| [1] Yen BL, Huang HI,CHIEN CC, et al. Isolation of muhipotent cells from human term placenta.Stem Ceils.2005;23(1):3-9.[2] Miki T, Marongiu F, Ellis EC, et al. Production of hepatocyte-like cells from human amnion. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;481:155-68. [3] Ouyang HW,Gob JC,Lee EH.Use of bone marrow stromal cells for tendon graft-to-bone healing:histological and immunohistochemical studies in a rabbit model.Am J Sports Mad.2004;2:321-327.[4] Lim JK,Hui J,Li L,et al.Enhancement of tendon graft osteointegration using mesenchymal stem cells in a rabbit model of anteriorcruciate ligament reconstruction.Arthroscopy. 2004;9:899-910.[5] 张红艳,杨乃龙,孙晓娟,等.人胎盘源与人骨髓源间充质干细胞的生物学性状比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010;14(45): 8386-8389.[6] Ventura C, Cantoni S, Bianchi F, et al. Hyaluronan mixed esters of butyric and retinoic acid drive cardiac and endothelial fate in term placenta human mesenchymal stem cells and enhance cardiac repair in infarcted rat hearts.J Biol Chem.2007; 282(19):14243-14252.[7] 沙文琼,王自能,王冬菊.人胚胎滋养细胞和胎盘间充质干细胞的分离与纯化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010;14(10): 1833-1837.[8] Benjamin M,Kumai T,Milz S,et al. The skeletal attachment of tendons:tendon“enthuses”.Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol.2002;133(4):931-945.[9] Qin L,Wang L,Wong MW,et al.0steogenesis induced by extracorporeal shockwave in treatment of delayed osteotendinous junction healing.J Orthop Res.2010;28(1): 70-76.[10] Zhai W,Wang N,Qi Z,et al.Platelet-rich plasma reverses the inhibition of tenocytes and osteoblasts in tendon-bone healing.Orthopedics.2012;35(4):e520-e525.[11] Chen CH,Chang CH,Wang KC,et al.Enhancement of rotator cuff tendon-bone healing with injectable periosteum progenitor cells-BMP-2 hydrogel in vivo.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2011;19(9):1597-1607.[12] Omae H, Mochizuki Y, Yokoya S, et al. Augmentation of tendon attachment to porous ceramics by bone marrow stromal cells in a rabbit model. International Orthopaedics (SICOT).2007;31:353-358.[13] Goradia VK.Tendon healing in a bone tunnel.Parts I and II.Atthroaty.2003;19(1):111.[14] Shelbourne KD,Cart DR.Meniscal repair compared with meniscectomy for bucket•-handle medial meniscal tears in anterior cruciate ligament-reconstructed knees.Am J Sportsl Med.2003;31(5):718-723.[15] Benjamin M,Kumai T.The skeletal attachment of tendons-tendon entheses.Comparative Biochemistry Physiology. 2002;133:931-945.[16] Wen CY, Qin L, Lee KM, et al. Influence of bone adaptation on tendon-to-bone healing in bone tunnel after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in a rabbit model. J Orthop Res.2009; 27(11):1447-1456.[17] 薛海滨,敖英芳.应用半腱肌腱重建前交叉韧带末端形成的特点[J].中国运动医学杂志,2002;2:127-130[18] Berg EE, Pollard ME,Kang Q.Interarticular bone tunnel healing. Arthroscopy. 2001;17(2):189-195 |

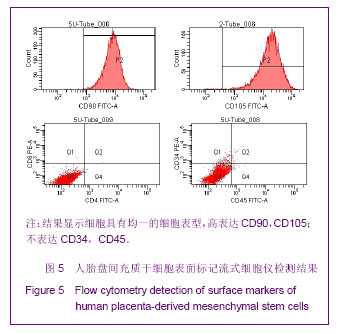


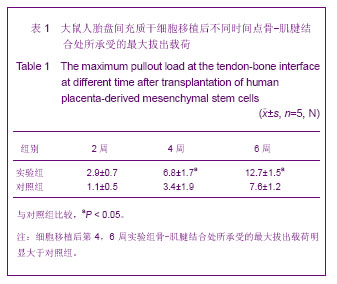
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)