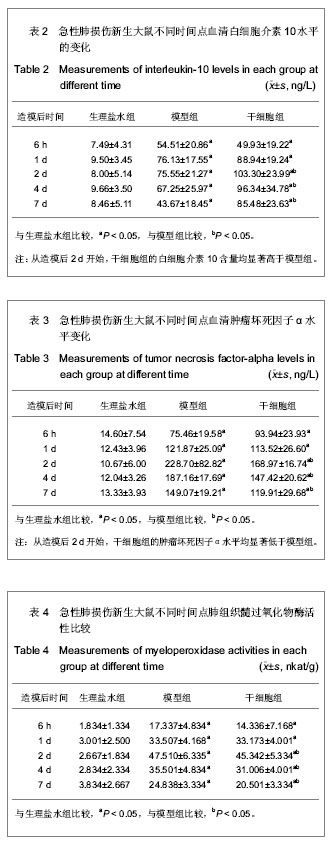
.jpg)