[1] XU K, YIN M, ZHONG Y, et al. Acute Effects of Assisted and Resisted Sprint Training on Subsequent Sprint Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Strength Cond Res. 2025;39(5):e711-e720.
[2] XU K, BLAZEVICH AJ, BOULLOSA D, et al. Optimizing Post-activation Performance Enhancement in Athletic Tasks: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis for Prescription Variables and Research Methods. Sports Med. 2025;55(4):977-1008.
[3] 徐恺,唐文静,路恒,等.激活后增强效应与激活后表现提升:重塑定义与认知[J].中国体育科技,2025,61(1):47-58.
[4] BLAZEVICH AJ, BABAULT N. Post-activation Potentiation Versus Post-activation Performance Enhancement in Humans: Historical Perspective, Underlying Mechanisms, and Current Issues. Front Physiol. 2019;10:1359.
[5] 梁美富,郭文霞.骨骼肌激活后增强效应的研究进展[J].体育科学,2019,39(5):70-80.
[6] BOULLOSA D. Post-activation performance enhancement strategies in sport: a brief review for practitioners. Human Movement. 2021;22(3):101-109.
[7] TILLIN NA, BISHOP D. Factors modulating post-activation potentiation and its effect on performance of subsequent explosive activities. Sports Med. 2009;39(2):147-166.
[8] ZENG N, LIU H, WANG J, et al. The effects of blood flow restriction training on post activation potentiation and fatigue level: systematic review with meta-analysis. Front Physiol. 2025;16:1558008.
[9] LOENNEKE JP, HAMMERT WB, KATAOKA R, et al. Twenty-five years of blood flow restriction training: What we know, what we don’t, and where to next? J Sports Sci. 2025;43(19):2115-2132.
[10] PIGNANELLI C, CHRISTIANSEN D, BURR JF. Blood flow restriction training and the high-performance athlete: science to application. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2021;130(4):1163-1170.
[11] PATTERSON SD, HUGHES L, WARMINGTON S, et al. Blood Flow Restriction Exercise: Considerations of Methodology, Application, and Safety. Front Physiol. 2019;10:533.
[12] SCOTT BR, LOENNEKE JP, SLATTERY KM, et al. Exercise with blood flow restriction: an updated evidence-based approach for enhanced muscular development. Sports Med. 2015;45(3):313-325.
[13] ZHANG Y, XU K, YIN M, et al. Effects of blood flow restriction training in athletes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Sports Med. 2025;46(7):467-481.
[14] YIN M, DENG S, DENG J, et al. Physiological adaptations and performance enhancement with combined blood flow restricted and interval training: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J Sport Health Sci. 2025;14: 101030.
[15] WORTMAN RJ, BROWN SM, SAVAGE-ELLIOTT I, et al. Blood Flow Restriction Training for Athletes: A Systematic Review. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(7):1938-1944.
[16] KONG H, ZHANG Y, YIN M, et al. Effects of blood flow restriction training on cardiometabolic health and body composition in adults with overweight and obesity: a meta-analysis. Front Physiol. 2025;15:1521995.
[17] ZHAO C, SU R, WU J, et al. The effects of blood flow restriction combined with resistance training on post-activation potentiation: A meta-analysis. Science & Sports. 2025;40(2):103-116.
[18] LIU H, JIANG L, WANG J. The effects of blood flow restriction training on post activation potentiation and upper limb muscle activation: a meta-analysis. Front Physiol. 2024;15:1395283.
[19] WANG J, LIU H, JIANG L. The effects of blood flow restriction training on PAP and lower limb muscle activation: a meta-analysis. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1243302.
[20] 徐恺,殷明越,王然.中文体育类核心期刊元分析的选题和方法学问题[J].体育科学,2024,44(1):88-97.
[21] KADLEC D, SAINANI KL, NIMPHIUS S. With Great Power Comes Great Responsibility: Common Errors in Meta-Analyses and Meta-Regressions in Strength & Conditioning Research. Sports Med. 2023;53(2):313-325.
[22] PUSTEJOVSKY JE, TIPTON E. Meta-analysis with Robust Variance Estimation: Expanding the Range of Working Models. Prev Sci. 2022;23(3):425-438.
[23] PAGE MJ, MCKENZIE JE, BOSSUYT PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2021;10(1):89.
[24] MCKAY AKA, STELLINGWERFF T, SMITH ES, et al. Defining Training and Performance Caliber: A Participant Classification Framework. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2022;17(2):317-331.
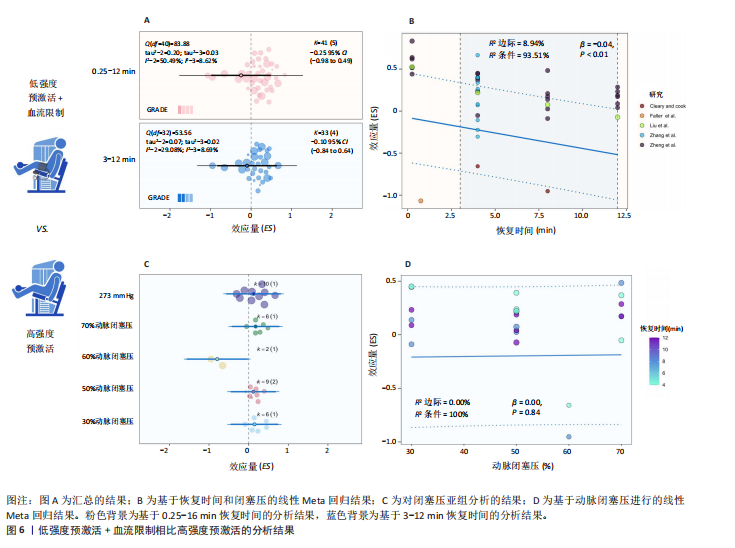
[25] ZHENG H, LIU J, WEI J, et al. The Influence on Post-Activation Potentiation Exerted by Different Degrees of Blood Flow Restriction and Multi-Levels of Activation Intensity. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(17):10597.
[26] STERNE JAC, SAVOVIĆ J, PAGE MJ, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2019;366:l4898.
[27] SCHÜNEMANN HJ, HIGGINS JP,VIST GE, et al. Completing ‘Summary of findings’ tables and grading the certainty of the evidence[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2019:375-402.
[28] BECKER BJ. Synthesizing standardized mean‐change measures. Br J Math Stat Psychol. 1988;41(2):257-278.
[29] ASSINK M, WIBBELINK CJM. Fitting three-level meta-analytic models in R: A step-by-step tutorial. Quant Method Psychol. 2016;12(3):154-174.
[30] JUKIC I, CASTILLA AP, RAMOS AG, et al. The Acute and Chronic Effects of Implementing Velocity Loss Thresholds During Resistance Training: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Critical Evaluation of the Literature. Sports Med. 2023;53(1): 177-214.
[31] COHEN J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1977.
[32] NAKAGAWA S, SCHIELZETH H. A general and simple method for obtaining R2 from generalized linear mixed‐effects models. Methods Ecol Evol. 2013;4(2):133-142.
[33] NAKAGAWA S, LAGISZ M, O’DEA RE, et al. The orchard plot: Cultivating a forest plot for use in ecology, evolution, and beyond. Res Synth Methods. 2021;12(1):4-12.
[34] EGGER M, DAVEY SMITH G, SCHNEIDER M, et al. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315(7109):629-634.
[35] VIECHTBAUER W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J Stat Softw. 2010;36:1-48.
[36] PUSTEJOVSKY J, PUSTEJOVSKY MJ. Package ‘clubSandwich’ . CRAN. 2020.
[37] MILLER RM, KEETER VM, FREITAS EDS, et al. Effects of Blood-Flow Restriction Combined With Postactivation Potentiation Stimuli on Jump Performance in Recreationally Active Men. J Strength Cond Res. 2018;32(7): 1869-1874.
[38] CLEARY CJ, COOK SB. Postactivation Potentiation in Blood Flow-Restricted Complex Training. J Strength Cond Res. 2020;34(4):905-910.
[39] DOMA K, LEICHT AS, BOULLOSA D, et al. Lunge exercises with blood-flow restriction induces post-activation potentiation and improves vertical jump performance. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2020;120(3):687-695.
[40] CHEN YT, HSIEH YY, HO JY, et al. Effects of Running Exercise Combined With Blood Flow Restriction on Strength and Sprint Performance. J Strength Cond Res. 2021;35(11):3090-3096.
[41] 魏宏文,向镜.快速伸缩复合练习伴随血流限制的激活后增强效应研究[J].河南师范大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(1): 144-149.
[42] 张俊杰,魏宏文,刘瑞东,等.低强度抗阻结合血流限制和高强度抗阻练习对男子短跑运动员爆发力的影响[J].广州体育学院学报,2022,42(6):23-31.
[43] 刘嘉俊,周喆啸,汤珊,等.血流阻断结合传统抗阻运动对男性大学生运动员激活后增强效应的影响[J].中国体育科技, 2023,59(8):21-27.
[44] FALLER JM, THOMPSON B, SOTIR S, et al. The Acute Impacts of Resistance Training Performed with and without Blood Flow Restriction on Lower Body Muscular Power. Int J Exerc Sci. 2023;16(6):1320-1333.
[45] SUN D, YANG T. Semi-Squat Exercises with Varying Levels of Arterial Occlusion Pressure during Blood Flow Restriction Training Induce a Post-Activation Performance Enhancement and Improve Vertical Height Jump in Female Football Players. J Sports Sci Med. 2023;22(2):212-225.
[46] CUI S, DU Z, WANG N, et al. Assessing the Post-Activation Performance Enhancement of Upper Limbs in Basketball Athletes: A Sensor-Based Study of Rapid Stretch Compound and Blood Flow Restriction Training. Sensors (Basel). 2024;24(14):4439.
[47] ZHENG Z, WANG Y, WEI H, et al. Effects of external limb compression and/or low-load resistance exercise on post-activation performance enhancement during countermovement jumps. Eur J Sport Sci. 2024;24(2):249-258.
[48] DAVIDS CJ, ROBERTS LA, BJØRNSEN T, et al. Where Does Blood Flow Restriction Fit in the Toolbox of Athletic Development? A Narrative Review of the Proposed Mechanisms and Potential Applications. Sports Med. 2023;53(11):2077-2093.
[49] TIAN H, LI H, LIU H, et al. Can Blood Flow Restriction Training Benefit Post-Activation Potentiation? A Systematic Review of Controlled Trials. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(19):11954.
[50] 唐文静,张立萍,许贻林,等.无创肌肉结构评估:肌骨超声成像技术在运动表现领域中的应用[J].体育科学,2024, 44(11):74-86+97.
[51] 黎涌明,李博,王雄,等.赛前准备活动:实践导向的科学证据[J].西安体育学院学报,2022,39(5):606-617+632.
[52] NAKATA K, MISHIMA T. Plyometric Exercise Transiently Enhances Twitch Torque but Fails to Enhance the Rate of Force Development Evaluated Using the Isometric Midthigh Pull. J Hum Kinet. 2024;94:171-180.
[53] FISCHER J, PATERNOSTER FK. Post-Activation-Performance Enhancement: Possible Contributing Factors. J Sports Sci Med. 2024;23(1):34-45.
[54] SPUDIĆ D, DAKSKOBLER J, ŠTIRN I. Differences in post-activation potentiation and post-activation performance enhancement between flywheel and barbell squat protocols. Kinesiol Sloven. 2023;29:5-29.
[55] MÁRQUEZ G, GONZÁLEZ-HERNANDEZ J, JIMÉNEZ-REYES P, et al. Co-existence of peripheral fatigue of the knee extensors and jump potentiation after an incremental running test to exhaustion in endurance trained male runners. Front Sports Act Living. 2023;5:1267593.
[56] VASCONCELOS GC, BRIETZKE C, CESARIO JCS, et al. No Evidence of Postactivation Performance Enhancement on Endurance Exercises: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2024;56(2):315-327.
[57] JESSEE MB, BUCKNER SL, DANKEL SJ, et al. The Influence of Cuff Width, Sex, and Race on Arterial Occlusion: Implications for Blood Flow Restriction Research. Sports Med. 2016;46(6):913-921.
[58] WILK M, KRZYSZTOFIK M, FILIP A, et al. Does Post-Activation Performance Enhancement Occur During the Bench Press Exercise under Blood Flow Restriction? Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(11):3752.
[59] GAWEL D, JAROSZ J, TRYBULSKI R, et al. Effects of different ischemic pressures on bar velocity during the bench press exercise: A randomized crossover trial. Biol Sport. 2024;41(3):89-96.
[60] ZHAO C, LI C, SU R, et al. Comparison of Different Methods on Post-Activation Performance Enhancement: A Meta-Analysis. Int J Sports Med. 2025;46(3):172-181.
[61] AMENT W, VERKERKE GJ. Exercise and fatigue. Sports Med. 2009;39(5):389-422.
|