| [1] Lin L, Fu X, Zhang X, et al. Rat adipose-derived stromal cells expressing BMP4 induce ectopic bone formation in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2006;27(12):1608- 1615.[2] Li G, Zhang XA, Wang H, et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human bone marrow, umbilical cord and placenta: implication in the migration. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;720:51-68.[3] Tac H, Rao R, Ma DD.Cytokine-induced stable neuronal differentiation of human bone inRrrow mesenehymal stem cells in a serum feeder cell-free condition.Dev Growth Differ. 2005;47(6):423-433.[4] Wang XS, Li HF, Zhao Y, et al. Radix Astragali-induced differentiation of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2009;4(7):497-502.[5] Tang Y,Yasuhara T,Hara K,et al.Transplantation 0f bone nlarrow derived stem cells: a promising therapy for stroke. Cell Transplant.2007;16(2):159-169.[6] Bang OY, k JS, k PH, et al.Autologous mesenchymal stem cells in chronic stroke.Cerebrovasc Dis Extra. 2011;1(1): 93-104.[7] Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, et al. Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2000;61(4):364-370.[8] Sanchez-Ramos J, Song S, Cardozo2Pelaez F, et al. Adult bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neural cells in vitro. Exp Neurol. 2000;164(2):247-256.[9] Kopen GC, Prockop DJ, Phinney DG. Marrow stromal cells migrate through forebrain and cerebellum, and they differentiate into astrocyte after injection into neonatal mouse brains. Proc N atl Acad SciUSA.1999;96(19):10711-10716.[10] Buzanska I,Machai EK,Zabloeka B,et al. Human cord blood-derived cells attain neuronal and glial features in vitro.J Cell Sci. 2002;115(Pt 10):2131-2138.[11] Lei Z,Yongda L,Jun M,et a1.Culture and neural differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro.Cell Biol Int. 2007;3l(9):916-923.[12] Jin K, Mao XO, Batteur S, et al. Induction of neuronal markers in bone marrow cells: differential effects of growth factors and patterns of intracellular expression. Exp Neurol. 2003;184(1): 78-89.[13] Choong PF,Mok PL,Cheong SK,et al.Generating neuron-like cells from BM-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in vitro. Cytotherapy. 2007;9(2):170-183.[14] Li Y, Chopp M,Chen J,et al. Intrastriatal transplantation of bone marrow nonhematopoietic cells improves functional recovery after stroke in adult mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000 ;20(9):1311-1319. [15] Chen J,Li Y,Wang L,et al. Therapeutic benefit of intracerebral transplantation of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neurol Sci. 2001;189 (1-2):49-57.[16] Chopp M, Zhang XH, Li Y,et al. Spinal cord injury in rat: treatment with bone marrow stromal cell transplantation. Neuroreport. 2000;11(13):3001-3005.[17] Mahmood A,Lu D, Yi L,et al. Intracranial bone marrow transplantation after traumatic brain injury improving functional out2come in adult rats. J Neurosurg. 2001; 94(4):589-595. [18] Schwarz EJ, Alexander GM, Prockop DJ. Multipotential marrow stromal cells transduced to produce L-DOPA: engraftment in a rat model of Parkinson disease. Hum Gene Ther. 1999;10(15):2539-2549.[19] Mezey E, Chandross KJ, Harta G,et al. Turning blood into brain: Cells bearing neuronal antigens generated in vivo from bone marrow. Science. 2000;290(5497):1779-1782.[20] Brazelton TR, Rossi FMV, Keshet GI, et al. From marrow to Brain: expression of neuronal phenotypes in adult mice. Science. 2000;290(5497):1775-1779.[21] Park K, Eglitis MA, Mouradian MM. Protection of nigral neurons By GDNF-engineered marrow cells transplantation. Neurosci Res. 2001;40(4):315-323. [22] Ogawa S.Biochemical and immunological laboratory findngs in Kawasaki disease.Nihon Rinsho. 2008;66(2):315-320.[23] Azizi SA, Stokes D, Augelli BJ, et al.Engraftment and migration of human bone marrow stromal cells implanted in the brain of albino rats-similiarities to astrocycle grafts. Proc Natl Sci USA. 1998;95(7):3908-3913.[24] 杨乃龙,杨芬,徐丽丽.共培养法神经细胞诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向神经元的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(29): 5611-5614.[25] Kuo CK, Tuan RS. Tissue engineering with mesenchymal stem cells. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag 2003;22(5):51-56.[26] Shin M, Yoshimoto H, Vacanti JP. In vivo bone tissue engineering using mesenchymal stem cells on a novel electrospun nanofibrous scaffold. Tissue Eng. 2004; 10(1-2): 33-41.[27] Lu P, Blesch A, Tuszynski MH. Induction of bone marrow stromal cells to neurons: differentiation, transdifferentiation, or artifact? J Neurosci Res. 2004;77(2):174-191. [28] 张荣俊,贡志刚,闫西刚,等.骨髓基质干细胞向神经元样细胞诱导分化前后相关基因表达谱的变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(23):4480-4484. [29] Chu K, Kim M, Park KI, et al. Human neural stem cells improve sensorimotor deficits in the adult rat brain with experimental focal ischemia. Brain Res. 2004; 1016(2): 145-153.[30] Fressinaud C, Jean I, Dubas F, et al. Selective decrease in axonal nerve growth factor and insulin-like growth factor I immunoreactivity in axonopathies of unknown etiology. Acta Neuropathol. 2003;105(5):477-483. [31] 张刚利,张汉伟. NSE在颅脑损伤中的临床意义[J]. 国际神经病学神经外科学杂志,2010,2:161-164.[32] Castro RF, Jackson KA, Goodell MA, et al. Failure of bone marrow cells to transdifferentiate into neural cells in vivo. Science. 2002;297(5585):1299.[33] Terada N, Hamazaki T, Oka M,et a1.Bone marrow cells adopt the phenotype of other cells by spontaneous cell fusion.Nature. 2002;416(6880):542-545.[34] Park KS, Lee YS, Kang KS. In vitro neuronal and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord blood. J Vet Sci. 2006;7(4):343-348.[35] Battula VL, Bareiss PM, Treml S,et al,Human placenta and bone marrow derived MSC cultured in serum-free, b-FGF-containing medium express cell surface frizzled-9 and SSEA-4 and give rise to multilineage differentiation. Differentiation. 2007;75(4):279-291. [36] Kogler G, Sensken S, Airey JA, et al.A new human somatic stem eell fromplaeentat cord blood with intrinsic pIurlpotent differentiation potential. ExpMed. 2004;200(2):123-135.[37] Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, et al. Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2000;61(4):364-370.[38] Long X, Olszewski M, Huang W, et al. Neural cell differentiation in vitro from adult human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2005;14(1):65-69. |
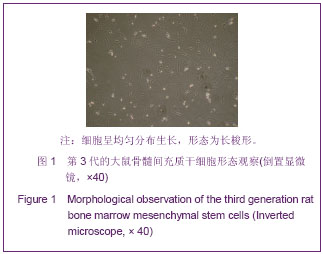
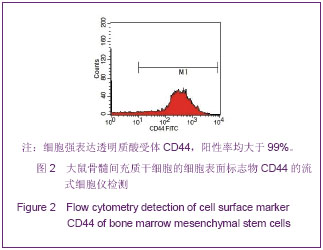
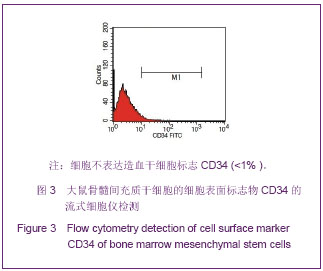
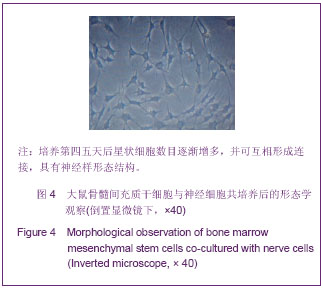

.jpg)