| [1] 吕璐璐,宋永平,魏旭东,等.人脐带和骨髓源间充质干细胞生物学特征的对比研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2008,16(1): 140-146.
[2] Wexler SA, Donaldson C, Denning-Kendall P, et al.Adult bone marrow is a rich source of human mesenchymal stem cells but umbilical cord and mobilized adult blood are not. Br J Haematol.2003;121(2):368-374.
[3] Secco M, Zucconi E, Vieira NM, et al.Multipotent stem cells from umbilical cord: cord is richer than blood. Stem Cells. 2008;26(1):146-150.
[4] Oswald J, Boxberger S, Jorgensen B, et al.Mesenchymal stem cells can be differentiated into endothelial cells in vitro.Stem Cells.2004;22(3):377-384.
[5] 邵琴,王长谦,何奔,等.脐血外周血内皮祖细胞成内皮细胞的体外比较研究[J].临床心血管杂志,2006,6(6):346-350.
[6] 朱斌,王云雅,张志勇,等.大鼠内皮祖细胞的分离、培养与定向诱导分化.[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2009,18(6):608-611.
[7] Ghosh G, Subramanian IV, Adhikari N, et al. Hypoxia-induced microRNA-424 expression in human endothelial cells regulates HIF-α isoforms and promotes angiogenesis. Clin Invest. 2010;120(11):4141-4154.
[8] Rev S, Semenza GL. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent mechanisms of vascularization and vascular remodelling. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;86(2):236-242.
[9] Kim KS, Rajagopal V, Gonsalves C, et al. A novel role of hypoxia-inducible factor in cobalt chloride- and hypoxia-mediated expression of IL-8 chemokine in human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 2006;177(10);7211-7224.
[10] 刘晓娟,惠延年,郭斌,等.缺氧下外源性血管内皮生长因子对体外大鼠Müller细胞的影响[J].国际眼科杂志, 2007,7(2):395- 399.
[11] 许樟荣,敬华.糖尿病足国际临床指南[M].北京:人民军医出版社, 2003:6-45.
[12] Nawaz A, Saboury B, Basu S, et al. Relation between popliteal-tibial artery atherosclerosis and global glycolytic metabolism in the affected diabetic foot: a pilot study using quantitative FDG-PET. Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2012;102(3): 240-246.
[13] Mehta NN, Toriqian DA, Gelfand JM, et al. Quantification of atherosclerotic plaque activity and vascular inflammation using [18-F] fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG-PET/CT). J Vis Exp. 2012;(63): 3777-3791.
[14] Li L, Yu H, Zhu J,et al. The combination of carotid and lower extremity ultrasonography increases the detection of atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Complications. 2012;26(1):23-28.
[15] Kirana S, Stratmann B, Prante C, et al. Autologous stem cell therapy in the treatment of limb ischaemia induced chronic tissue ulcers of diabetic foot patients. Clin Pract. 2012;66(4): 384-393.
[16] 朱旅云,王广宇,马利成,等.脐血单个核细胞移植治疗糖尿病足23例[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(1):175-178.
[17] 侯跃龙,李彤,严晓晔,等.缺氧预处理对脐带间充质干细胞bFGF分泌的影响[J].解放军医学杂志,2010,35(3):297-300.
[18] Ardyanto TD, Osaki M, Tokuyasu N, et al . Cocl2-induced HIF-1 alpha expression correlates with proliferation and apoptosis in MKN-1 cells: a possible role for the P13K/Akt path way. Int Jm Oncol.2006;29(3):549-555.
[19] Balaiya S, Khetpal V, Chalam KV. Hypoxia initiates sirtuin1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor activation in choroidal endothelial cells through hypoxia inducible factor-2α. Mol Vis. 2012;18(17):114-120.
[20] Fujita H,Koshida K,Keller ET, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 promotes prostate cancer progression. Prostate. 2002;53(3): 232-240.
[21] Hu X,Ys SP ,Fraser JL,et al.Transplantation of hypoxia-preconditione mesenchymal stem cells improve infracted heart function via enhanced survival of implanted cells and angiogenesis.Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.2008; 135(4): 799-808.
[22] Haider KH,Kim HW,Ashraf M. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in stem cell preconditioning: mechanistic role of hypoxia-related micro-RNAs. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009; 138(1):257.
[23] Zhao Y, Cai SX. Isolation, culture and differentiation into endothelial-like cells from rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2010;26(1):60-65.
[24] Lai WH, Ho JC, Chan YC, et al. Attenuation of hind-limb ischemia in mice with endothelial-like cells derived from different sources of human stem cells. PLoS One. 2013; 8(3):57876.
[25] Portalska J, Dean Chamberlain M,Lo C, et al . Collagen modules for in situ delivery of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived endothelial cells for improved angiogenesis. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013;17 (10):1738.
[26] Vishnubalaji R, Manikandan M, Al-Nbaheen M, et al, In vitro differentiation of human skin-derived multipotent stromal cells into putative endothelial-like cells. BMC Dev Biol. 2012;12:7.
[27] Marchal JA, Picon M,Bueno C, et al . Purification and long-term expansion of multipotent endothelial-like cells with potential cardiovascular regeneration. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21(4):562-574.
[28] Yan D, Wang X, Li D, et al. Macrophages overexpressing VEGF, transdifferentiate into endothelial-like cells in vitro and in vivo. Biotechnol Lett. 2011;33(9):1751-1758.
[29] Berger S, Dyugovskaya L, Polyakov A,et al, Short-term fibronectin treatment induces endothelial-like and angiogenic properties in monocyte-derived immature dendritic cells: involvement of intracellular VEGF and MAPK regulation. Eur J Cell Biol. 2012;91(8):640-653.
[30] Comsa S, Ciuculescu F, Henschler R, et al. MCF7-MSC co-culture assay: approach to assess the co-operation between MCF-7s and MSCs in tumor-induced angiogenesis. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2011;52(3):1071-1076.
[31] Oskowitz A, McFerrin H, Gutschow M,et al. Serum-deprived human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) are highly angiogenic. Stem Cell Res. 2011;6(3):215-225.
[32] 陈旭春,程颖,杨蕾,等.三维及二维培养大鼠胰腺导管来源干细胞的体外对比实验研究[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2012,19(7): 722-726. |


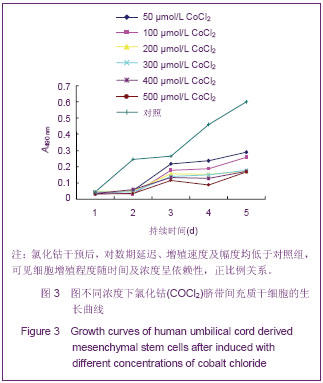


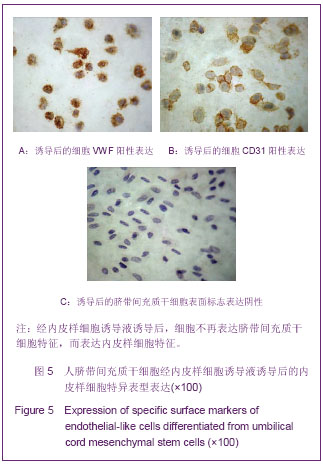

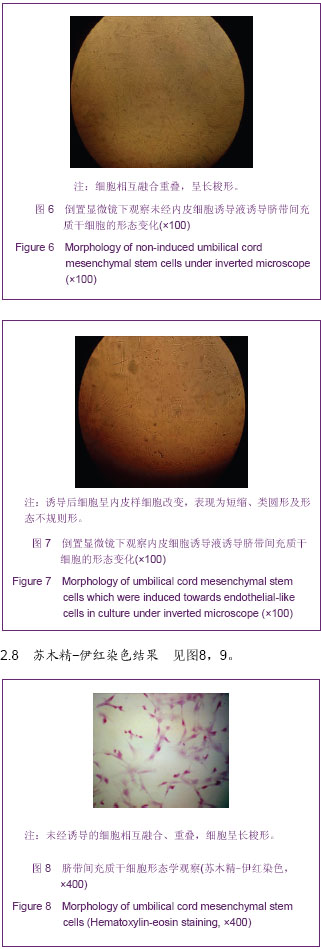
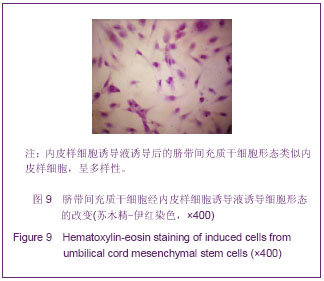

.jpg)