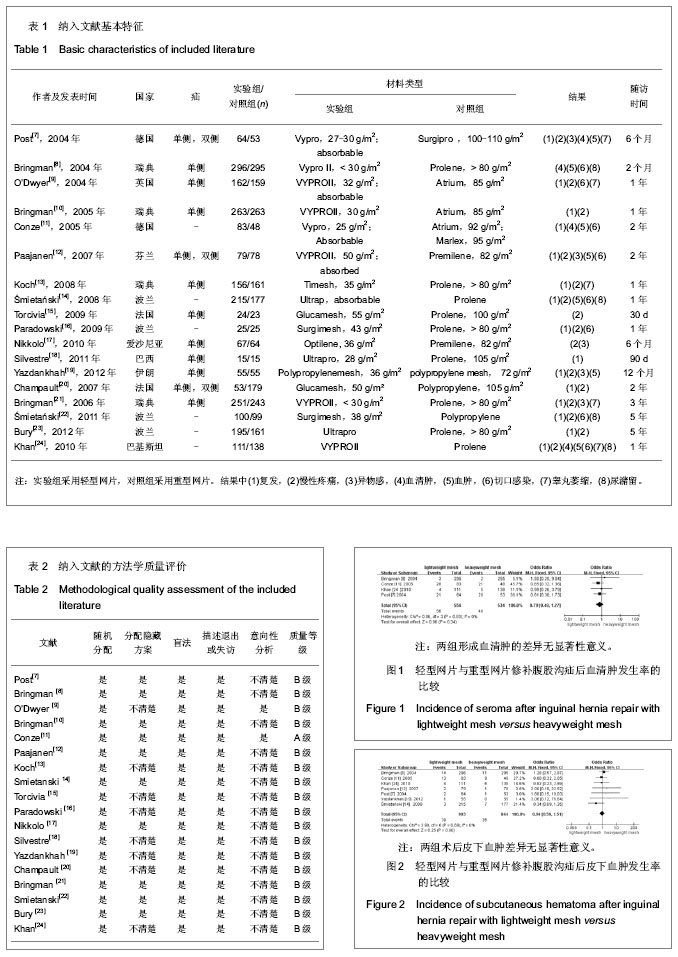
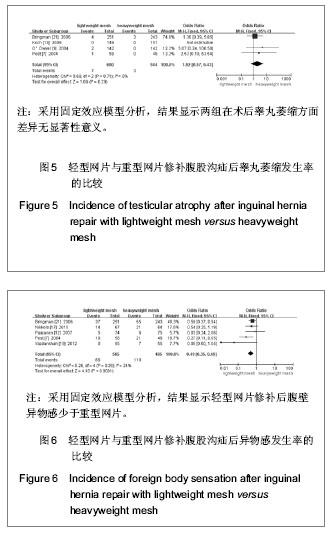
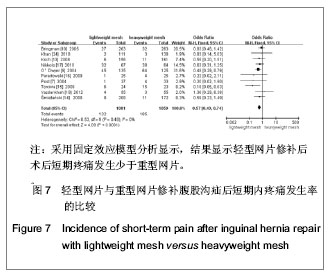
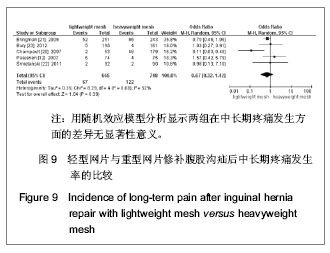
| [1] Lichtenstein IL,Shulman AG,Amid PK,et al.The tension-free hernioplasty.Am J Surg.1989;157(2): 188-193.
[2] Bay-Nielsen M,Perkins FM,Kehlet H,et al.Pain and functional impairment 1 year after inguinal herniorrhaphy: a nationwide questionnaire study.Ann Surg.2001;233(1):1-7.
[3] Nienhuijs S,Staal E,Strobbe L,et al.Chronic pain after mesh repair of inguinal hernia: a systematic review.Am J Surg.2007; 194(3):394-400.
[4] Rutkow IM,Robbins AW.Demographic, classificatory, and socioeconomic aspects of hernia repair in the United States .Surg Clin North Am.1993; 73(3):413-426.
[5] Weyhe D,Belyaev O,Muller C,et al.Improving outcomes in herniarepair by the use of light meshes: a comparison of differentimplant constructions based on a critical appraisal of the literature. World J Surg.2007; 31(1):234-244.
[6] Bowne WB,Morgenthal CB,Castro AE,et al.The role of endoscopic extraperitoneal herniorrhaphy: where do we stand in 2005?Surg Endosc.2007;21(5):707-712.
[7] Post S,Weiss B,Willer M,et al.Randomized clinical trial of lightweight composite mesh for Lichtenstein inguinal hernia repair.Br J Surg. 2004;91(1):44-48.
[8] Bringman S,Heikkinen TJ,Wollert S,et al.Early results of a single-blinded, randomized, controlled, Internet-based multicenter trial comparing Prolene and Vypro II mesh in Lichtenstein hernioplasty.Hernia.2004;8(2): 127-134.
[9] O'Dwyer PJ,Kingsnorth AN,Molloy RG,et al.Randomized clinical trial assessing impact of a lightweight or heavyweight mesh on chronic pain after inguinal hernia repair. Br J Surg.2005;92(2):166-170.
[10] Bringman S,Wollert S,Osterberg J,et al.One year results of a randomised controlled multi-centre study comparing Prolene and VyproII mesh in Lichtenstein hernioplasty.Hernia.2005; 9(3):223-227.
[11] Conze J,Kingsnorth AN,Flament JB,et al.Randomized clinical trial comparing lightweight composite mesh with polyester or polypropylene mesh for incisional hernia repair.Br J Surg. 2005; 92 (12):1488 -1493
[12] Paajanen H.A single-surgeon randomized trial comparing three composite meshes on chronic pain after Lichtenstein hernia repair in local anesthesia.Hernia.2007;11(4):335-339.
[13] Koch A,Bringman S,Myrelid P,et al.Randomized clinical trial of groin hernia repair with titanium-coated lightweight mesh compared with standard polypropylene mesh.Br J Surg.2008; 95(10):1226-1231.
[14] Polish Hernia Study Group.?mietański M.Randomized clinical trial comparing a polypropylene with a poliglecaprone and polypropylene composite mesh for inguinal hernioplasty.Br J Surg.2008;95(12):14 62-1468.
[15] Torcivia A,Vons C,Barrat C,et al.Influence of mesh type on the quality of early outcomes after inguinal hernia repair in ambulatory setting controlled study: Glucamesh®vs Polypropylene®.Langenbecks Arch Surg.2011;396(2): 173-178.
[16] Paradowski T,Olejarz A,Kontny T,et al.Polypropylene vs. ePTFE vs. WN mesh for Lichtenstein inguinal hernia repair a prospective, randomized, double blind pilot study of one-year follow-up.Videosurgery and other miniinvasive techniques. 2009; 4(1): 6-9.
[17] Nikkolo C,Lepner U,Murruste M,et al.Randomised clinical trial comparing lightweight mesh with heavyweight mesh for inguinal hernioplasty.Hernia.2010;14(3):253-258.
[18] Silvestre AC,De Mathia GB,Fagundes DJ,et al.Shrinkage evaluation of heavyweight and lightweight polypropylene meshes in inguinal hernia repair: a randomized controlled trial.Hernia.2011;15 (6): 629-634.
[19] Yazdankhah Kenary A,Afshin SN,Ahmadi Amoli H,et al.Randomized clinical trial comparing lightweight mesh with heavyweight mesh for primary inguinal hernia repair. Hernia. 2012.[Epub ahead of print]
[20] Champault G,Bernard C,Rizk N ,et al.Inguinal hernia repair: the choice of prosthesis outweighs that of technique.Hernia. 2007; 11(2):125-128.
[21] Bringman S,Wollert S,Osterberg J,et al.Three-year results of a randomized clinical trial of lightweight or standard polypropylene mesh in Lichtenstein repair of primary inguinal hernia.Br J Surg.2006; 93(9):1056-1059.
[22] ?mietański M,Bury K,?mietański IA,et al.Five-year results of a randomised controlled multi-centre study comparing heavy-weight knitted versus low-weight, non-woven polypropylene implants in Lichtenstein hernioplasty.Hernia. 2011; 15(5):495-501.
[23] Bury K,?mietański M,Polish Hernia Study Group.Five-year results of a randomized clinical trial comparing a polypropylene mesh with a poliglecaprone and polypropylene composite mesh for inguinal hernioplasty.Hernia.2012; 16(5):549-553.
[24] Khan N,Bangash A,Sadiq M,et al.Polyglactine/polypropylene mesh vs. propylene mesh: is there a need for newer prosthesis in inguinal hernia? Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2010; 16(1):8-13.
[25] Sajid MS,Leaver C,Baig MK,et al.Systematic review and meta-analysis of the use of lightweight versus heavyweight mesh in open inguinal hernia repair.Br J Surg.2012;99(1): 29-37.
[26] Zhong C,Wu B,Yang ZA,et al.A meta-analysis Comparing Lightweight Meshes With Heavyweight Meshes in Lichtenstein Inguinal Hernia Repair.Surg Innov.2013; 20(1): 24-28.
[27] Gao M,Han J,Tian J,et al.VYPRO II mesh for inguinal hernia repair: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Ann Surg.2010; 251(5):838-842.
[28] 李俊.无张力疝修补术后慢性腹股沟痛[J].中国实用外科杂志, 2012, 32(6):499-501.
[29] Klinge U,Klosterhalfen B,Müller M,et al.Foreign body reaction to meshes used for the repair of abdominal wall hernias.Eur J Surg.1999; 165:665-673.
[30] 张卫玮,曹润福.经腹腹腔镜与后腹膜腹腔镜根治性肾切除治疗肾癌的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(53): 10003-10006. |