| [1] Karl T, Weber MD.Extracellularmatrix remodeling in heart failure: A role for DeNovo Angiotensin II generation . Circulation. 1997; 96 (11): 4065-4082.
[2] Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Hinz B, et al. Myofibroblasts and mechano regulation of connective tissue remodeling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.2002; 3(5): 349-363.
[3] Zile MR, Mehurg SM, Arroyo JE, et al. Relationship between the temporal profile of plasma microRNA and left ventricular remodeling in patients after myocardial infarction. Circ Cardiovasc Genet.2011; 4:614-619.
[4] Barrel DP.MicroRNA:genomics, biogenesis, mechanism and function.Cell 2004;116(2):281-297.
[5] Felekkis K,Touvana E,Stefanou CH,et al.MicroRNAs:a newly described class of encoded molecules that play a role in health and disease.Hippokmm, 2010;14(4):236-240.
[6] Chen T, Liao XP, Wen GQ, et al. Influence of RNA interference on the mitochondrial subcellular localization of alpha-synuclein and on the formation of Lewy body-like inclusions in the cytoplasm of human embryonic kidney 293 cells induced by the overexpression of alpha-synuclein. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(2):85-90.
[7] Costinean S,Zanesi N,Pekarsky Y,et al.Pre-B cell proliferation and lymphoblastic leukemia/high-grade lymphoma in E(mu)-miR155 transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(18):7024-7029.
[8] O'Donnell KA,Wentzel EA,Zeller KI,et al.c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature.2005; 435 (7043):839-843.
[9] Ivey KN, Muth A, Arnold J, et al. MicroRNA regulation of cell lineages in mouse and human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell.2008;2(3): 219-229.
[10] Zhao Y, Samal E,Srivastava D.Serum response factor regulates a muscle speci?c microRNA that targets Hand2 during cardiogenesis. Nature.2005;436(7048):214-220.
[11] Wilson K D, Hu S, Venkatasubrahmanyam S,et al. Dynamic MicroRNA Expression Programs during Cardiac Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells: Role for miR-499. Circ Cardiovasc Genet.2010;3(5): 426-435.
[12] Sluijter JP,van Mil A,van Vliet P,et al.Doevendans PA,Goumans MJ .MicroRNA-1 and -499 Regulate Differentiation and Proliferation in Human-Derived Cardiomyocyte Progenitor Cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2010;30(4):859-868.
[13] Ross JS,Carlson JA,Brock G. miRNA: the new gene silencer. Am J Clin Pathol 2007;128(5):830-836.
[14] Yue J.miRNA and vascular cell movement. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2011;63(8):616-622.
[15] Tie Y,Liu B,Fu H,Zheng X. Circulating miRNA and cancer diagnosis.Sci China C Life Sci.2009;52(12):1117-1122.
[16] Jakob P,Landmesser U . Role of microRNAs in stem/ progenitor cells and cardiovascular repair. Cardiovasc Res 2012;93(4):614-622
[17] Landgraf P, Rusu M,Sheridan R, et al. A mammalian, microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell.2007;129(7): 1401-1414
[18] Zhang C. MicroRNAs: role in cardiovascular biology and disease. Clin Sci (Lond).2008;114 (12):699-706.
[19] Suh MR, Lee Y, Kim JY, et al. Human embryonic stem cells express a unique set of microRNAs. Dev Biol.2004;270(2): 488-498.
[20] Chen JF,Mandel EM,Thomson JM.et a1.The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and differentiation.Nat Genet.2006;38 (2): 228-233.
[21] Zhao Y,Samal E,Srivastava D.Serum response factor regulates a muscle-specific microRNA that targets Hand2 during cardiogenesis. Nature.2005; 436(7048):214-220
[22] Cordes KR,Srivastava D.MicroRNA reguIation of cardiovascular development.Circ Res.2009;104(6):724-732.
[23] Ivey KN, Muth A, Arnold J, et al. MicroRNA regulation of cell lineages in mouse and human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell.2008;2(3): 219-229.
[24] van Rooij E, Sutherland LB, Liu N, et al. A signature pattern of stressres ponsive microRNAs that can evoke cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2006; 103 (48):182552 18260.
[25] van Rooij E, Sutherland LB,Qi X, et al. Control of stress dependent cardiac growth and gene expression by a micr oRNA . Science.2007;316(5824):575-579.
[26] I keda S, He A, Kong SW, et al. MicroRNA-1 negatively regulates expression of the hypertrophy associated cal modulin and Mef2a genes. Mol Cell Biol.2009;29 (8): 2193-2204.
[27] da Costa Martins PA, BourajjajM, Gladka M, et al. Conditional dicer gene deletion in the postnatal myocardium p rovokes spontaneous cardiac remodeling. Circulation.2008;118 (15): 1567-1576.
[28] Maitra M, Schluter man MK, Nichols HA. Interaction of Gata4 and Gata6 with Tbx5 is critical for normal cardiac development. Dev Biol.2009;326(2): 368-377. |
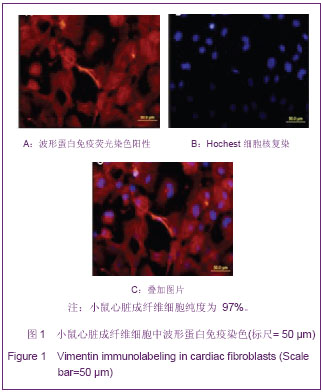
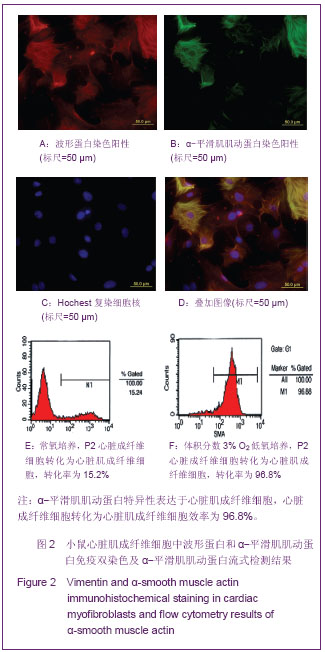
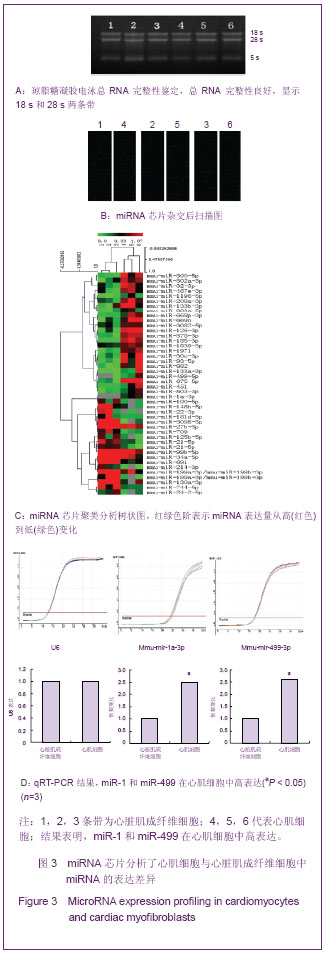
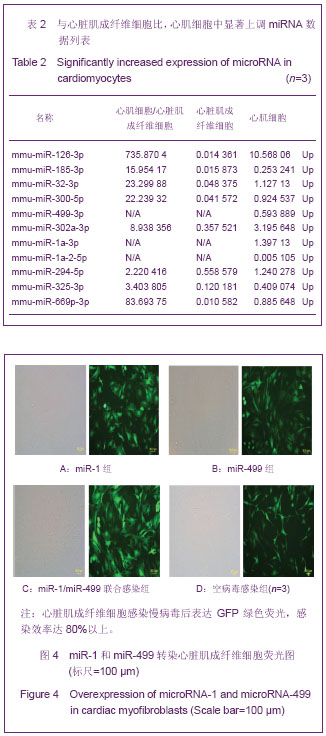

.jpg)
.jpg)