设计:细胞体外体内对比观察实验。
时间及地点:于2012年10月至2013年3月在北京协和医学院阜外心血管病医院心血管疾病国家重点实验室完成。
材料:
实验动物:健康雄性三四周龄SD大鼠10只,体质量60 g左右;健康雌性6-8周龄SD大鼠6只,体质量220 g左右,由北京大学医学部提供,许可证号:SCXK(京) 2001-0012。动物饲养环境为清洁级,实验过程对动物的处置符合相关动物伦理学要求。
CM-DIL和DAPI标记骨髓间充质干细胞的体外体内对比主要试剂、设备:
实验方法:
骨髓间充质干细胞的分离、培养和传代:采用全骨髓贴壁法分离获得骨髓间充质干细胞[9]。三四周龄大鼠颈椎脱臼处死,用体积分数为75%的乙醇浸泡3 min,在无菌条件下,取出大鼠的股骨和胫骨,去除长骨两端的软骨帽,轻轻刮去骨端的骨骺,5 mL注射器吸去完全培养基(DMEM+体积分数10%胎牛血清)反复冲洗骨髓腔于培养皿内,接种于T75培养瓶内,于体积分数5%CO2、37 ℃细胞培养箱内培养,接种后24,48 h换液,去除未贴壁细胞。三四天后细胞可达到80%融合,用37 ℃预热的含0.02%EDTA的2.5 g/L胰蛋白酶消化,于倒置显微镜下观察,当细胞开始皱缩由梭形变圆,部分脱壁,立即吸出胰酶,拍打瓶壁至细胞完全脱落,加入完全培养基,以1∶2的比例分至新的培养瓶中。本实验均选取第2代对数增长期的骨髓间充质干细胞。
骨髓间充质干细胞标记:
CM-DIL标记:收集P2代细胞(1×109-1×1010 L-1), 1 mL PBS重悬,加入1 g/L的CM-DIL(50 μL DMSO溶解50 μg CM-DIL)5 μL,标记浓度达到5 μmol/L,37 ℃孵育5 min,4 ℃冰箱放置15 min,PBS洗涤2次,去除未结合的CM-DIL,记为标记后P1,以后每传代1次,增加1代。
DAPI标记:收集P2代细胞(1×109-1×1010 L-1),1 mL PBS重悬,加入5 g/L的DAPI 20 μL,标记浓度达到 100 mg/L,37 ℃孵育30 min,PBS洗涤4遍,去除未结合的DAPI,记为标记后1代,以后每传代1次,增加1代。
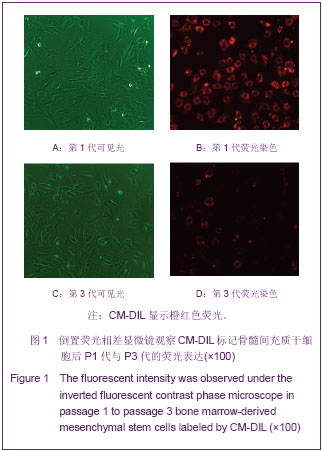
倒置荧光相差显微镜观察荧光衰减:将标记后的细胞接种在T25培养瓶中,8 h进行首次换液,去除未贴壁细胞,于荧光显微镜下观察标记后P1、P2、P3代细胞的荧光表达情况。
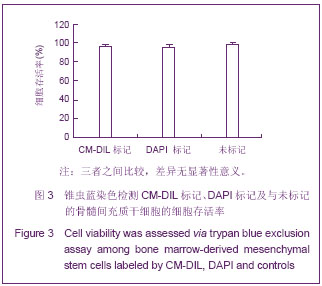
锥虫蓝染色检测细胞活力:将CM-DIL标记后、DAPI标记后以及无标记的细胞制成浓度为1×109 L-1的细胞悬液,取90 μL的细胞悬液与10 μL的0.4%的锥虫蓝混合均匀,3 min内倒置相差显微镜下用细胞计数板对活细胞(细胞膜完整,拒染锥虫蓝)和死细胞(细胞膜完整性丧失,染成蓝色)计数,并计算细胞存活率。
细胞存活率=(细胞总数-蓝染细胞)/细胞总数×100%
|
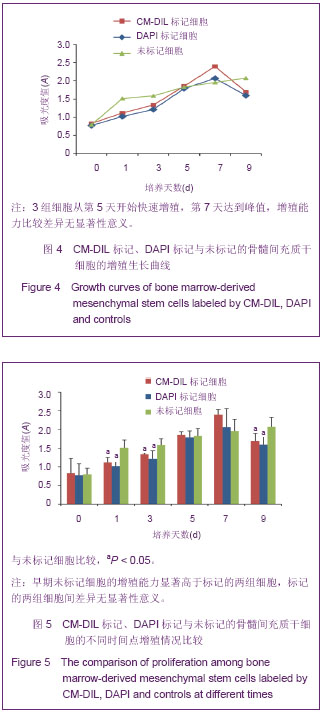
MTS法检测细胞的增殖能力:将CM-DIL标记后、DAPI标记后以及无标记的细胞按2×107 L-1浓度接种于96孔板中,每孔加培养基200 μL,每组各设4个复孔,设加培养基孔为空白孔,置于培养箱中培养,24 h后首次换液,以后每隔48 h后换液。于接种后的第0,1,3,5,7,9天每组随机取5孔,每孔加入MTS液20 μL,培养箱内孵育2 h。用酶联免疫检测仪在490 nm处读取各孔吸光度值,以空白孔调零后得到校正吸光度值。
动物模型的制备:6-8周龄SD大鼠用10%水合氯醛(300 mg/kg)腹腔注射进行麻醉,行气管插管连接小动物呼吸机。大鼠左侧卧位,第4肋间入胸,沿心底部剪开心包。在左心耳下缘1 mm处用7-0滑线结扎前降支,其成功标志是心脏前室壁颜色变为苍白以及室壁运动减弱[10]。
实验动物分组及移植:SD大鼠心肌梗死后1周,随机分为CM-DIL组和DAPI组。按照分组,将标记好的1×106个骨髓间充质干细胞注射到梗死边缘区,移植后第3天取材。
病理学检测移植细胞的分布:动物麻醉后,用20 mL生理盐水从下腔静脉灌注冲洗心脏,快速取材。用解剖刀自二尖瓣乳头肌水平沿心脏短轴方向切开,大致将移植区均分为2部分,心尖部行中性甲醛固定,心底部行OCT包埋剂包埋。行中性甲醛固定的组织,固定24-48 h后,进行脱水、透明、浸蜡、包埋及切片处理。每个石蜡标本连续切片3张,切片厚度5 μm,然后进行烤片、脱蜡、水化、封固,荧光显微镜下观察移植细胞的分布。行OCT包埋剂包埋的组织,放在-80 ℃冰箱冷冻,在冰冻切片机上将组织块切成6 μm厚度的切片,每个组织块连续切片3张,40 g/L多聚甲醛固定后,用甘油进行封固,于荧光显微镜下观察。
主要观察指标:细胞形态,荧光衰减,细胞存活率,细胞增殖能力,移植细胞的荧光表达及分布。
统计学分析:应用SPSS 17.0进行统计处理,结果以x±s表示。组间比较行单因素方差分析,两两比较采用LSD法,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。


.jpg)